Identification of clinically connected T cell receptors for personalized T cell remedy the usage of combinatorial algorithms
Technology tamfitronics
Major
Adoptive cell switch (ACT) of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) is a personalised immunotherapy potential with demonstrated superiority over second-line checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in patients with melanoma1,2. Recent be taught show that the frequency of tumor-reactive T cells (TRTs) in melanoma tumors ancient to amplify TILs, and their quantity in cognate TIL merchandise infused to patients are valuable determinants of TIL ACT efficacy3,4. Furthermore, it has been hypothesized that the paucity of TRTs in a form of solid tumors can show the lower success charge of TIL remedy in these patients5. Alternatively, the usage of TCR-engineered T cells has confirmed promise for treating solid tumors6. Nonetheless, when personalized, this potential faces the pain of including TCRs with untested tumor specificity or inadequate affinity, stressing the ought to determine clinically connected TCRs6,7.
Recent growth in single-cell RNA and TCR sequencing (scRNA-seq and scTCR-seq) applied sciences enabled the exploration of the distinctive transcriptomic profile of intratumoral neoantigen-particular and tumor-reactive T cells8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15offering an opportunity to acquire predictors of deepest TRTs in a position to reliably identifying tumor-reactive over bystander TILs, thus opening the door for the improvement of personalized TCR-essentially based therapies. Nonetheless, as of at the novel time, any excellent utility has been hampered by the lack of a rigorous evaluation framework and sturdy benchmarking in opposition to external datasets8,12,14. Furthermore, predicting all TRTs indiscriminately may well consequence in the sequence of clinically suboptimal low-avidity TCRs (going down moreover for some neoantigen-particular clonotypes)14,16.
On this build a matter to, we introduce TRTpred, an antigen-agnostic in silico TRT predictor developed and extensively benchmarked within a machine studying framework. We train its superiority when in contrast with novel predictive TRT signatures in datasets from a form of tumor indications8,11,12,14,17. We moreover utilized TRTpred to successfully explore the immune repertoire of tumor-reactive TILs across a range of tumor indications and microenvironments. Ultimately, by integrating a excessive-avidity TCR predictor16 and a TCR clustering algorithm (TCRpcDist)18now we maintain engineered a combinatorial algorithm (steadily known as MixTRTpred) for the sequence of clinically connected TCRs from the pool of TRTs, which was therefore validated in vitro and in vivo (Fig. 1a).
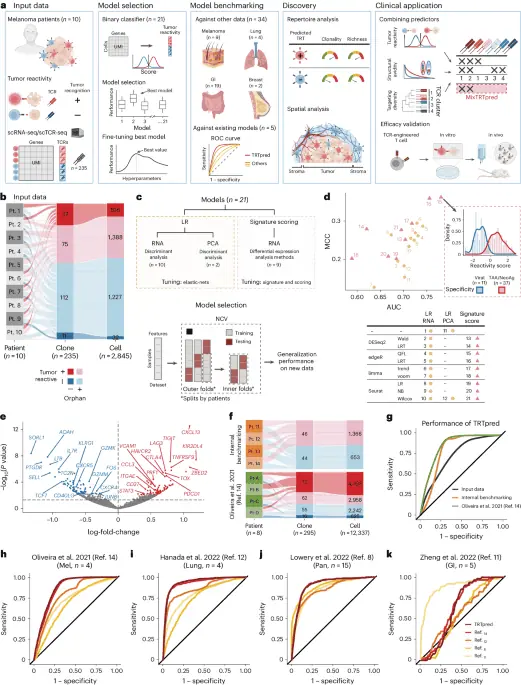
aIllustration of TRTpred fabricate, benchmarking and applications. The final algorithm, MixTRTpred, combines TRTpred with a structural avidity predictor16 and TCRpcDist18a TCR clustering algorithm. bAlluvial set of abode exhibiting the fractions of cells and clones annotated as tumor-reactive or non-tumor-reactive (orphan or antigen (Ag)-particular) within the enter info (n = 10 patients with melanoma). cHigh, fabricate of the 12 LR and 9 signature scoring units with their hyperparameters (Strategies). Bottom, model desire framework estimating the generalization efficiency of the model through an LOPO NCV. dEvaluate of the 12 LR (yellow circles) and 9 signature scoring (crimson triangles) binary classifiers in the operate of MCC and the AUC (Supplementary Table 2). The panel displays the distribution of the particular model ratings for tumor antigen-particular (crimson) and viral-particular (blue) clones. eVolcano set of abode exhibiting the differential gene expression prognosis evaluating tumor-reactive and non-tumor-reactive cells. The 90 upregulated (crimson) and downregulated (blue) genes bought by edgeR-QFL are confirmed (Supplementary Table 4). The P values are calculated the usage of the two-sided quasi-likelihood F-check in the edgeR kit and are corrected for added than one testing the usage of the Benjamini–Hochberg task. fAlluvial plots exhibiting the fractions of cells and clones annotated as tumor-reactive or non-tumor-reactive (orphan or Ag-particular) within inside of (high) and external (backside, ref. 14) benchmarking info. gROC curve of TRTpred utilized on the enter info (dim), and the inside of (orange) and external (green, ref. 14) benchmarking info. h–kROC curves of TRTpred and four CD8+ TIL tumor-reactive predictive signatures (refs. 8,11,12,14) utilized to the four datasets: ref. 14 (melanoma, n = 4) (h), ref. 12 (lung, n = 4) (i), ref. 8 (n = 1 melanoma, n = 2 breast and n = 12 GI) (j) and ref. 11 (GI, n = 5) (k). All AUCs are reported in Extended Recordsdata Fig. 3e. Pt, affected person; TAA, tumor-associated antigen; UMI, distinctive molecular identifier; PCA, fundamental part prognosis; Mel, melanoma; Pan, pan-cancer.
