35 Years Ago: STS-30 Launches Magellan to Venus

NASA Space Technology
On Could per chance 4, 1989, residence shuttle Atlantis took off on its third flight, STS-30, from NASA’s Kennedy Place Center (KSC) in Florida. Its 5-person crew of Commander David M. WalkerPilot Ronald J. Grabeand Mission Specialists Brand C. Lee, Norman E. Thagardand Mary L. Lop flew a four-day mission that deployed the Magellan spacecraft, managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, to acknowledge Venus, uniting NASA’s human and interplanetary spaceflight programs. It additionally marked the first U.S. planetary open since 1978. The astronauts deployed Magellan and its upper stage on their first day in residence, sending the spacecraft on its 15-month hasten to Venus. Following its arrival on the cloud-shrouded planet, Magellan spent four years mapping Venus in unparalleled factor, vastly rising our info of the planet.
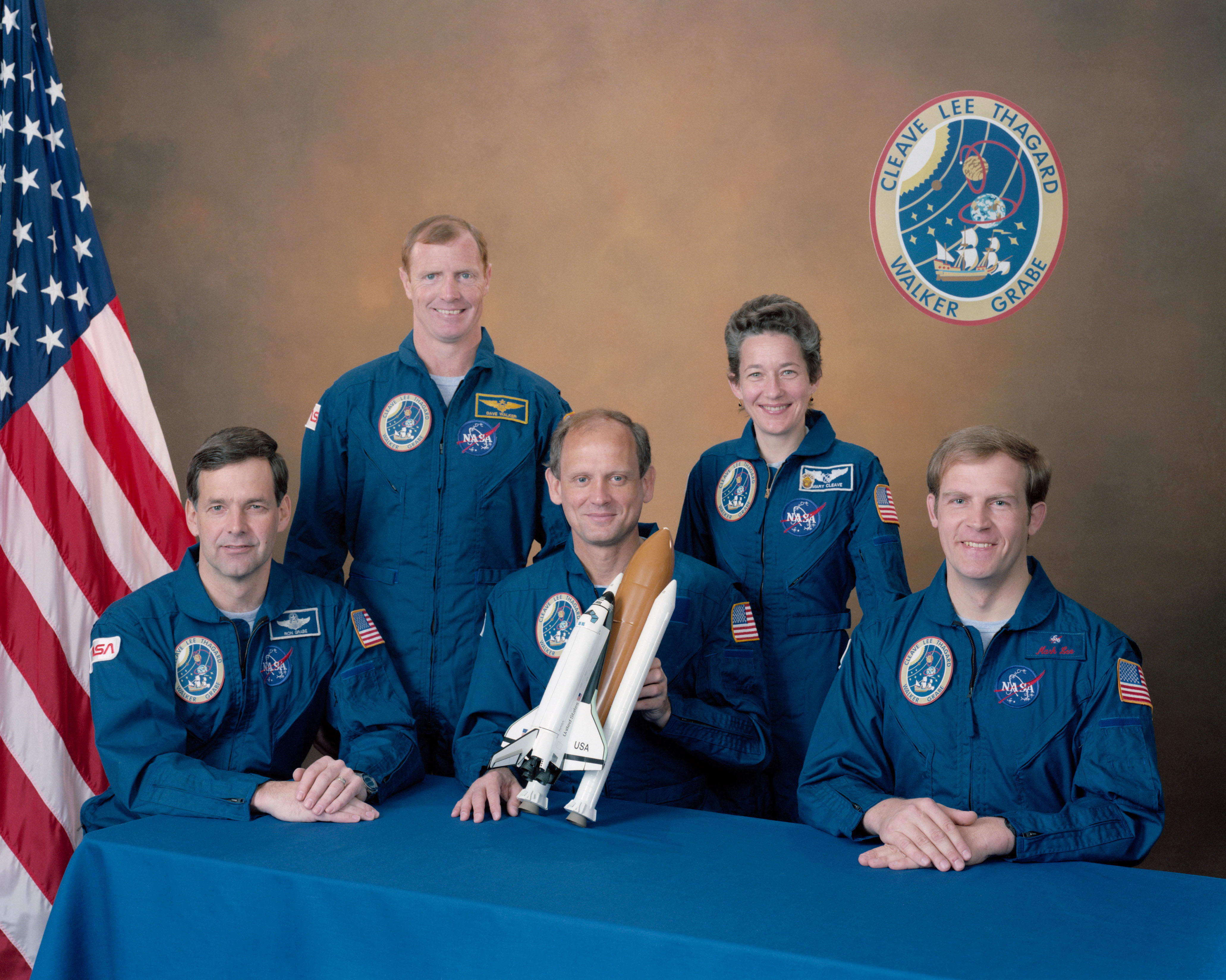
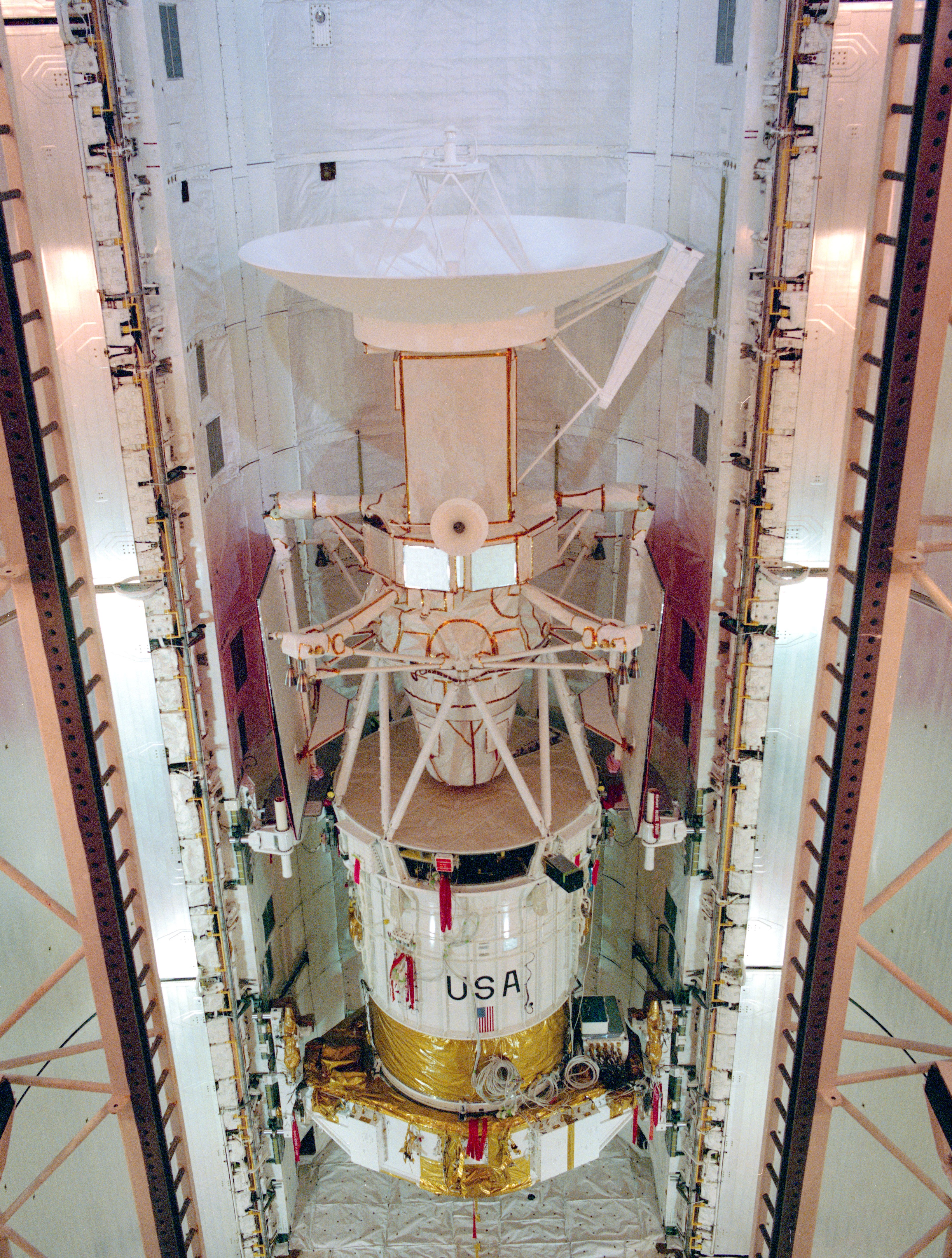



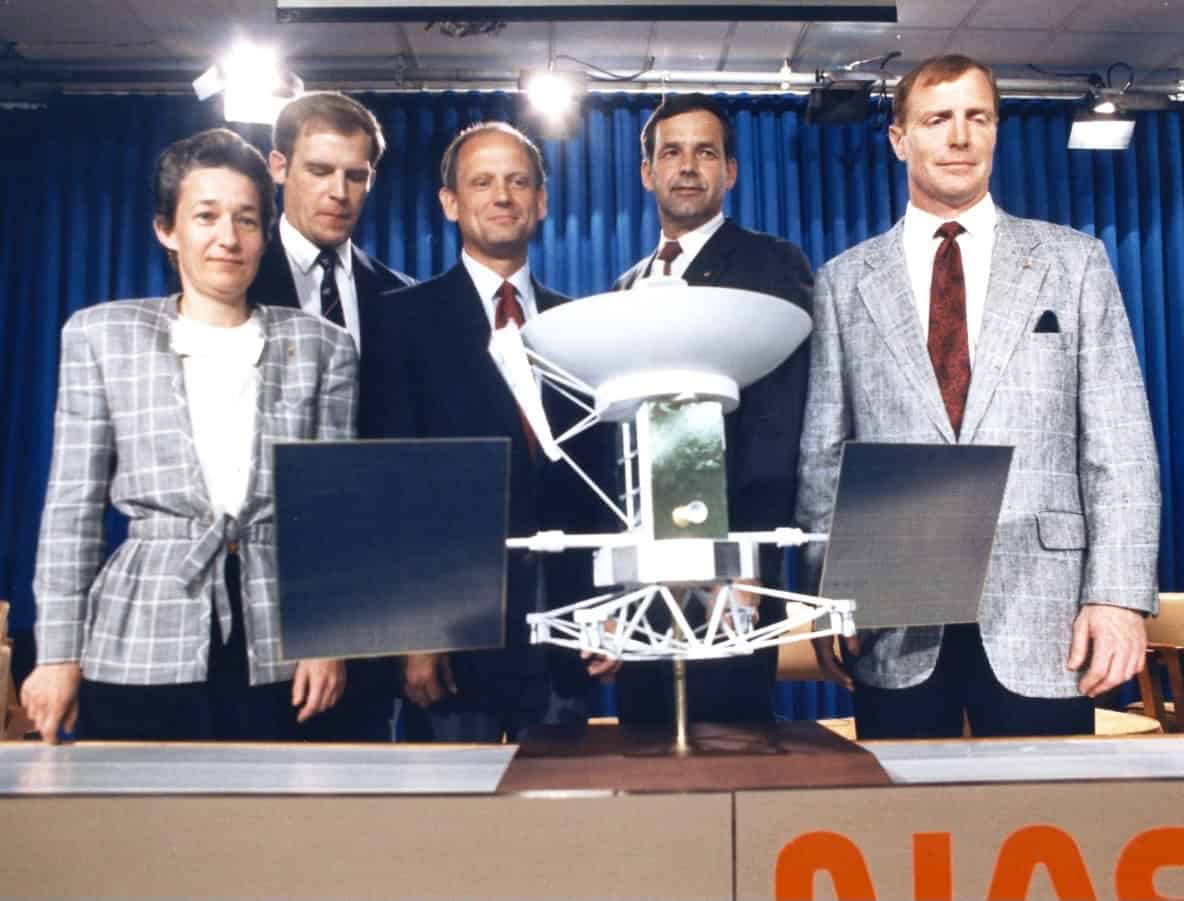
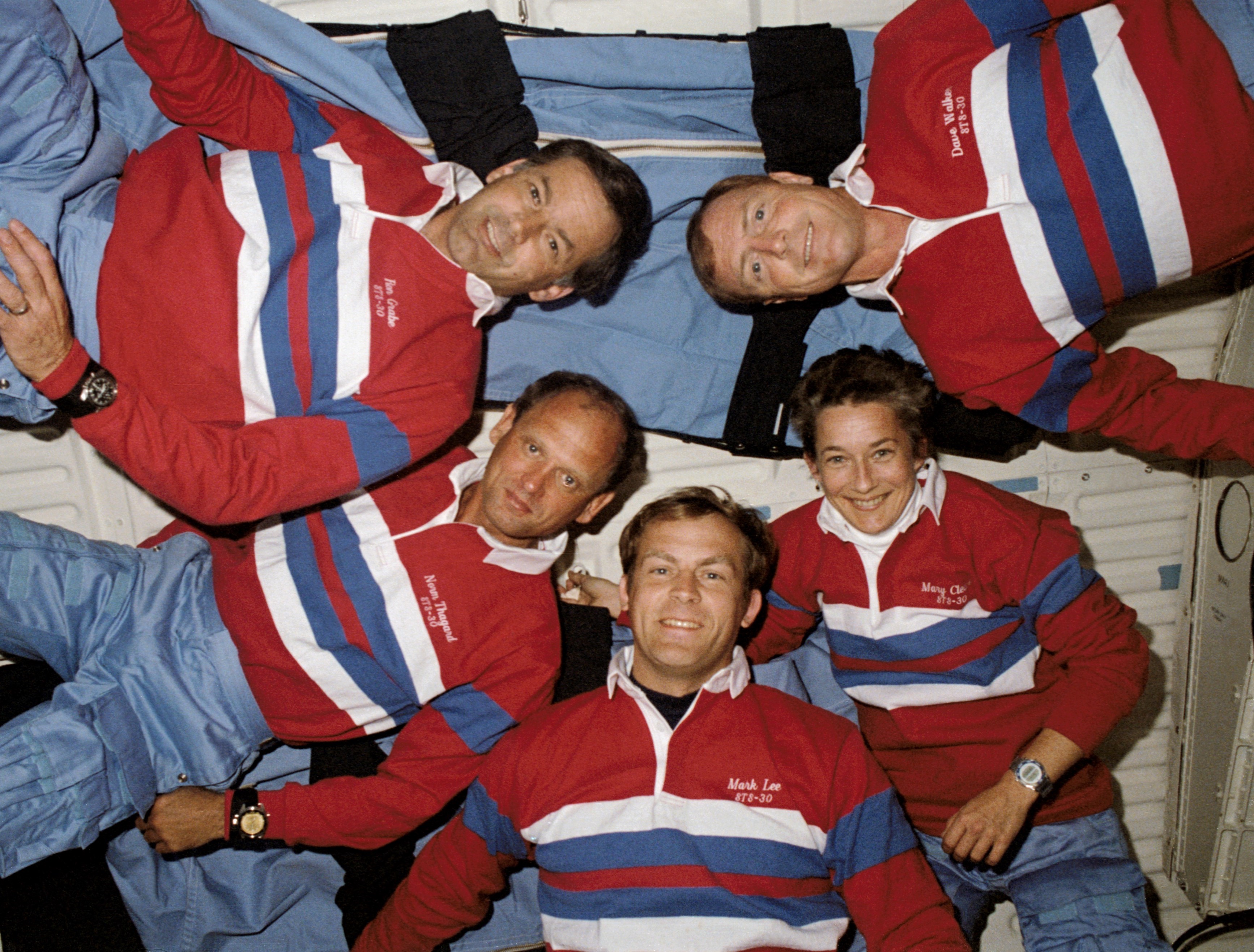
Left: The STS-30 crew of Pilot Ronald J. Grabe, left, Commander David M. Walker, and Mission Specialists Norman E. Thagard, Mary L. Lop, and Brand C. Lee. Center: The STS-30 crew patch. Correct: The Magellan spacecraft in Atlantis’ payload bay in preparation for STS-30.
In March 1988, NASA announced Walker, Grabe, Lee, Thagard, and Lop because the STS-30 crew for the flight planned for slack April 1989. Thagard had flown twice earlier than, on STS-7 in June 1983 and the STS-51B Spacelab 3 mission in April-Could per chance 