Technology tamfitronics
- Research Briefing
- Published:
Subjects
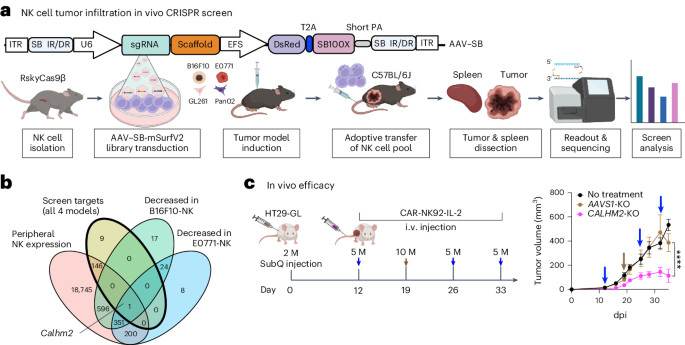
We use a CRISPR screening platform based on adeno-associated virus and the Sleeping Beauty transposon (AAV-SB-CRISPR) to perform in vivo CRISPR screens in primary natural killer (NK) cells across four different tumor models, and identify calcium homeostasis modulator family member 2 (CALHM2) as an NK cellular checkpoint protein.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
214,86 € per year
only 17,91 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

References
Marin, D. et al. Safety, efficacy and determinants of response of allogeneic CD19-specific CAR-NK cells in CD19+ B cell tumors: a phase 1/2 trial. Night. With. 30772–784 (2024). A recent clinical trial demonstrating the robust efficacy and superior safety of CAR-NK.
Vivier, E. et al. Natural killer cell therapies. Nature 626727–736 (2024). Comprehensive review discussing the current status of NK therapy.
Dong, M. B. Systematic immunotherapy target discovery using genome-scale in vivo CRISPR screens in CD8 T cells. Cell 1781189–1204 (2019). This paper reports an early in vivo CRISPR screens in primary T cells.
Ye, L. et al. In vivo CRISPR screening in CD8 T cells with AAV-Sleeping Beauty hybrid vectors identifies membrane targets for improving immunotherapy for glioblastoma. Nat. Biotechnol. 371302–1313 (2019). This paper demonstrates the application of an AAV-SB-CRISPR system in T cells.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This is a summary of: Peng, L. et al. In vivo AAV–SB-CRISPR screens of tumor-infiltrating primary NK cells identify genetic checkpoints of CAR-NK therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02282-4 (2024).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CRISPR screens of tumor-infiltrating NK cells identify genetic checkpoints for CAR-NK therapy. Nat Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02319-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02319-8