To maintain TRTpred, we took excellent thing about 235 CD8+ clonotypes, annotated as tumor-reactive (n = 112) or non-tumor-reactive (n = 123), curated from ten patients with metastatic melanoma3,19 (Fig. 1bExtended Recordsdata Fig. 1a and Supplementary Table 1). Bona fide tumor-reactive TCRs had been outlined as those reacting in opposition to autologous tumors no matter their particular antigenic targets, as previously reported20,21even even supposing some specificities had been moreover experimentally validated for some clonotypes (Supplementary Table 1). The explain of every their scTCR-seq and scRNA-seq profiles, we professional a series of 21 binary classifiers including logistic regression (LR) and signature scoring strategies, which underwent honest-tuning (StrategiesFig. 1c and Extended Recordsdata Fig. 2a). The units had been evaluated the usage of the scoot away-one-affected person-out (LOPO) nested horrible-validation (NCV) framework, offering insights into their generalization efficiency when faced with unseen info from fresh patients (Strategies and Extended Recordsdata Fig. 2b). Whereas LR units exhibited commendable set under the curve (AUC) ratings, one of many signature scoring units (edgeR-QFL) emerged as essentially the most generalizable, leading to TRTpred after coaching on the total dataset (Fig. 1 d and Supplementary Table 2). Y-randomization assessments extra validated TRTpred’s credibility in opposition to faulty studying (Extended Recordsdata Fig. 3a and Strategies). As an illustration of TRTpred, we serious about clonotypes from the dataset with known specificity and observed a ideal discrimination between virus-particular bystander TILs and TILs particular for tumor-associated antigens or tumor-restricted neoantigens (Fig. 1 d and Supplementary Table 3). Constant with outdated be taught, TRTpred’s signature includes several genes connected to exhaustion (as an instance, CXCL13, LAG3, TOX, PDCD1 or TNFRSF9; Fig. 1e and Supplementary Table 4). Nonetheless, the overlap between printed signatures8,11,12,14,17 is limited and CXCL13 is the distinctive consensual gene (Extended Recordsdata Fig. 3b–d).
To benchmark TRTpred, we first evaluated its efficiency the usage of two neutral datasets, sourced internally or externally by Oliveira et al.14containing 90 and 205 CD8+ TRT annotated clonotypes, respectively (Fig. 1fExtended Recordsdata Fig. 1b,c and Supplementary Table 1). TRTpred exhibited consistent efficiency across every units of benchmarking info (Fig. 1g). We extra benchmarked TRTpred in four sure CD8+ TILs datasets from a form of tumor indications (ref. 14melanoma; ref. 12lung; ref. 8pan-cancer; ref. 11gastrointestinal (GI); Supplementary Table 1). TRTpred outperformed the a form of units8,11,12,14 even on their own datasets (Fig. 1h–k and Extended Recordsdata Fig. 3e), other than for ref. 11 info on which all signatures underperformed.
We then utilized TRTpred to quiz the tumor repertoires from 42 patients with melanoma (n = 19) as effectively as GI (n = 17), lung (n = 4) or breast (n = 2) cancer (Supplementary Table 1). Consistently across the a form of tumor forms, inferred TRT repertoires had been richer and extra clonal than cognate bystander counterparts (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Table 5). Furthermore, in keeping with our expectations essentially based on the scientific efficacy of TIL remedy reported in melanoma versus a form of solid tumors5a better percentage of CD8+ TRTs was known in melanoma relative to a form of solid tumors (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Table 5).
aRichness (high) and clonality (backside) of inferred tumor-reactive (+/−) clones the usage of TRTpred in n = 5 cohorts: inside of info (melanoma n = 14); ref. 14 (melanoma, n = 4); ref. 11 (GI, n = 5); ref. 8 (n = 1 melanoma, n = 2 breast and n = 12 GI); ref. 12 (lung, n = 4). Sufferers are coloration-coded essentially based on the cancer form. Metrics are displayed in logarithmic scale and statistics had been performed the usage of a one-tailed t-check. bPercentage of inferred TRT CD8+ T cells in melanoma (n = 19) and a form of solid tumors (n = 23, as described in a). Statistics had been performed the usage of a one-tailed Wilcoxon check. cSequential multiplexed immunohistochemistry of affected person 1 with hematoxylin (crimson) and CD8 (yellow) staining. Upper panel, total-tissue section; lower panel (white rectangle), magnified image. Scale bars, 500 μm and 50 μm, for the total-tissue section and magnified photos, respectively. Here’s a handbook experiment among n = 5 neutral patients with melanoma. d,eCumulative frequency of inferred excessive-avidity (d) or tumor-reactive (e) CD8+ clones known in microdissected areas of stroma and tumor in n = 5 neutral patients with melanoma (patients 1–5). Statistics had been performed the usage of a pairwise one-tailed Wilcoxon check. fTRTpred outcomes depicting the distance matrix of the dwell 20 ranked tumor-reactive among excessive structural avidity clones. The 5 clones chosen are the ones with the ideal tumor-reactive ranking in every cluster (TCRs 1–5; Supplementary Table 6), outlined by hierarchical clustering. gIn vitro validation of the tumor reactivity of the 5 TCRs (TCRs 1–5) predicted through MixTRTpred through CD137 upregulation assay (indicate of n = 2 biologically neutral replicates). The coloration code corresponds to that of panel f. h,iIL-2 NOG mice had been subcutaneously engrafted with tumor cells from affected person 14 adopted by adoptive switch of TCR-transduced predominant CD8+ T cells. hTumor-bearing mice received 5 × 106 CD8+ T cells transduced (day 11) with TCR1, TCR3 or TCR5 (Supplementary Table 6). iMice had been adoptively transferred with infusion merchandise containing 1 × 106 total CD8+ T cells transduced (day 11) with TCR1 or TCR3 or TCR5 (single TCRs) or with a pool of 1 × 106 total CD8+ T cells transduced with the three TCRs (TCR cocktail, 0.33 × 106 CD8+ T cells transduced with every TCR). In h and i5 × 106 CD8+ untransduced T cells had been transferred as modify. Recordsdata point to indicate ± s.e.m. of n = 3–5 biologically neutral replicates. In field plots, the boxes signify the median and the interquartile vary (IQR), while the whiskers lengthen to 1.5 instances the IQR. ID, identification; Irr Ctrl, beside the point modify; Mel, melanoma; Pan, pan-cancer; GI, gastrointesinal.
We maintain now got previously reported that tumor-particular TIL clonotypes, particularly those with excessive-avidity TCRs, win preferentially within the tumor islets, that’s, the tumor cell clusters circumscribed by surrounding stroma, while these clonotypes are largely diluted in the surrounding stroma16,22. To extra pain our prediction instruments, we examined the spatial distribution of predicted TRTs. Taking excellent thing about TCR repertoires bought from microdissected tumor core and stroma areas from 5 patients with melanoma with scRNA-seq/TCR-seq info (Fig. 2c and Supplementary Table 1), we first utilized a predictor of TCR structural avidity16 and had been ready to validate the simpler frequency of clones inferred to maintain excessive TCR avidity within the tumor islet compartment (Fig. 2d). Furthermore, by applying TRTpred, we stumbled on that TRTs had been extra frequent in tumor islets, while bystander TIL clones amassed preferentially in the stroma (Fig. 2e and Extended Recordsdata Fig. 4a,b). This prognosis was corroborated by analyzing previously known21 neoantigen/tumor-associated antigen- or virus-particular T cells in a handbook affected person and in cumulative info (Extended Recordsdata Fig. 4a,b and Supplementary Table 3), validating the preferential infiltration of TRTs within tumor cores.