1985. Walker, Grabe, and Lop had every flown once earlier than, on STS-51ASTS-51J, and STS-61B, respectively, whereas STS-30 marked Lee’s first day out into residence. Walker and Thagard joined NASA in the astronaut class of 1978Grabe and Lop joined in 1980and Lee in 1984. At some point soon of their four-day mission, the astronauts planned to deploy Magellan and its Inertial Greater Stage (IUS) on the first flight day. Magellan wanted to open inside of a 29-day window, dictated by the alignments of Venus and Earth to finish the fitting trajectory for the hasten to its vacation residing.
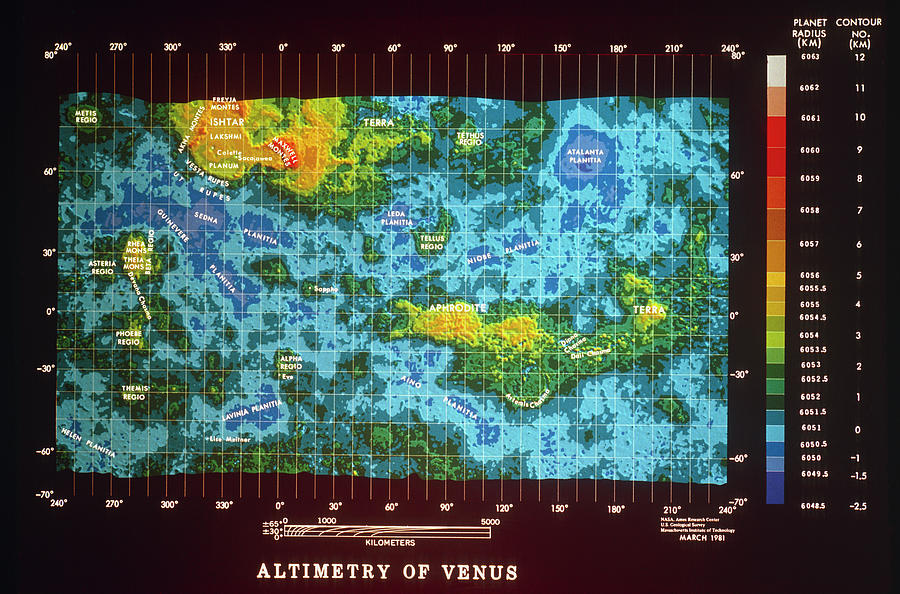
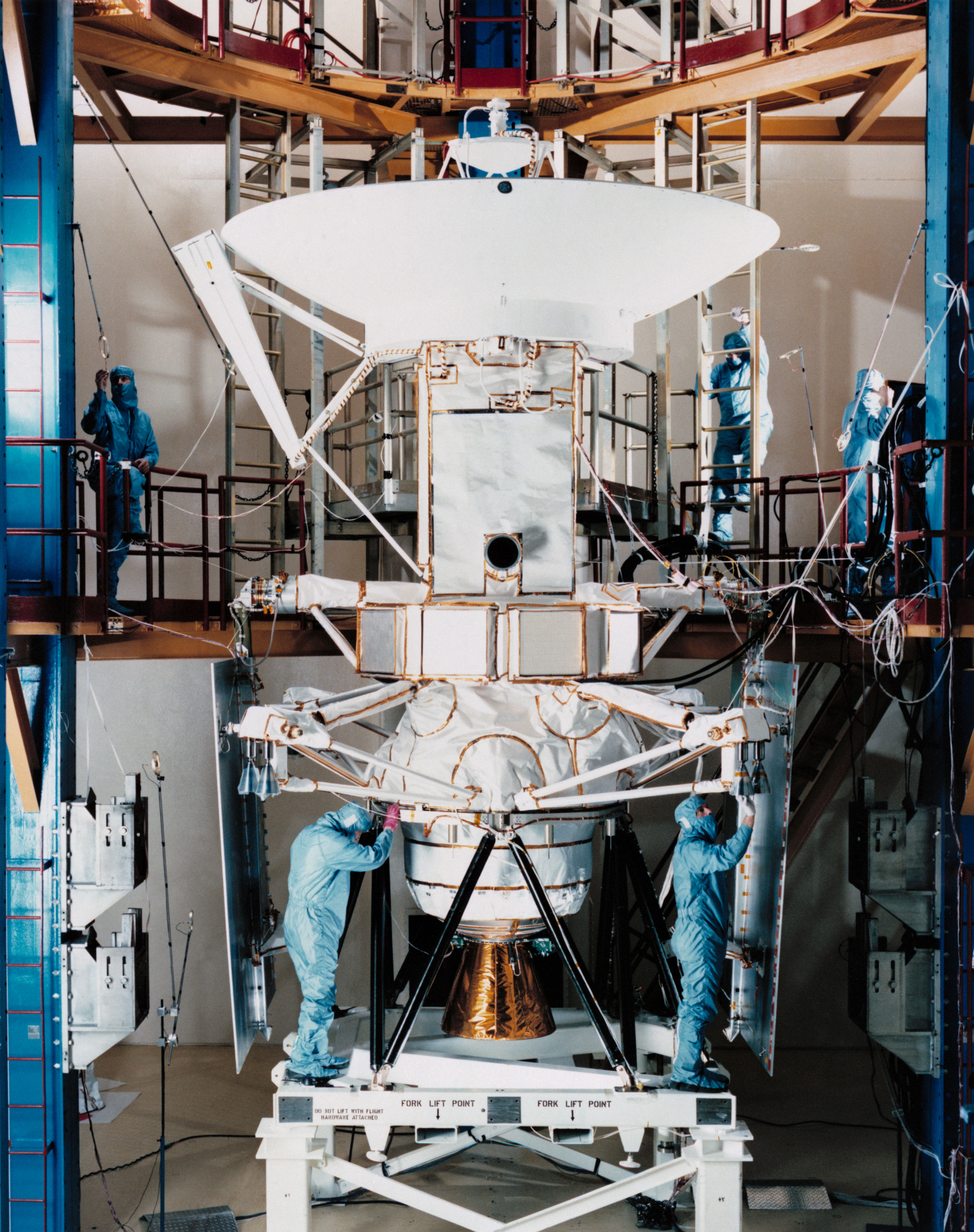
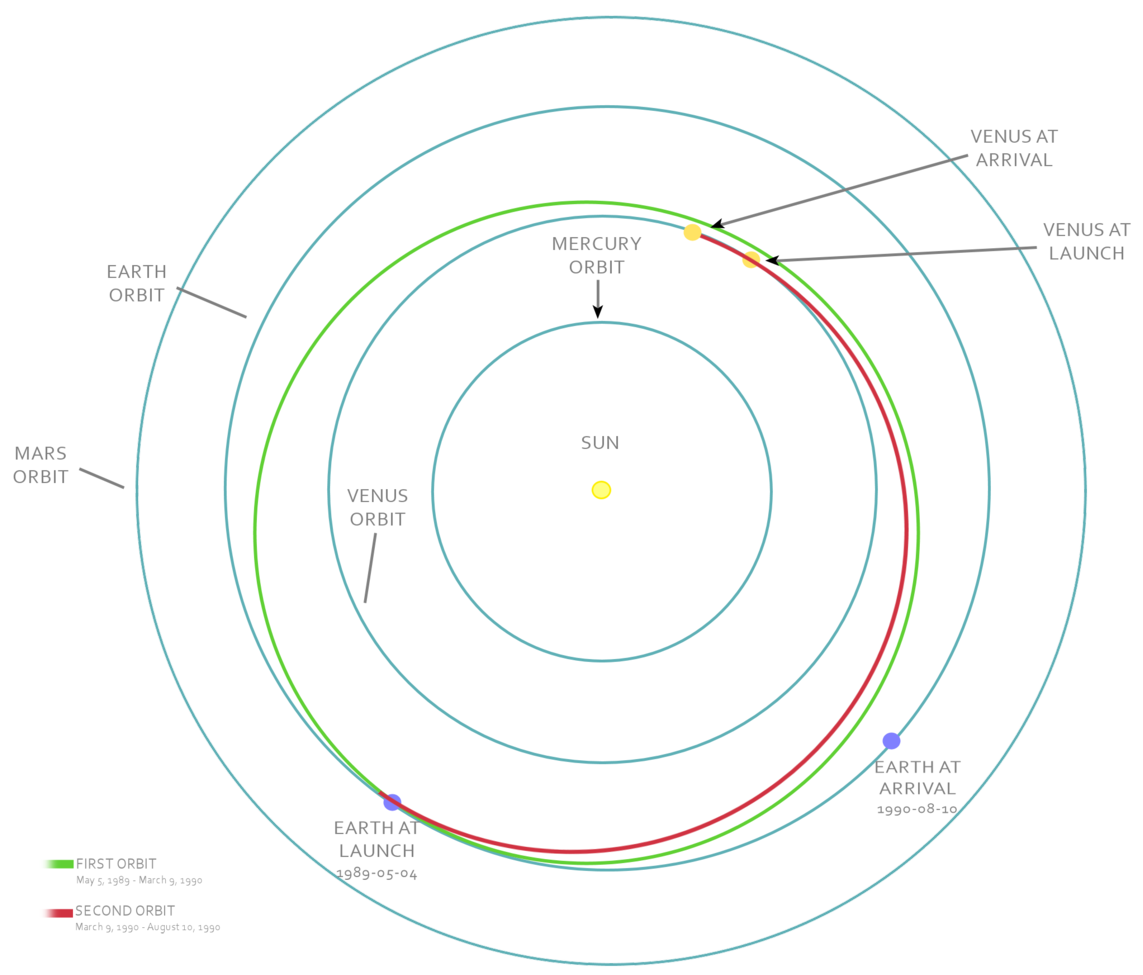
Left: Global design of Venus in step with Pioneer Venus Orbiter radar knowledge. Center: Engineers at Martin Marietta prepare Magellan for cargo to NASA’s Kennedy Place Center in Florida. Correct: Schematic of Magellan’s trajectory from Earth to Venus.
Magellan sought to comprise the perfect decision radar imagery of Venus, bettering on knowledge got by earlier spacecraft. At some point soon of its 14 years orbiting Venus between 1978 and 1992, Pioneer Venus Orbitermanaged by the NASA Ames Analysis Center in California’s Silicon Valley, amongst other observations former its radar to design approximately 90% of Venus at a decision of about 10 kilometers. Scientists yearned for larger decision radar imagery, and the Soviet Union’s Venera 15 and 16, with their larger antennas, mapped just a few quarter of the planet’s ground to a decision of 1 to 2 kilometers between October 1983 and