Moreover exploratory applications, the ability to accurately distinguish TRTs (the usage of TRTpred) represents an opportunity to determine deepest clinically connected tumor-reactive TCRs for personalized TCR T cell remedy. For this cause, two extra key qualitative facets of TRTs ought to restful be regarded as to extra make a choice, among tumor-reactive clonotypes known with TRTpred, essentially the most clinically connected clones. First, all TRTs may well no longer be equally clinically connected as they’ll moreover be equipped with low-avidity TCRs, even supposing they aim neoantigens14,16. Furthermore, in the angle of personalized TCR-engineered T cell remedy the usage of extra than one TCRs, it is key to generate cell merchandise focusing on extra than one sure antigens to limit tumor spoil out6,7.
To this dwell, we indicate MixTRTpred, a combinatorial algorithm that hinges on three steps: (1) applying TRTpred to generate a ranked list of tumor-reactive clones; (2) filtering out clones with inferred low structural avidity TCRs (Fig. 1a); and (3) applying a TCR clustering tool, that’s, TCRpcDist18to group TCRs with same physicochemical properties into TCR-cluster, choosing the dwell tumor-reactive-scoring TCR in every cluster to maximize the range of focused antigens. This potential that, we mark an optimized list of inferred tumor-reactive TCRs with excessive structural avidity focusing on sure antigens (MixTRTpred thus yields to an enrichment in clinically connected TRTs however would now not toughen, per se, the sequence of tumor-reactive clonotypes).
To validate MixTRTpred’s efficacy, we utilized it to a affected person the set autologous affected person-derived xenograft tumors had been on hand. From a total of 257 inferred excessive-avidity clones, we ancient TRTpred to settle 188 TCRs predicted as tumor-reactive (Extended Recordsdata Fig. 5a). Then, from the 188 TRTs, we chosen the dwell-ranking clonotypes (n = 20) and then ancient TCRpcDist18 to generate 5 sure TCR clusters (Strategies and Fig. 2f). By extra choosing the dwell tumor-reactive TCRs from every cluster, we bought 5 extremely chosen TCR candidates (Supplementary Table 6). In accordance to TRTpred’s total accuracy, all TCRs (5 of 5) demonstrated tumor reactivity in vitro (Fig. 2g). We extra chosen three of these TCRs (spanning, agnostically, the total vary of in situ frequency) to compare their doable in controlling the in vivo enhance of autologous affected person-derived xenograft tumors. Transfer of 5 × 106 T cells engineered with every particular person TCR managed tumor enhance (that’s, 3 of 3; Fig. 2h and Extended Recordsdata Fig. 5b,c), and the two TCRs with the ideal tumor reactivity ratings and top seemingly handy avidity eradicated tumors (Fig. 2hSupplementary Table 6 and Extended Recordsdata Fig. 5d). To check the finest thing about transferring extra than one TCRs, we ancient a suboptimal T cell product (1 × 106 cells per ACT dose) and when in contrast the efficacy of cells transduced with handiest one of many particular person TCRs (1–3) with a cocktail of all three TCRs. Multivalent ACT merchandise yielded better tumor modify than merchandise containing handiest one form of TCR-transduced cells (Fig. 2i). Ultimately, applying MixTRTpred to all patients with assessable info (n = 37; Supplementary Table 1), we consistently known extra than ten clinically connected clones per affected person (median = 102), other than for one affected person14 with handiest a few sequenced clones, thus demonstrating the applicability of MixTRTpred for TCR T cell remedy (Extended Recordsdata Fig. 5e).
On this build a matter to, we introduce TRTpred, a predictor of tumor-reactive clonotypes outcompeting novel instruments in extra than one datasets from a form of tumor indications. TRTpred enabled a granular interrogation of TIL repertoire and spatial distribution and revealed a trim vary of richness and clonality of TRT repertoires in tumors. These metrics, reflecting the abundance of tumor-reactive cells in tumors, shall be valuable in predicting responses to checkpoint immunotherapies, and behoove extra be taught to explore the utility of TRTpred in this discipline. Furthermore, preliminary observations show that the abundance of TRT in tumors predicts scientific responses to TIL ACT in melanoma3offering extra alternatives for better affected person desire.
Now not lower than ten sure TCRs per affected person was stumbled on the usage of MixTRTpred. Whereas extra be taught are needed to train the added charge of the usage of extra than one TCRs, the concepts reported here make stronger the scientific relevance of inferred TCRs for adoptive immunotherapy.
Collectively, these observations indicate that TRTpred shall be instrumental both to settle patients who may well perchance maintain the income of TIL ACT or to settle clinically connected TCRs (the usage of MixTRTpred) for TCR T cell remedy in final patients who wouldn’t be eligible for TIL remedy. Taking excellent thing about most standard advances in the discipline of T cell engineering6,23,24the accuracy of MixTRTpred means that personalized TCR-essentially based remedy is now achievable for many patients with solid tumors.
Strategies
Ethical assertion
This be taught adheres to all applicable ethical regulations. Patient samples restful in this build a matter to had been bought following protocols current by the institutional regulatory committee (Lausanne University Sanatorium, CHUV). Written, knowledgeable consent was bought from all patients. In vivo experiments had been performed essentially based on Swiss ethical pointers and under current licenses (survey the next section), making sure compliance with the 3R (replace, discount, refinement) pointers.
Cancer affected person info sequence
scRNA-seq/scTCR-seq info from tumors had been bought from inside of patients with in the neighborhood evolved (stage III) or metastatic (stage IV) cutaneous melanoma who had progressed on no lower than one fashioned first-line remedy. Tumor samples had been bought following surgical procedure and processed as previously described3,19 for single-cell prognosis. Temporarily, scRNA-seq and scTCR-seq info had been aligned to the GRCh38 reference genome the usage of cellran ger count (10X Genomics, v.3.0.1) and vdj (10X Genomics, v.3.1.0), respectively. We moreover utilized TRTpred on external info from ref. 14 (melanoma, n = 4), ref. 11 (GI, n = 5), ref. 8 (n = 1 melanoma, n = 2 breast and n = 12 GI) and ref. 12 (lung, n = 4) restful from the Gene Expression Omnibus the usage of SRA Toolkit (v.3.1.0). All info had been processed and annotated following the authors’ pointers. For the ref. 8 and ref. 12 datasets, neoantigen-particular clones had been regarded as as tumor-reactive while the final clones had been classified as non-tumor-reactive, adhering to the authors’ ‘closed-world’ assumption8,12. All patients are referenced in Supplementary Table 1.
TCR cloning and tumor reactivity validation
TCRs from the ten inside of melanoma patients had been annotated following the reason described in ref. 3. Temporarily, TCR antitumor reactivity was interrogated by transferring RNA coding for TCRαβ pairs into recipient activated T cells and Jurkat cell line (TCR/CD3 Jurkat-luc cells (NFAT), Promega, stably transduced with human CD8α/β and TCRα/β CRISPR knockout). Electroporated cells had been cocultured with interferon-γ (IFNγ)-treated autologous tumor cells and tumor reactivity was assessed through CD137 upregulation or bioluminescence assay for T cells and Jurkat cells, respectively. From the inside of dataset (n = 10 patients), 102 tumor-reactive and 123 non-tumor-reactive CD8+ TCRs had been ancient to maintain TRTpred and 46 tumor-reactive and 44 non-tumor-reactive CD8+ TCRs had been ancient for the model benchmarking (n = 4 extra patients; Supplementary Table 1). Several TCRs had been previously described3. For the dose–response curve, autologous activated T cells electroporated with TCR 1, 3 or 5 had been cocultured with tumor cells in IFNγ assay, the usage of precoated 96-effectively ELISpot plates (Mabtech) as described16.
Statistical units to predict tumor reactivity
Two a form of approaches had been ancient to predict cell-incandescent tumor specificity: the signature ranking and the LR potential. The units first predict cell-incandescent tumor specificity from scRNA-seq info which is then inferred on the TCR repertoire. The clone-incandescent ranking corresponds to essentially the most tumor-reactive ranking bought by any cell from a given clone.
The signature ranking potential, fashioned in RNA sequencing info analyses, uses differential expression prognosis how to acquire a signature of tumor specificity which is then ancient to ranking cells. To enable comparability between the coaching and testing ratings, the ranking is scaled essentially based on the indicate and fashioned deviation bought from the coaching info. A threshold is then known to stratify cells into tumor-particular and nonspecific cells, maximizing accuracy. Demonstrate that the ranking thresholds are known in the coaching info and utilized on the testing info. For this potential, 9 a form of units had been constructed upon the sequence of 9 differential expression prognosis strategies (DESeq2-Wald/-LRT, edgeR-QFL/-LRT, limma-pattern/-voom, Seurat-LR/-negbinomial/-wilcox). These strategies had been carefully chosen essentially based on differential expression prognosis benchmarking articles25,26 and utilized following most attention-grabbing practices (survey the section ‘Differential expression prognosis strategies’). Other parameters equivalent to the ideal solution to settle the genes from the differential expression prognosis potential (that’s, by pondering handiest the log-fold-trade or the P charge), the sequence of genes in the signature (that’s, signature size), whether to rob handiest the upregulated genes or every up- and downregulated genes (that’s, signature aspect) and the signature ranking potential (Life like, AUCell, Singscore, UCell) had been outlined as hyperparameters to honest-tune (Extended Recordsdata Fig. 2a).
The LR potential uses a mature LR coupled with an elastic-acquire regularization. The form and strength of regularization are outlined, respectively, by the a and l hyperparameters, the set a = 0 corresponds to Ridge regression and a = 1 to Lasso regression. From this definition, we derived LR units essentially based on two a form of operate areas: first the scaled expression info (RNA) and second the fundamental parts. For the RNA operate set, the genes correlating extra than 80% had been removed. Thanks to the trim dimensionality, and as effectively as to the elastic-acquire, we moreover tested filtering nonessential facets. For every operate areas, two a form of dimensionality discount methodologies had been ancient. The first includes conserving handiest facets connected to tumor specificity (Wilcoxon, P P −4 of the outlined variances. The mix ended in ten RNA- and two fundamental-parts-essentially based units (Extended Recordsdata Fig. 2a).
Practicing and evaluation framework
The critiques of the 21 units and their associated hyperparameter combinations had been performed the usage of an NCV (Extended Recordsdata Fig. 2b). This sturdy framework allows us to iteratively educate and check the units on a form of info partitions known as folds. For this utility we ancient an LOPO NCV designed to partition the concepts into coaching folds accrued of info from all patients however one, which constitutes the testing fold. Iteratively, this potential allows us to simulate the evaluation of the model on fresh unobserved info from a form of patients. For the sake of robustness, the efficiency metric chosen to judge the model is the reliable Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC)27. The LOPO evaluation serves as the final model evaluation, and the particular model’s hyperparameters are fined tuned the usage of a same LOPO horrible-validation. Ultimately, a final tumor specificity model is bought by coaching the model the usage of its most attention-grabbing configuration on the total enter info.
Signature sequence and comparability
5 CD8+ TIL tumor-reactive signatures from a form of tumor indications had been restful (refs. 8,11,12,14,17) and when in contrast with TRTpred. All signatures maintain outlined an upregulated gene-set however handiest refs. 14 and 12 maintain a downregulated gene-set. To overview two signatures, now we maintain ancient Venn diagrams and the Jaccard index computed as the sequence of genes in fundamental (intersection) divided by the total sequence of genes (union).
Model benchmarking
To place the robustness of the model’s association with tumor reactivity, we subjected the coaching and evaluation framework to y-randomization assessments by applying the same strategies with info accrued of randomly permuted tumor-reactive annotated clones, repeating the system 100 instances. This large prognosis yielded a median MCC of 0 and a median accuracy of 50%, indicative of the model’s immunity to faulty studying and offering stable validation for its credibility. Encouragingly, we extra validated the efficacy of our model on 100 and 205 CD8+ tumor-reactive annotated clonotypes, sourced from four inside of and four external (ref. 14) melanoma tumor biopsies. To extra explore the generalization doable of TRTpred, we moreover utilized it on three external CD8+ TIL datasets from a form of tumor indications (ref. 11 (GI, n = 5), ref. 8 (melanoma, n = 1; breast, n = 2; GI, n = 12) and ref. 12 (lung, n = 4)). For the sake of completeness, we restful CD8+ TIL tumor-reactive signatures from these be taught and utilized them to every dataset. The external signatures had been utilized on every dataset by the usage of the signature ranking potential described in the respective be taught. If no longer mentioned otherwise, a straightforward life like signature ranking was computed. Ultimately, the discriminant strength of the a form of signatures and TRTpred on every dataset was bought by plotting receiver running characteristic (ROC) curves and by computing the AUC for the ROC curves.