June 1984. Initiated because the Venus Radar Mapper mission in 1983, NASA renamed the challenge in 1985 after the 16th century Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan. Martin Marietta Astronautics Team in Denver built the spacecraft, well-known of it from residence ingredients, at the side of the utilization of a spare main spacecraft bus from the Voyager program. Within the origin, plans called for Magellan to open in April 1988 aboard the residence shuttle the utilization of a Centaur upper stage to ship it on a four-month hasten to Venus. Following the Challenger accident, NASA canceled the Centaur as a residence shuttle upper stage, remanifesting Magellan on the IUS. The fundamental obtainable open window for a four-month flight occurred in October 1989, but the Jupiter-trip Galileo spacecraft wanted that likelihood because it required a gravity-relief at Venus to acquire it to its last vacation residing. Specialists settled on a longer flight time for Magellan to make exercise of the sooner April-Could per chance 1989 window. After deployment from the shuttle, the 2-stage IUS would plight Magellan on its interplanetary hasten that will presumably well rob it 1.5 occasions all the way in which by the Sun. Arriving at Venus, Magellan’s steady-rocket Superstar 48B motor would fire to plight it into orbit round Venus to originate up its main mission lasting 243 days, the duration of 1 Venusian day. Utilizing its excessive-acquire antenna as a radar dish, Magellan would design no much less than 70 percent of the cloud-shrouded planet’s ground to a decision of 1 kilometer.