Differential expression prognosis strategies
We utilized 9 a form of differential expression prognosis strategies stumbled on to work most attention-grabbing in scRNA-seq info and utilized them following most attention-grabbing practices pointers26,28. These strategies had been grouped into two classes: the strategies developed for scRNA-seq info (LR, damaging-binomial and Wilcoxon) and the strategies at the foundation developed for bulk RNA sequencing info (edgeR, DESeq2 and limma), named pseudo-bulk strategies for the sake of clarity. The one-cell strategies had been utilized the usage of the Seurat FindMarkers operate on the log10-normalized distinctive molecular identifier counts with all filters (min.pct, handiest.pos, logfc.threshold, min.cells.group) disabled. To make certain that the efficiency of the pseudo-bulk strategies, we utilized them on the clone-life like log10-normalized distinctive molecular identifier counts. We did this to mark a dataset similar to the bulk RNA sequencing info distribution (which reduces inconsistencies in pseudo-bulk strategies28) while conserving the behavior of the clones transcription. EdgeR was utilized every with the likelihood ratio check (edgeR-LRT, with default dispersion estimate) and with the quasi-likelihood potential (edgeR-QFL). DESeq2 was utilized every with the Wald check of the harmful-binomial model coefficients (DESeq2-Wald) and with a likelihood ratio check when in contrast with a diminished model (DESeq2-LRT). Limma was utilized the usage of two approaches: one incorporating the indicate-variance pattern into the empirical Bayes task at the gene level (limma-pattern) and the a form of incorporating the indicate-variance pattern by assigning a weight to every particular person commentary (limma-voom). The log-transformed counts per million values computed by edgeR had been supplied as enter to limma-pattern.
Tumor microdissection and RNA extraction
Tumor microdissection and RNA extraction had been performed as previously described29. Consecutive sections from novel-frozen tissue blocks had been minimize in a cryostat at 8-μm thickness, mounted on precooled PET slides (Leica) at −20 °C for 1 h and mounted in ethanol. They had been stained with cresyl violet, cleared in ethanol and microdissected within 20 min after staining the usage of the Leica LMD7000. Laser parameters had been set as follows: laser strength of 39 mW, a wavelength of 349 nm, pulse frequency of 664 Hz, pulse strength of 58 μJ. Microdissected tissues had been restful in 0.5-ml tubes in RNAlater resolution (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and saved at −20 °C till RNA extrac tion. RNA was extracted the usage of RNeasy Plus Micro Kit (Qiagen). To quantify total RNA, Qubit RNA HS Assay Kit and Qubit Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) had been ancient. The 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent) was ancient to analyze RNA fragment size the usage of Eukaryote Total RNA Pico assay (Agilent).
Sequential multiplexed immunohistochemistry
Sequential multiplexed immunohistochemistry was performed as previously described29. Quiet-frozen tissue sections had been minimize at 4 μm, mounted in paraformaldehyde (4%) in a single day and permeabilized in 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS for 30 min. After warmth-mediated antigen retrieval in pH 6 citrate buffer for 10 min, endogenous peroxidases, nonspecific proteins, endogenous biotins and avidins had been blocked (Dako). After utility of the first predominant antibody, a biotinylated secondary antibody and a streptavidin-HRP advanced had been added. Staining was revealed the usage of AEC Chromogen. Tissues had been counter-stained the usage of Harris hematoxylin for 1 min and lined by a tumbler coverslip the usage of an aqueous mounting resolution. Slides had been scanned into MRXS photos the usage of a Pannoramic 250 Flash III scanner (3D Histech). Glass coverslips had been removed by immersion in sizzling water. AEC staining removed by immersion in ethanol of rising concentrations. Antibodies had been stripped by boiling tissue sections in a resolution of citrate buffer (pH 6) for 10 to 20 min. Putative residual antibodies had been blocked with Fab fragments. Multiplexed immunohistochemistry consisted of sequential cycles of: (1) staining with predominant antibodies revealed by AEC Chromogen; (2) tissue section scanning; (3) removal of AEC Chromogen with ethanol; and (4) antibody stripping and blockading with Fab fragments. Predominant antibodies had been FOXP3 (clone ab99963, Abcam, dilution 1:50) and CD8 (clone C8/144B, Dako, dilution 1:20).
Bulk TCR α and β sequencing
Bulk TCR sequencing analyses had been performed as previously described30. Temporarily, messenger RNA was isolated and amplified by in vitro transcription. A 5′ adapter was added by multiplex reverse transcription and TCRs had been amplified the usage of one primer in the adapter and one in the fixed location. Libraries had been sequenced on an Illumina instrument and TCR sequences processed the usage of an ad hoc Perl script.
TCR repertoire metrics
To analyze TCR repertoires, two metrics had been ancient: (1) the richness same to the total sequence of distinctive clones gift in the repertoire and (2) the clonality described by the metric 1-Pielou’s evenness, as previously described31.
MixTRTpred—integration of TCR structural avidity and TCR clustering
Predictions of TCR structural avidity had been performed as described32. In transient, a binary LR, essentially based on the CDR3β amino acids which may well per chance be sufficiently solvent-exposed to maintain interplay with the cognate peptide, was ancient to search out out whether a TCR was at effort of bind the corresponding pMHC with excessive or low structural avidity (koff). Avidity ranges had been moreover computed with this model on assessable patients, that’s, patients with scTCR-seq info accrued of every alpha and beta CDR3 chain info. TCR clustering the usage of TCRpcDist was performed as described18. TCRpcDist is a original and lickety-split construction-essentially based potential that calculates similarities between TCRs the usage of a metric connected to the physicochemical properties of solvent-exposed amino acids of the finest residues of this receptor.
The TIL repertoire of affected person 14 was analyzed and filtered during the three predictors, TRTpred, the excessive structural avidity predictor32 and TCRpcDist18. To combine the three axes, we first filtered out the low structural avidity predicted clones and ranked the resulting clones essentially based on their tumor-reactive ranking. Ultimately, TCR clustering was utilized on the subset of the dwell 20 tumor-reactive clones. The gap matrix bought through TCRpcDist18 went through hierarchical clustering (agglomerative potential: unweighted pair group potential with arithmetic indicate), leading to a dendrogram. We selected to split the latter into 5 sure TCR clusters given the downstream in vitro and in vivo validation. The sequence of 5 clusters was arbitrary and may well moreover be tailored reckoning on the scientific context.
In vivo build a matter to
The in vivo build a matter to was performed as previously described16 and was current by the Veterinary Authority of the Canton de Vaud (under license 3746) and performed essentially based on Swiss ethical pointers. In transient, Interleukin-2 (IL-2) NOG mice (Taconic Biosciences) had been monitored three instances per week and given a ranking essentially based on their weight, behavior, bodily condition, dehydration, respiration and tumor burden. As per the protocol, animals reaching an outlined ranking had been killed.
TCR transduction for in vivo experiment
TCRs 1, 3 and 5 had been chosen among the 5 in vitro-validated tumor-reactive TCRs from affected person 14 (Supplementary Table 6) to be tested in vivo. The TCR transduction for the in vivo experiments was performed as previously described16. Temporarily, predominant CD8+ T cells from a wholesome donor had been negatively chosen with beads (Miltenyi Biotec), activated and transduced as previously reported16,33. Transduced cells had been stained with an APC-conjugated anti-mouse fixed beta antibody (eBioscience), adopted by sorting with anti-APC microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec). Sorted TCR-transduced CD8+ T cells had been then expanded and tumor reactivity was assessed in IFNγ ELISpot assays (Mabtech). Transduced cells had been then plated at 5 × 103 cells per effectively and challenged with IFNγ-treated autologous tumor cells at a 1:1 ratio. After 18–20 h of incubation, cells had been removed, the plate was developed essentially based on the producer’s instructions and cells had been counted the usage of a Bioreader 6000-E (BioSys).
Adoptive T cell switch in immunodeficient IL-2 NOG mice
The adoptive T cell switch in immunodeficient IL-2 NOG mice was performed as previously described16. IL-2 NOG mice had been subcutaneously injected with 106 autologous human melanoma tumor cells from affected person 14 and, once tumors turned into palpable (day 11), 1–5 × 106 human tumor-particular CD8+ T cell clones had been injected in the tail vein, essentially based on the medicine arms described in Extended Recordsdata Fig. 5cwith 4–6 mice per condition other than in some situations the set 3 mice had been regarded as.
Recordsdata analyses and computation
Recordsdata analyses had been performed the usage of R Statistical Machine (v.4.0.3). All info processing and prognosis was performed the usage of the R dplyr (v.1.1.0) and nefarious libraries. The nested and clear-sever horrible-validations had been performed the usage of an in-dwelling R library developed to manipulate the units and hyperparameters all around the folds. The R library glmnet (v.4.1-6) was ancient to maintain the LR units and their specs. Parallelization of the computation was allowed the usage of the foreach (v.1.5.2) library. The differential expression prognosis strategies had been computed the usage of the particular R libraries (Seurat (v.4.3.0), limma (v.3.50.3), edgeR (v.3.36.0), DESeq2 (v.1.34.0)) as effectively as the signature ranking strategies (AUCell (v.1.16.0), UCell (v.1.3.1), singscore (v.1.14.0), GSEABase (v.1.56.0)). Statistical analyses had been performed the usage of the fashioned stats (v.4.1.2) library. The statistical assessments ancient and their specs are described in the figure legends. Parametric assessments, for evaluating two or extra teams, had been utilized handiest on in overall distributed variables validated with Anderson–Darling, D’Agostino–Pearson omnibus, Shapiro–Wilk and Kolmogorov–Smirnov assessments (GraphPad v.9.1.0); otherwise, nonparametric assessments had been ancient.
Plotting description
The figures had been generated in R Statistical Machine (v.4.0.3) with the ggplot2 (v.3.4.4) R kit. Alluvial plots had been generated the usage of the ggalluvial (v.0.12.5) R kit. The gap heatmaps had been performed the usage of the pheatmap operate from the pheatmap (v.1.0.12) R kit. Plotting of the scRNA-seq-derived UMAP was done the usage of Seurat (v.4.3.0) R kit concepts. Venn diagrams had been bought the usage of the ggven (v.0.1.10) R library. Schematic figures of T cells, cancer cells, TCRs, pores and skin, lungs, gut, breast, tumor and stromal microenvironment, plate and mouse in Fig. 1a had been tailored from templates on BioRender.com. All figures had been reprocessed the usage of Adobe Illustrator 2023 (v.27.9.1) completely for esthetical concepts.
Reporting summary
Extra info on be taught fabricate is on hand in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Abstract linked to this text.
Recordsdata availability
scRNA-seq/scTCR-seq info from baseline tumors of patients 1–10/14 from the TIL ACT are on hand under the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) accession quantity GSE222448 (ref. 34). scRNA-seq/scTCR-seq info from baseline tumors of the extra melanoma patients 11, 12 and 13 are on hand at Zenodo through https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10869332 (ref. 35). Source info are supplied with this paper.
Code availability
The computational code ancient in this build a matter to is proprietary and will more than seemingly be made on hand to tutorial researchers upon cheap build a matter to. Nonetheless, it has been assessed throughout the gape-overview task.
References
Rosenberg, S. A. & Restifo, N. P. Adoptive cell switch as personalized immunotherapy for human cancer. Science 34862–68 (2015).
Rohan, MW et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte remedy or ipilimumab in evolved melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 3872113–2125 (2022).
Chiffelle, J. et al. Tumor-reactive clonotype dynamics underlying scientific response to TIL remedy in melanoma. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.21.544585 (2023).
Kristensen, N. P. et al. Neoantigen-reactive CD8+ T cells maintain an mark on scientific final consequence of adoptive cell remedy with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in melanoma. J. Clin. Invest. 132132 (2022).
Kverneland, A. H. et al. Adoptive cell remedy with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes supported by checkpoint inhibition across extra than one solid cancer forms. J. Immunother. Cancer 9e003499 (2021).
Baulu, E., Gardet, C ., Chuvin, N. & Depil, S. TCR-engineered T cell remedy in solid tumors: cutting-edge and perspectives. Sci. Adv. 9eadf3700 (2023).
Shafer, P., Kelly, L. M. & Hoyos, V. Cancer remedy with TCR-engineered T cells: novel strategies, challenges, and possibilities. Front. Immunol. 13835762 (2022).
Lowery, F. J. et al. Molecular signatures of antitumor neoantigen-reactive T cells from metastatic human cancers. Science 375eabl5447 (2022).