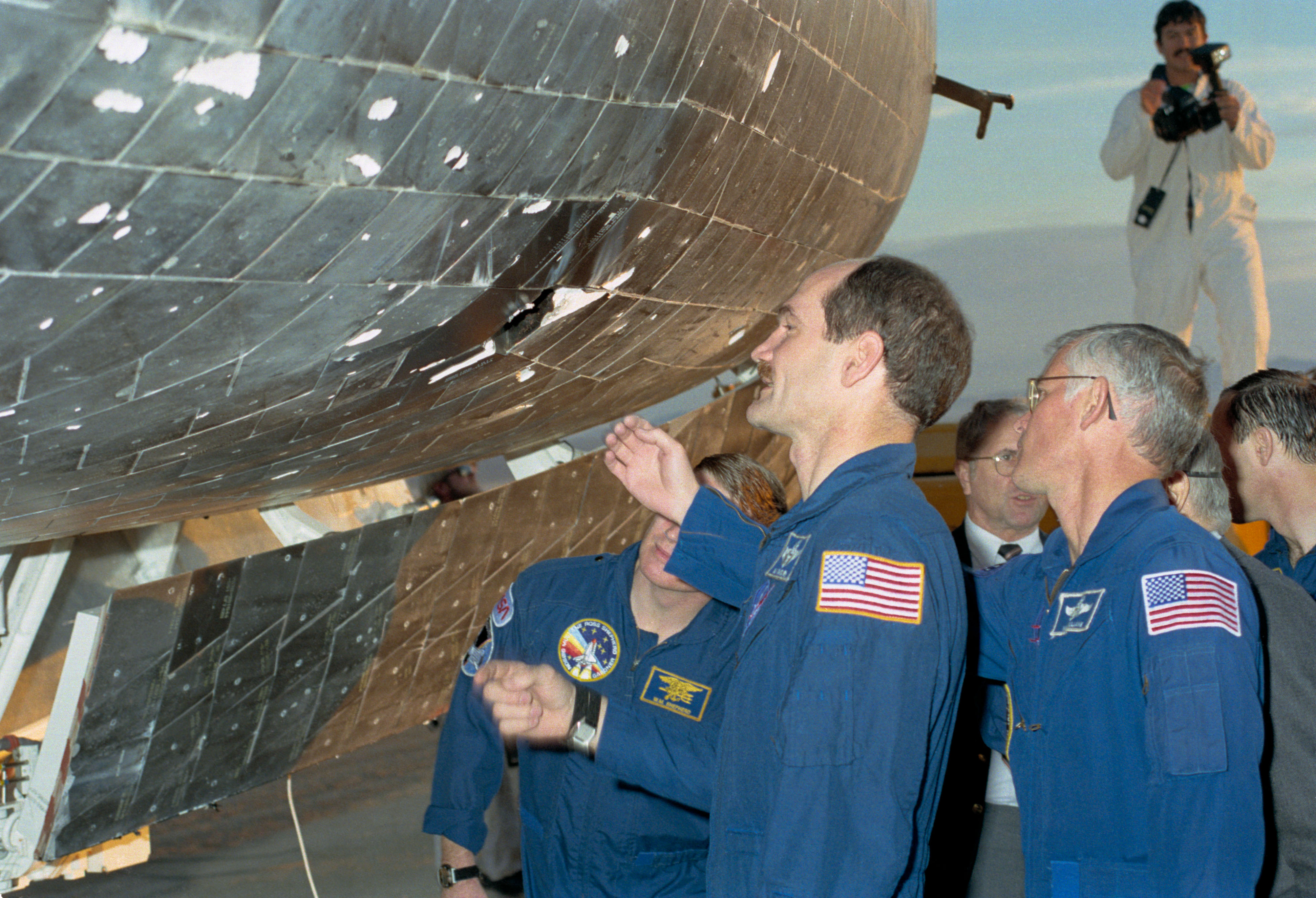
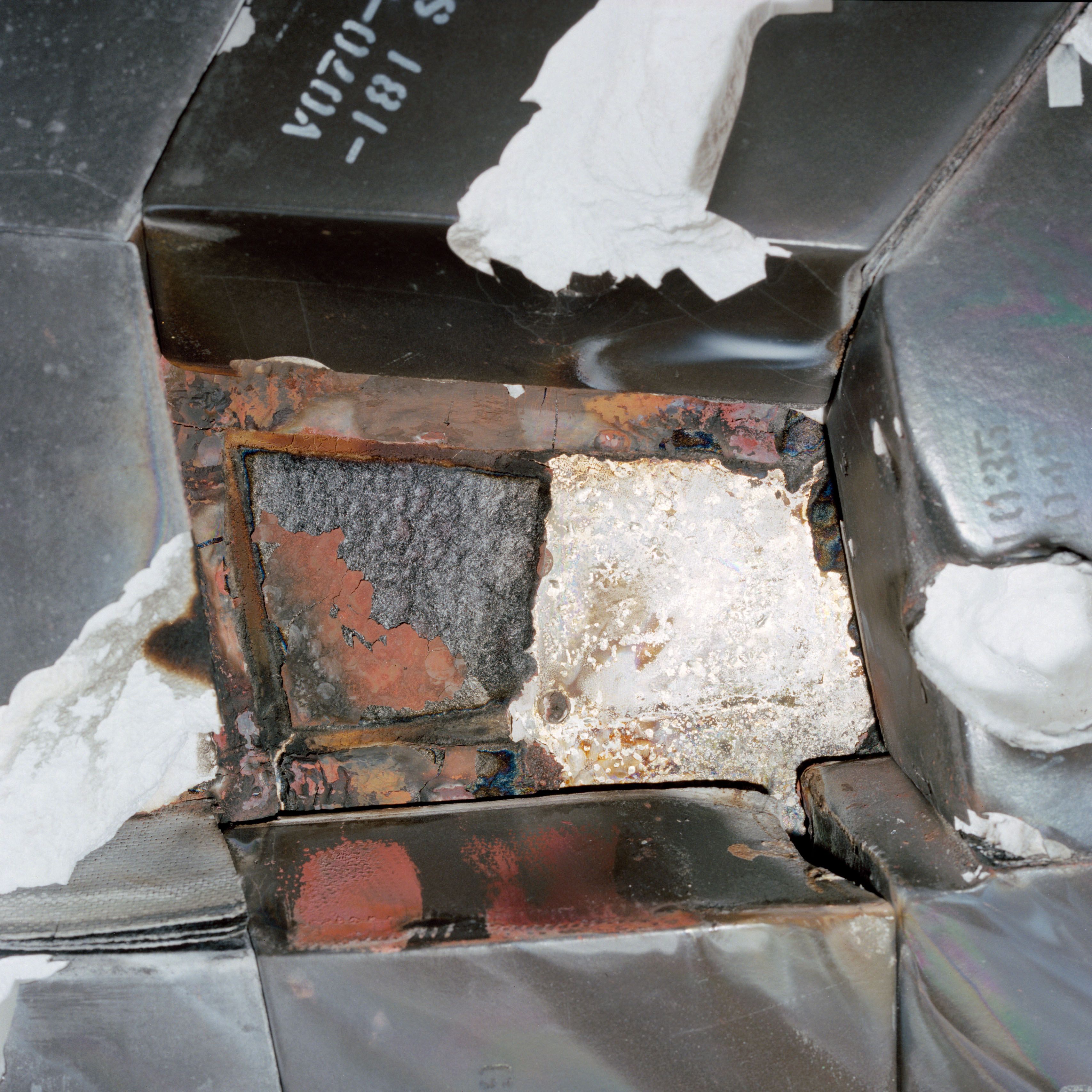



Left: STS-27 astronauts sight the tile fracture on Atlantis. Center: Closeup of missing tile plight on Atlantis. Correct: Atlantis returns to NASA’s Kennedy Place Center in Florida following STS-27.
Atlantis landed at Edwards Air Force Atrocious in California’s Mojave Desert on Dec. 6, 1988, concluding the STS-27 mission. At some point soon of open four days earlier, 85 seconds after liftoff a a part of insulation from the tip of the truthful-hand steady rocket booster broke away and struck Atlantis’ truthful aspect. While in orbit, the crew former the shuttle’s Faraway Manipulator Machine, or robotic arm, to picture Atlantis for any signs of fracture. The astronauts clearly seen intensive fracture on their onboard monitors, but attributable to the categorized nature of the mission, downlinking the video required encryption that a good deal degraded the picture quality. Floor controllers did not absolutely esteem the extent of the fracture and remained unconcerned all the way in which by Atlantis’ reentry. No longer till the postlanding inspection did engineers and executives realize with fright how shut they came to catastrophe. Atlantis arrived abet at KSC on Dec. 13, where workers towed it to the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) the subsequent day for investigation into and repair of basically the most necessary tile fracture seen as much as that time. Extra than 700 tiles bought some fracture, with one tile missing entirely and the underlying steel in part melted.
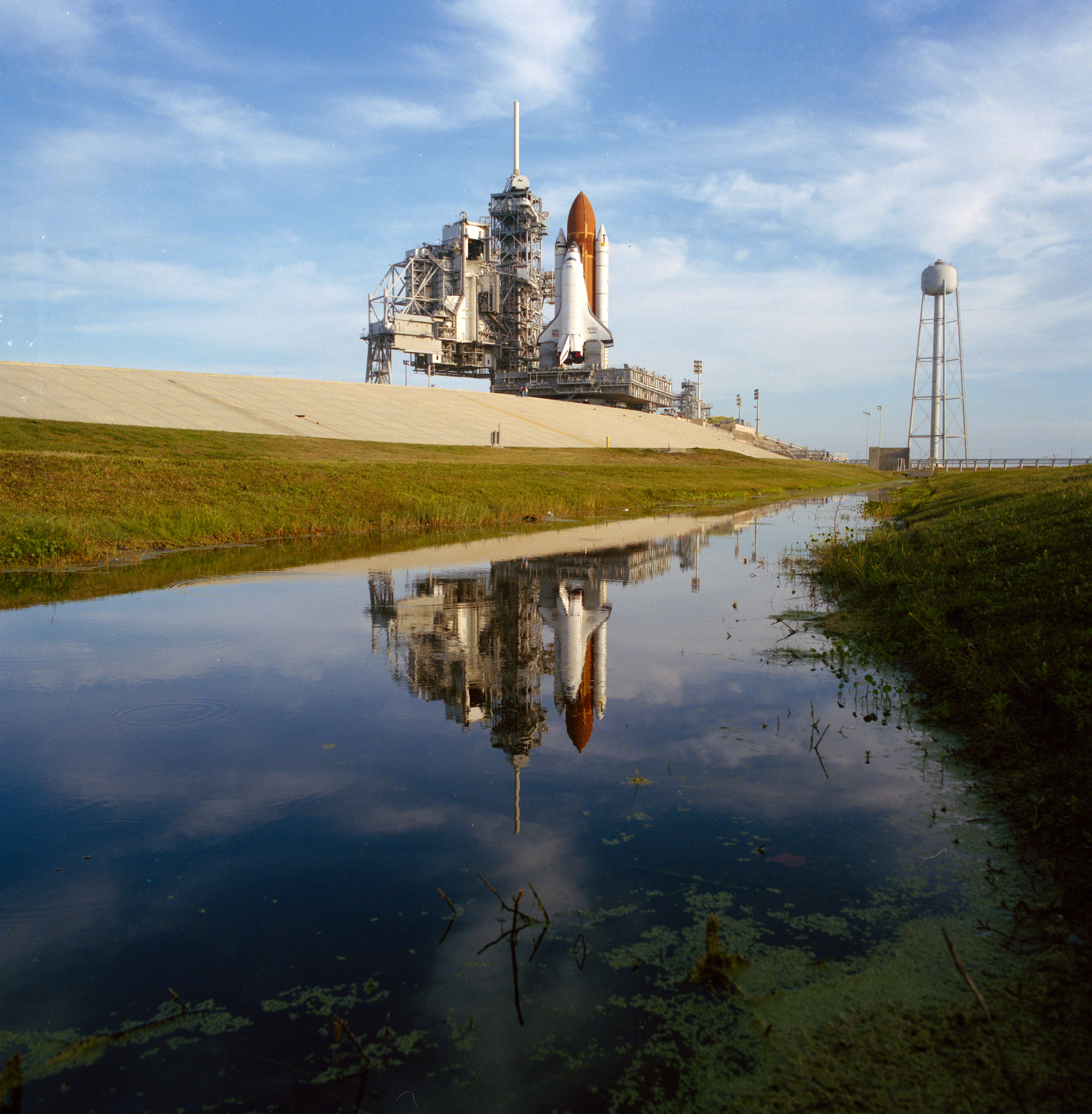
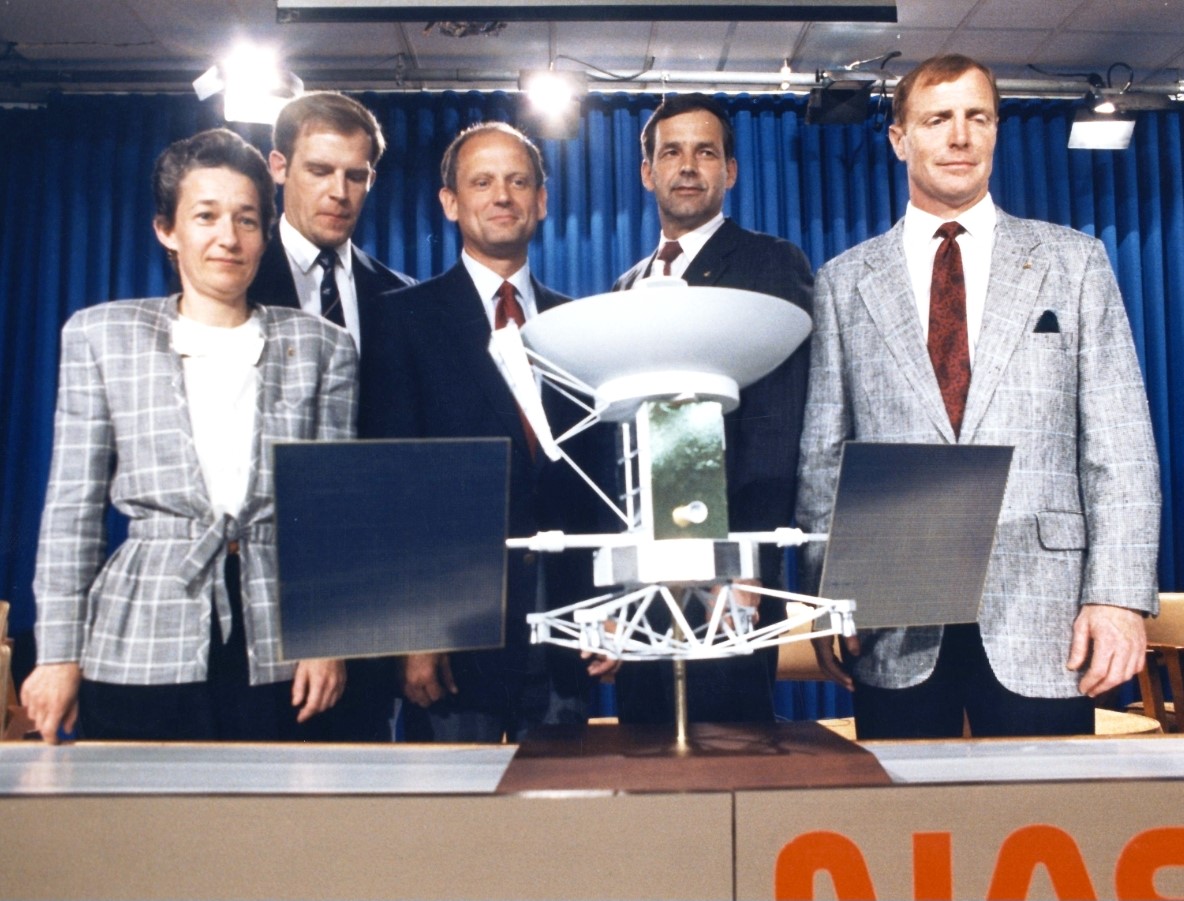



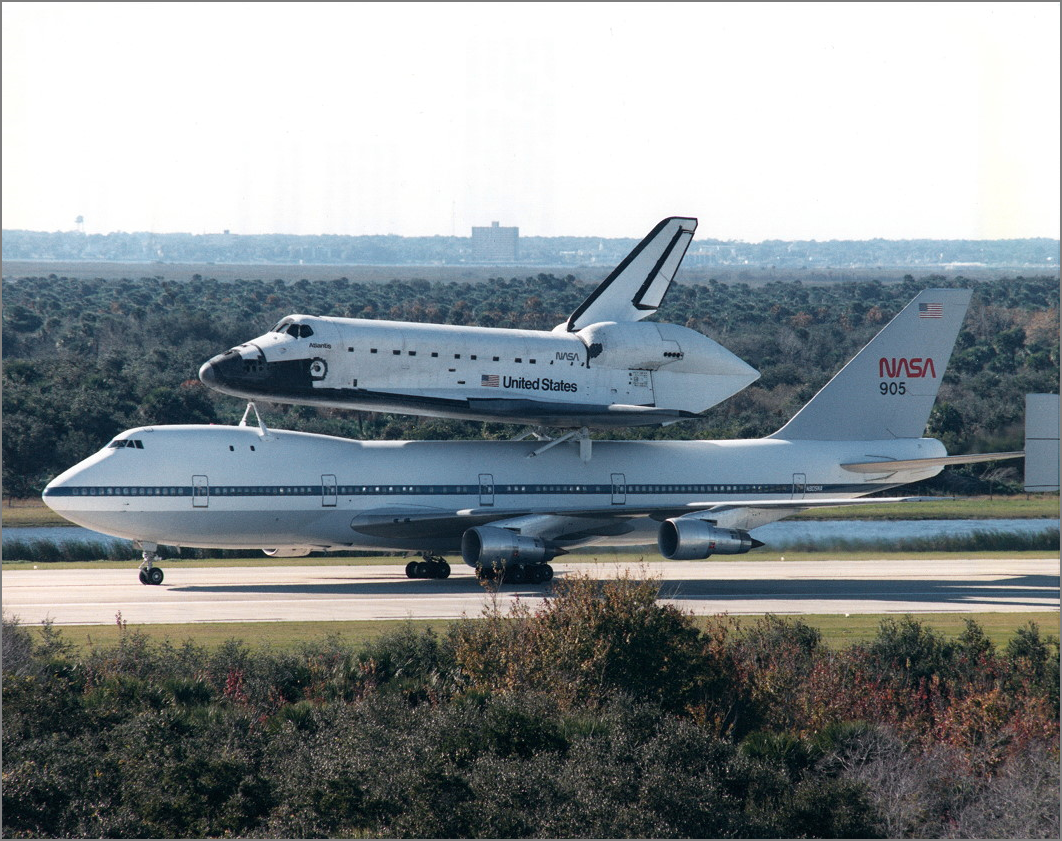
Left: Place shuttle Atlantis arrives at Launch Pad 39B. Center: STS-30 astronauts pose with a mannequin of Magellan following their March 27 preflight press conference. Correct: Atlantis rises into the sky.
Magellan arrived at KSC on Oct. 8, 1988, for preflight processing in a vivid room on the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAFE). On Feb. 15, 1989, workers moved Magellan from the SAFE to the Vertical Processing Facility for mating with the IUS and reinstallation of its excessive-acquire antenna. On March 17, they transported Magellan out to Launch Pad 39B, where it awaited Atlantis’ arrival.
On March 11, workers rolled Atlantis from the OPF to the Automobile Assembly Building for mating with its Exterior Tank and twin Solid Rocket Boosters. Atlantis rolled out to Launch Pad 39B on March 22, truthful 9 days after Discovery lifted off from the an analogous pad on the STS-29 mission, the shortest such turnaround time. Team installed Magellan into Atlantis’ payload bay on March 25. The Terminal Countdown Demonstration Check took plight on April 6-7, with the astronauts taking part in the old couple of hours as on open day. Senior NASA managers held the Flight Readiness Overview on April 13-14 and declared Atlantis and Magellan ready for open on April 28. The 5-member astronaut crew arrived at KSC on April 25 for last preparations for the open.
An global delegation at the side of Soviet scientists and Soviet cosmonaut Igor D. Volk, coaching to waft the Soviet shuttle Buran, arrived at KSC to hunt the planned open. The countdown persevered easily for the mid-afternoon liftoff till one amongst the vary security computer programs went offline. Faced with a rapid 23-minute open window, vary security officers bought the computer abet on-line, having delayed the planned liftoff by easiest 5 minutes. Then at T-31 seconds, the bottom open sequencer called a stay to the countdown attributable to the failure of a recirculating pump in main engine #1, scrubbing the open for the day. The crew exited Atlantis 46 minutes later and returned to crew quarters to envision out one other day. That day came on Could per chance 4, after technicians replaced the immoral pump and a hydrogen line. The open window had grown to a more tickled one hour and 4 minutes, with the fickle Florida climate the utilization of up well-known of that time.