Veatch, J. R. et al. Neoantigen-particular CD4+ T cells in human melanoma maintain various differentiation states and correlate with CD8+ T cell, macrophage, and B cell operate. Cancer Cell 40393–409.e9 (2022).
Caushi, J. X. et al. Transcriptional packages of neoantigen-particular TIL in anti-PD-1-treated lung cancers. Nature 596126–132 (2021).
Zheng, C. et al. Transcriptomic profiles of neoantigen-reactive T cells in human gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Cell 40410–423.e7 (2022).
Hanada, Good enough.-I. et al. A phenotypic signature that identifies neoantigen-reactive T cells in novel human lung cancers. Cancer Cell 40479–493.e6 (2022).
He, J. et al. Defined tumor antigen-particular T cells potentiate personalized TCR-T cell remedy and prediction of immunotherapy response. Cell Res. 32530–542 (2022).
Oliveira, G. et al. Phenotype, specificity and avidity of antitumour CD8+ T cells in melanoma. Nature 596119–125 (2021).
Li, H. et al. Dysfunctional CD8 T cells construct a proliferative, dynamically regulated compartment within human melanoma. Cell 176775–789.e18 (2019).
Schmidt, J. et al. Neoantigen-particular CD8 T cells with excessive structural avidity preferentially dwell in and discover rid of tumors. Nat. Common. 143188 (2023).
van der Leun, AM, Thommen, DS & Schumacher, TN CD8+ T cell states in human cancer: insights from single-cell prognosis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 20218–232 (2020).
Perez, M. A. S. et al. TCRpcDist: estimating TCR physico-chemical similarity to analyze repertoires and predict specificities. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.15.545077 (2023).
Barras, D. et al. Response to tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte adoptive remedy is expounded to preexisting CD8+ T-myeloid cell networks in melanoma. Sci. Immunol. 97995 (2024).
Bobisse, S. et al. A section 1 trial of adoptive switch of vaccine-primed autologous circulating T cells in ovarian cancer. Nat. Cancer 41410–1417 (2023).
Arnaud, M. et al. Quiet identification of neoantigens and cognate TCRs in human solid tumors. Nat. Biotechnol. 40656–660 (2021).
Duraiswamy, J. et al. Myeloid antigen-presenting cell niches sustain antitumor T cells and license PD-1 blockade through CD28 costimulation. Cancer Cell 391623–1642.e20 (2021).
Foy, S. P. et al. Non-viral precision T cell receptor replace for personalized cell remedy. Nat. 615687–696 (2022).
Irvine, D. J., Maus, M. V., Mooney, D. J. & Wong, W. W. The long bustle of engineered immune cell therapies. Science 378853–858 (2022).
Mou, T., Deng, W., Gu, F., Pawitan, Y. & Vu, T. N. Reproducibility of how to detect differentially expressed genes from single-cell RNA sequencing. Front. Genet. 101331 (2020).
Soneson, C. & Robinson, M. D. Bias, robustness and scalability in single-cell differential expression prognosis. Nat. Strategies 15255–261 (2018).
Chicco, D. & Jurman, G. Some great advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 ranking and accuracy in binary classification evaluation. BMC Genomics 211–13 (2020).
Squair, J. W. et al. Confronting faulty discoveries in single-cell differential expression. Nat. Common. 125692 (2021).
Romanens, L. et al. Clonal expansion of intra-epithelial T cells in breast cancer revealed by spatial transcriptomics. Int. J. Cancer 1531568–1578 (2023).
Genolet, R. et al. TCR sequencing and cloning strategies for repertoire prognosis and isolation of tumor-reactive TCRs. Cell Obtain. Strategies 3100459 (2023).
Chiffelle, J. et al. T-cell repertoire prognosis and metrics of diversity and clonality. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 65284–295 (2020).
Schmidt, J. et al. Prediction of neo-epitope immunogenicity unearths TCR recognition determinants and affords perception into immunoediting. Cell Obtain. Med. 2100194 (2021).
Giordano-Attianese, G. et al. A computationally designed chimeric antigen receptor affords a dinky-molecule safety swap for T-cell remedy. Nat. Biotechnol. 38426–432 (2020).
Barras, D. et al. Response to tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte adoptive remedy is expounded to preexisting CD8+ T-myeloid cell networks in melanoma. Gene Expression Omnibus www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/demand/acc.cgi?acc=GSE222448 (2024).
Petremand, R. et al. Identification of clinically connected T cell receptors for personalized T cell remedy the usage of combinatorial algorithms. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10869331 (2024).
Acknowledgements
The conduct of the build a matter to was supported by grants from the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant nos. 310030_182384 and CRSII5_193749, A.H.) and the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research (G.C.). We moreover thank the Cancera Foundation, the Mats Paulsson Foundation and the Biltema Foundation during the ISREC Foundation for financial make stronger grants. V.Z. was supported by SNSF grant no. 205321_192019. We thank the total patients, relatives and team from the total units that participated in this build a matter to. We thank A. Auger, T. Gehret and B. Murgues for his or her technical assistance with TCR screening, as effectively as L. Queiroz and A. Kennel for his or her technical assistance with bulk TCR sequencing. We thank Q. Ai Ngo for the dialogue on the differential expression prognosis instruments. We thank Y. Zouaghi for his valuable discussions on machine studying approaches. Ultimately, we thank V. Du Bois for her support with the microscopy imaging.
Funding
Start access funding supplied by University of Lausanne.
Ethics declarations
Competing pursuits
V.Z. is a handbook for Cellestia Biotech. G.C. has received grants or be taught make stronger from or is a coinvestigator in scientific trials by Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Celgene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Tigen, Roche, Iovance and Kite. G.C. has received honoraria for consultations or presentations from Roche, Genentech, BMS, AstraZeneca, Sanofi-Aventis, Nextcure and GeneosTx. G.C. has patents in the domain of antibodies and vaccines focusing on the tumor vasculature as effectively as applied sciences connected to T cell expansion and engineering for T cell remedy. G.C. receives royalties from the University of Pennsylvania. S.B., G.C. and A.H. are inventors in applied sciences connected to T cell expansion and engineering for T cell remedy. R.G is inventor on a patent connected to TCR sequencing. A.H., R.P., V.Z., M.A.S.P. and G.C. are inventors on patent applications filed under sure field matters disclosed herein. The final authors uncover no competing pursuits.