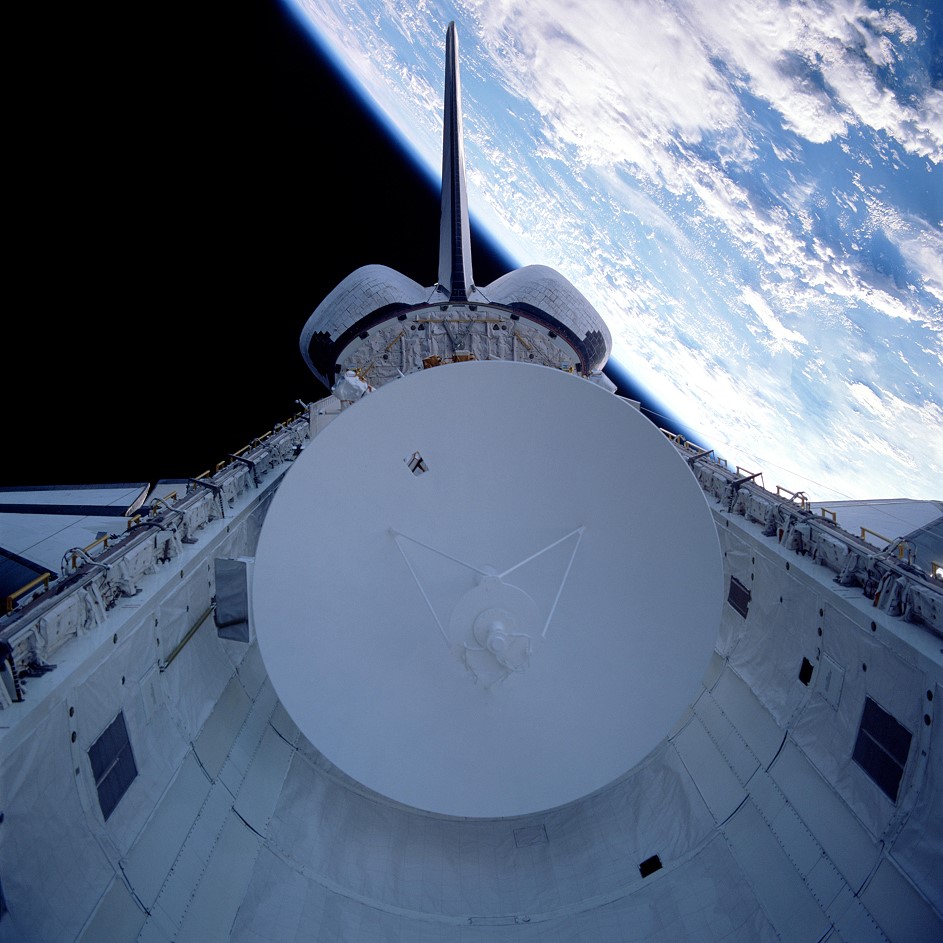
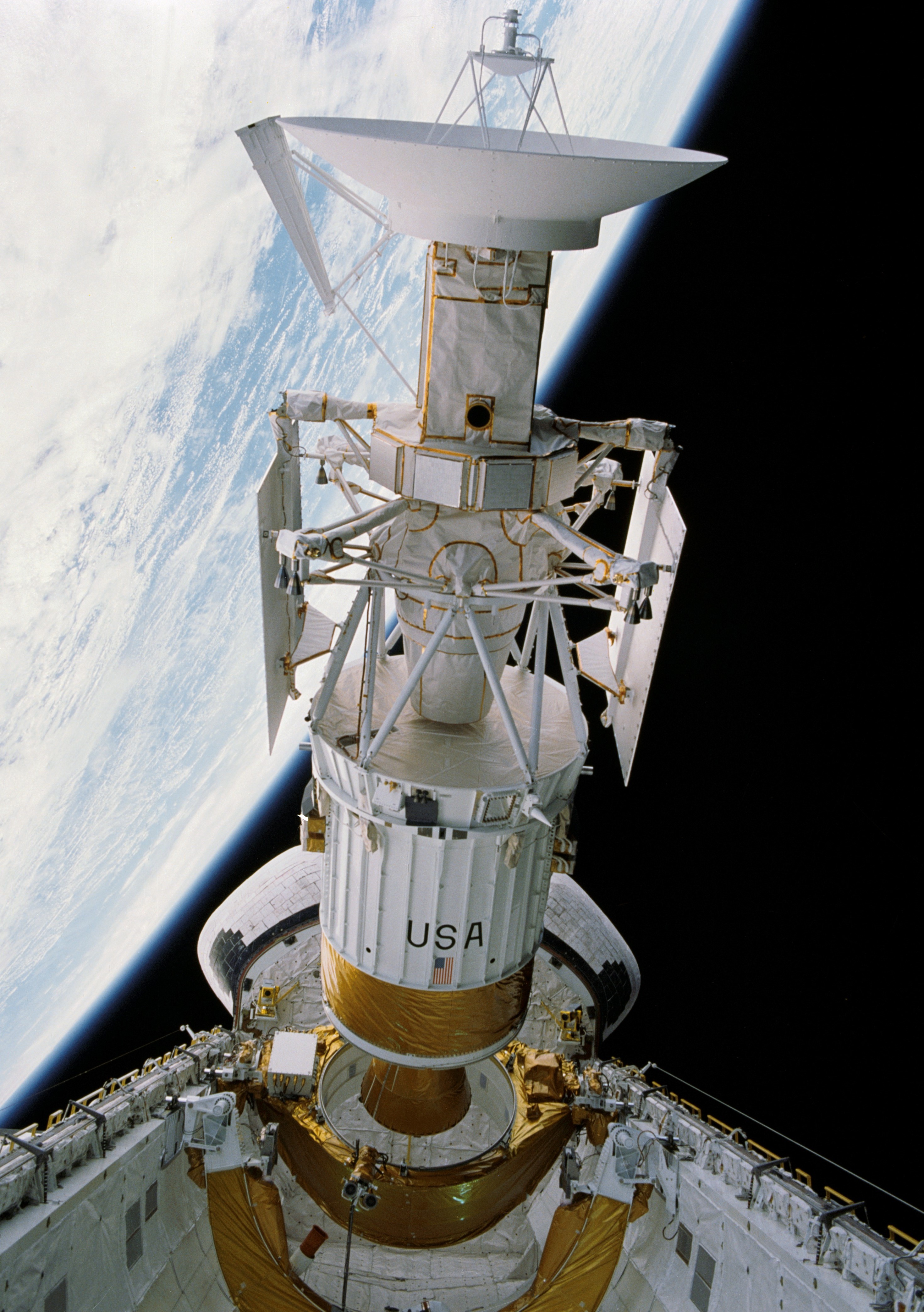



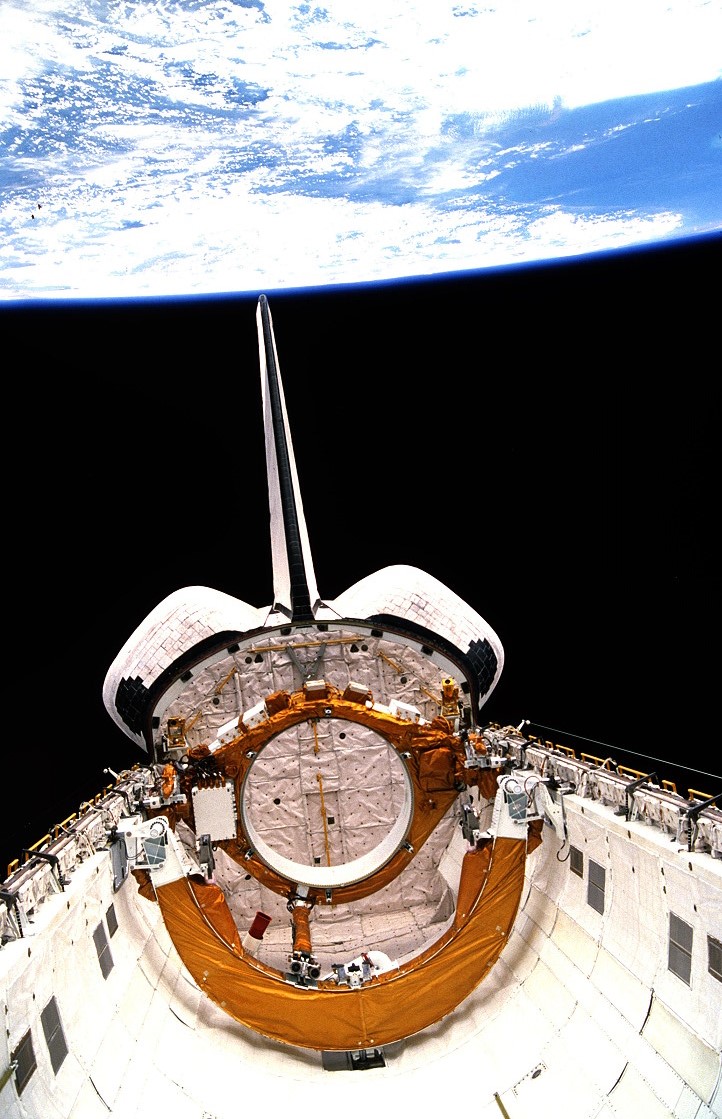
Left: Magellan in Atlantis’ payload bay, its huge excessive-acquire antenna prominently seen. Center left: Magellan and its Inertial Greater Stage moments after deployment from Atlantis. Center truthful: With its solar arrays now deployed, Magellan departs from the shuttle. Correct: Atlantis’ empty payload bay after Magellan’s departure.
With clouds and winds threatening to vivid the open, Atlantis found a rapid while of acceptable climate reach the stay of the open window and lifted off at 2:47 p.m. EDT, sending The USA’s first planetary spacecraft in 11 years on a mission to design Venus’ cloud-shrouded ground. As soon because the shuttle cleared the open tower, control shifted to the Mission Support watch over Center at NASA’s Johnson Place Center in Houston, where Ascent Flight Director A. Lee Briscoe and his group of operators, at the side of astronaut Frank L. Culbertson serving because the tablet communicator, or capcom, monitored all aspects of the open. Following main engine cutoff, Atlantis and its crew had reached residence but no longer yet finished orbit. Two minutes later, a 2-minute 39-2d firing of the Orbital Maneuvering Machine (OMS) engines placed them in a 184-by-75-mile orbit. Forty minutes later, a 2d 2-minute OMS burn circularized the orbit at 184 miles. The astronauts eliminated their paunchy Launch and Entry Suits (LES) and willing Atlantis for orbital operations, at the side of opening the payload bay doorways. Preparations for Magellan’s deployment started rapidly thereafter. In Mission Support watch over, Flight Director J. Milton Heflin and his group, at the side of capcom Pierre J. Thuottook over to relief the crew with deployment operations. The astronauts activated Magellan and the IUS and ground groups started attempting out their programs, with the first TV from the mission showing the spacecraft and its upper stage in the payload bay. Wa lker and Grabe oriented Atlantis to the deployment perspective whereas Lee raised Magellan’s tilt desk first to 29 levels then to the deploy plight of 52 levels. With all programs operating in overall, Mission Support watch over gave the run for deploy. Six hours and 14 minutes into the mission, Walker called down, “Magellan is deployed.” The 40,118-pound spacecraft and upper stage combination glided over the shuttle’s crew compartment. Ten minutes later, Magellan deployed its two solar array wings to originate up producing energy. Walker and Grabe fired the 2 OMS engines to circulate Atlantis a gradual distance some distance from the IUS burn that took plight one hour after deployment, sending Magellan on its means to Venus. The fundamental job of the mission performed, the astronauts ready for his or her first night’s sleep in residence.
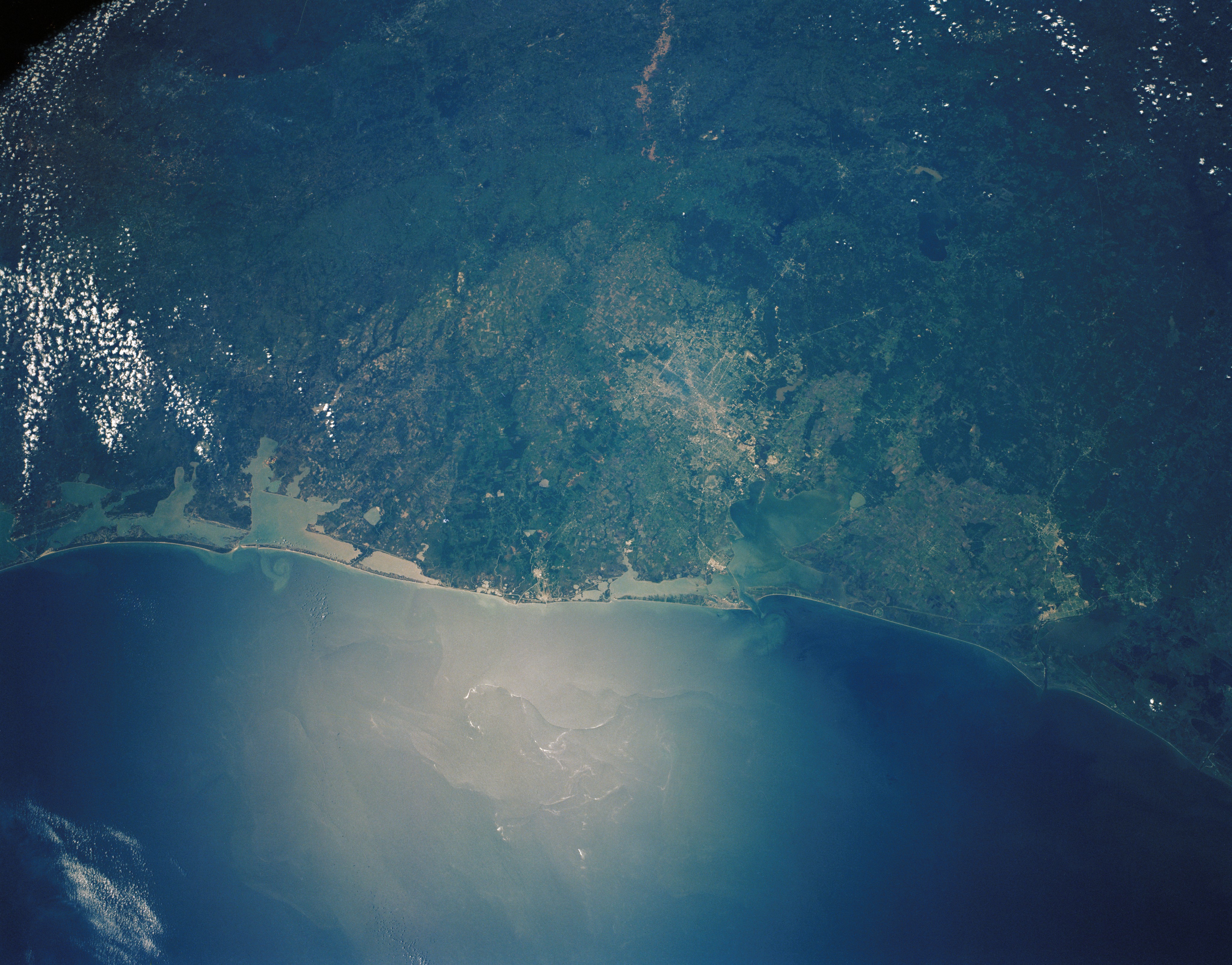



STS-30 crew Earth commentary photos. Left: The Texas Gulf Soar at the side of Houston. Center: Unique Orleans. Correct: The Cape Canaveral plight in Florida at the side of NASA’s Kennedy Place Center.
Mission Support watch over awoke the crew with the theme tune from the movie “Superman” to originate up their 2d mission day, their first pudgy day in residence. When when put next with their very busy first day, the relaxation of the mission’s timeline regarded fairly more relaxed. Lop started work on the Fluids Experiment Apparatus (FEA), a modular chemistry and physics laboratory particularly designed for residence shuttle missions. On STS-30, Lop and Lee processed samples of indium and selenium in the FEA to sight the consequences of microgravity on the crystals produced. The astronauts took many photos of the Earth because it passed by below them. Walker saluted the bottom control groups on the Guam and Santiago, Chile, monitoring stations, scheduled for closure on the stay of STS-30. The deployment of the Monitoring and Data Relay Satellite tv for pc Machine made many ground stations former.
To originate up their third day in residence, Mission Support watch over awaked the astronauts with fight songs from their alma maters. The rousing tune triggered Walker to instruct, “Correct morning, Houston! Thanks for the astronomical tune!” After giving Mission Support watch over a video tour of Atlantis’ cabin, Thagard and Lee started a take a look at to sight if the LES helmet with a Helmet Retention Assembly can lend a hand to prebreathe pure oxygen prior to a spacewalk. Without a spacewalk planned for STS-30, their take a look at merely intended to display cowl the thought that. After Thagard and Lee began to breathe pure oxygen, the crew lowered the cabin stress from the nominal 14.7 pounds per sq. jog (psi) to 10.2 psi to relief in the prevention of decompression sickness, additionally called the bends. After ending the one-hour take a look at, Thagard and Lee eliminated their helmets.
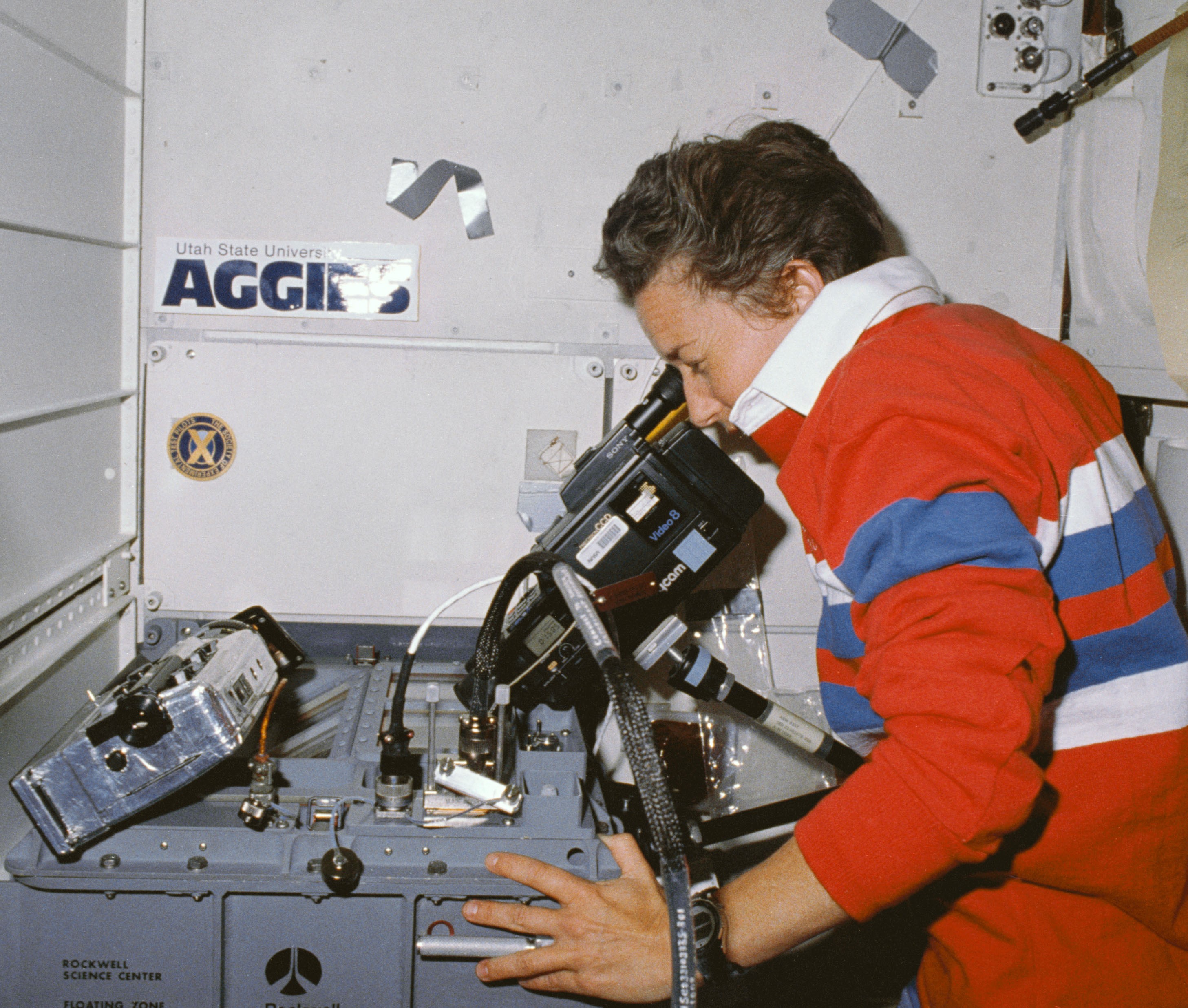
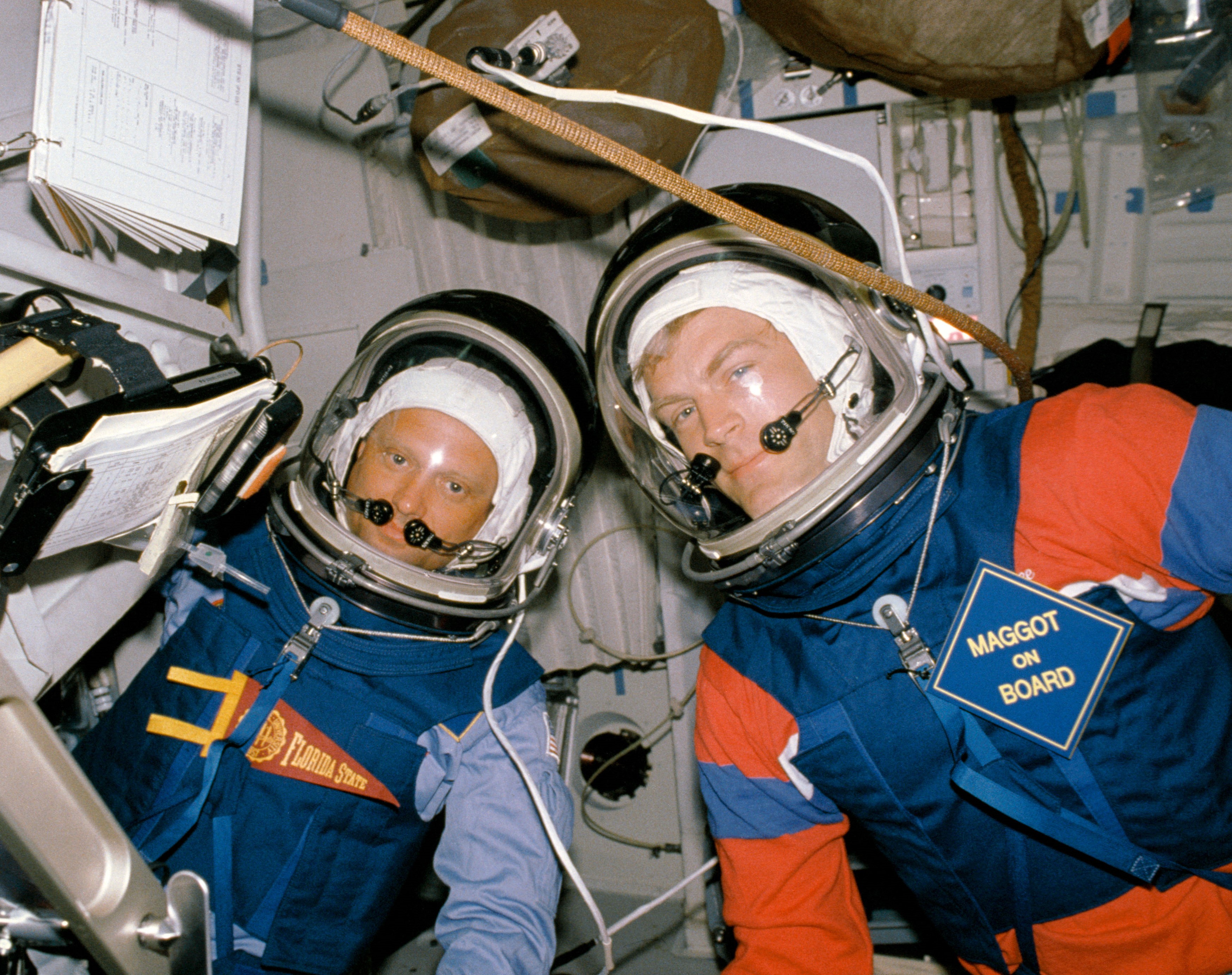



Left: Mary L. Lop videotapes the event of an experiment in the Fluids Experiment Apparatus. Center: Norman E. Thagard, left, and Brand C. Lee all the way in which by the helmet retention assembly prebreathe take a look at. Correct: Inflight photograph of the STS-30 crew.
Mission Support watch over started the astronaut’s fourth day in residence, their last pudgy day in orbit, with the theme tune from the movie “Rocky.” The day’s first major occasion enthusiastic a 15-minute info conference with United Press Worldwide newshounds Rob Navias and Bill Harwood. In preparation for the entry and touchdown the following day, the astronauts tested the automobile’s Auxiliary Energy Devices, aerodynamic surfaces, and reaction control system thrusters. They then repressurized the cabin abet to 14.7 psi. , one amongst the spacecraft’s Frequent Motive Computers (GPC-4) went offline, failing to synchronize with the opposite GPCs. While no longer an rapid impression to their work, Mission Support watch over used to be