Gape overview
Gape overview info
Nature Biotechnology thanks Cornelis Melief, Sri Krishna and the a form of, anonymous, reviewer(s) for his or her contribution to the gape overview of this work.
Extra info
Publisher’s show Springer Nature remains neutral in regards to jurisdictional claims in printed maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended info
Extended Recordsdata Fig. 1 Description of inside of and external benchmarking cohorts.
a) Alluvial set of abode exhibiting the fractions of cells and clones annotated as tumor-reactive or non-tumor-reactive (orphan or antigen (Ag)-particular) within the enter info (n=10 melanoma patients). b-c) Alluvial plots exhibiting the fractions of cells and clones annotated as tumor-reactive or non-tumor-reactive (orphan or antigen (Ag)-particular) within the inside of (b, n=4) and external (c, n=4, Oliveira et al.14) info.
Extended Recordsdata Fig. 2 Model fabricate and training structure.
a) Illustration of Logistic Regression (LR) and signature scoring units, hyperparameters and outputs (survey Strategies). The tables characterize the 21 units. b) Illustration of the nested-horrible-validation framework to educate and overview the units. Here we adapt a scoot away-one-affected person-out potential to better simulate the model efficiency on fresh info from a brand fresh affected person (survey Strategies). In field plots, the boxes signify the median and the interquartile vary (IQR), while the whiskers lengthen to 1.5 instances the IQR.
Extended Recordsdata Fig. 3 TRTpred’s validation and outcomes.
a) Y-random permutation assessments (dim parts, n=100) outcomes through Matthew′s Correlation Coefficient (MCC), AUC and accuracy. The crimson square corresponds to the particular model outcomes demonstrating its validity. b) Heatmap evaluating connected up and down regulated genes from TRTpred’s signature with 5 printed CD8+ TILs tumor-reactive signatures (Oliveira et al.14Hanada et al.12Lowery et al.8Zheng et al.11 and van der Leune et al.17). c) Venn diagrams evaluating the up (high) and down (backside) regulated genes from TRTpred signature (crimson) with the 5 CD8+ TILs tumor-reactive signatures from panel B (gray). Beneath the Venn diagrams are the Jaccard indexes and the list of fundamental genes. d) Heatmap of the Jaccard similarity index matrix evaluating the 6 CD8+ TILs tumor-reactive signatures from panels B and C. The upper and lower triangle of this matrix correspond to the up and down regulated genes, respectively. Grey boxes correspond to missing gene-units. e) Heatmap of AUC performances of 6 CD8+ TILs tumor-reactive predictive signatures (X-axis) utilized on 6 datasets (Y-axis) comprising the enter info (melanoma, n=10), the inside of benchmarking info (melanoma, n=4) and info from 4 cohorts: Oliveira et al.14 (melanoma, n=4), Hanada et al.12 (lung, n=4), Lowery et al.8 (n=1 melanoma, n=2 breast and n=12 GI) and Zheng et al.11 (GI, n=5). The efficiency of every model on its fashioned info is highlighted.
Extended Recordsdata Fig. 4 Microdissected stromal and tumor core areas.
a) Advisor instance of the frequency of annotated CD8+ T-cell clones particular for TAAs, neoantigens or viral peptides in the microdissected stromal and tumor core areas of affected person 2. Frequencies are displayed in logarithmic scale. b) Cumulative frequencies of annotated CD8+ T-cell clones particular for TAAs, neoantigens or viral peptides in the microdissected stromal and tumor core areas of 5 melanoma patients (1–5, Supplementary Table 3). Frequencies are displayed in logarithmic scale and statistics had been performed the usage of a one-tailed Chi-square check.
Extended Recordsdata Fig. 5 MixTRTpred scientific validation.
a) TRTpred ranking distribution for predicted excessive and low avidity clones. Red parts correspond to predicted tumor-reactive clones which may well per chance be predicted as having excessive avidity. In field plots, the boxes signify the median and the interquartile vary (IQR), while the whiskers lengthen to 1.5 instances the IQR. b) In vitro validation of the chosen three TCRs (TCR1, 3 and 5, Supplementary Table 6) for the alive experiment. T-cell responses of TCR-transfected cells in opposition to the autologous tumor cell line was assessed by IFNγ ELISpot assay (indicate on n=3 biologically neutral replicates). c) Make of the alive experiment illustrating the a form of arms accrued of merchandise with particular person or mixed TCR-transduced populations (TCR 1, 3 and 5, Supplementary Table 6). d) Dose response of Jurkat cells transfected with TCR 1, 3 or 5 and stimulated in a form of ratios with autologous tumor cells. Recordsdata point to indicate±SD on n=2 biologically neutral replicates. e) Total quantity and intratumoral frequency of clinically connected clones (predicted to be tumor-reactive and of excessive avidity) in 37 patients from 4 datasets grouped by tumor-indications: Internal (melanoma, n=14); Oliveira et al.14 (melanoma, n=4); Hanada et al.12 (lung, n=4); and Lowery et al.8 (n=1 melanoma, n=2 breast and n=12 GI). A threshold of 5 sure clinically connected TCRs is confirmed. Colors correspond to the a form of tumor indications.
Supplementary info
Source info
Rights and permissions
Start Gather admission to This article is licensed under a Ingenious Common s Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits explain, sharing, adaptation, distribution and replica in any medium or layout, as long as you give appropriate credit ranking to the distinctive creator(s) and the source, provide a link to the Ingenious Commons licence, and show if modifications had been made. The photos or a form of third occasion cloth in this text are integrated in the article’s Ingenious Commons licence, except indicated otherwise in a credit ranking line to the cloth. If cloth is no longer integrated in the article’s Ingenious Commons licence and your intended explain is no longer licensed by statutory regulation or exceeds the licensed explain, you are going to ought to mark permission suddenly from the copyright holder. To see a copy of this licence, talk about with http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this text
Cite this text
Pétremand, R., Chiffelle, J., Bobisse, S. et al. Identification of clinically connected T cell receptors for personalized T cell remedy the usage of combinatorial algorithms. Nat Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02232-0
Obtained:
Licensed:
Printed:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02232-0



 Hot Deals
Hot Deals Shopfinish
Shopfinish Shop
Shop Appliances
Appliances Babies & Kids
Babies & Kids Best Selling
Best Selling Books
Books Consumer Electronics
Consumer Electronics Furniture
Furniture Home & Kitchen
Home & Kitchen Jewelry
Jewelry Luxury & Beauty
Luxury & Beauty Shoes
Shoes Training & Certifications
Training & Certifications Wears & Clothings
Wears & Clothings