interested by its characteristic all the way in which by the serious entry and touchdown the subsequent day, and so they ordered the crew to interchange the immoral unit, by no way earlier than performed in residence. The astronauts efficiently performed the four-hour job and had the replacement GPC up and operating, but the time spent on the computer replacement triggered the cancellation of the last FEA pattern escape. The crew stayed up an further hour to complete all their stowage projects earlier than retiring for his or her last night’s sleep in residence.



Left: Its touchdown instruments lowered, Atlantis approaches the runway at Edwards Air Force Atrocious in California. Center: Atlantis touches down. Correct: The STS-30 astronauts exit Atlantis.
On Could per chance 8, the astronauts awoke for his or her last day in residence. The be-careful call from Mission Support watch over consisted of a barking dogs followed by The Beatles tune “A Laborious Day’s Night time.” Capcom Kenneth D. Cameron greeted them with, “Correct morning! It’s time to return residence.” In preparation for reentry, the astronauts donned their orange LESs and closed the payload bay doorways. Walker and Grabe oriented Atlantis into the deorbit perspective, with the OMS engines facing throughout hasten. Over the Indian Ocean, they fired the 2 engines for 2 minutes Forty eight seconds to carry the spacecraft out of orbit. They reoriented the orbiter to waft with its warmth defend uncovered to the course of flight because it encountered Earth’s atmosphere at 419,000 toes. The buildup of ionized gases triggered by the warmth of reentry refrained from communications for approximately quarter-hour but supplied the astronauts a astronomical gentle present. Variable winds at Edwards Air Force Atrocious in California refined the choice on which runway to land on to complete a planned crosswind take a look at. Mission Support watch over made up our minds to lend a hand till 20 minutes earlier than touchdown to make the last decision. With Atlantis out of the blackout, Mission Support watch over directed the crew to land on concrete runway 22 with acceptable crosswinds for the take a look at. After ending the 200-level Heading Alignment Circle turn, Walker aligned Atlantis with the runway, and Grabe lowered the touchdown instruments. Atlantis touched down and rolled to a quit, ending a 4-day 56-minute flight, having performed 65 orbits of the Earth.
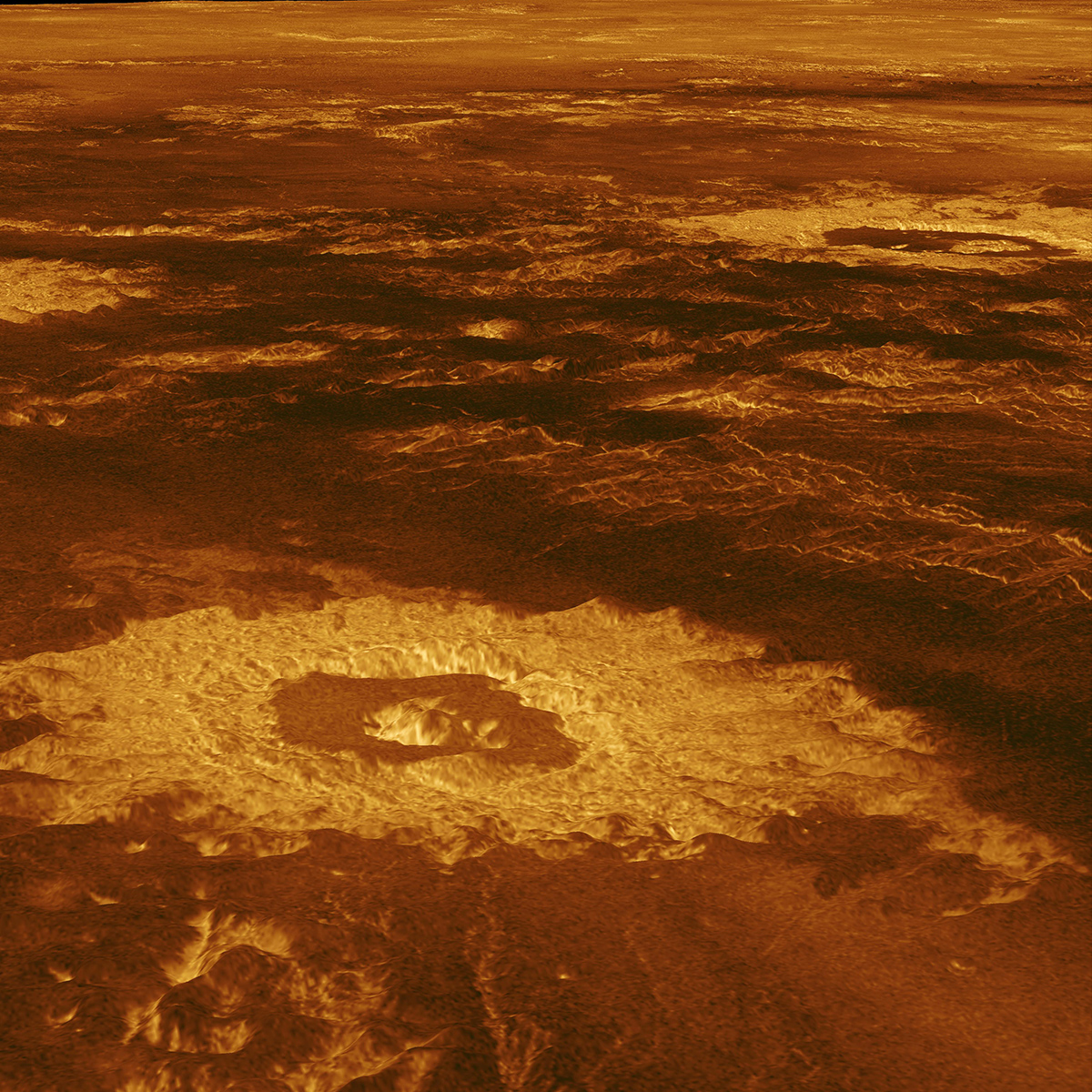


A pattern of Magellan radar photos of Venus. Left: Three impression craters in Venus’ Lavinia Planitia. Center: Volcano Sapas Mons. Correct: Maat Mons, 2d very most practical peak on Venus.
After deployment from the residence shuttle, Magellan started its interplanetary hasten. Midcourse corrections on Could per chance 21, 1989, March 13, 1990, and July 25, 1990, refined the trajectory as Magellan performed its 15-month hasten to Venus on Aug. 10, 1990, entering an elliptical reach-polar orbit all the way in which by the planet. Recovering from two early communications glitches, Magellan started returning excessive-quality radar photos of the cloud-shrouded planet on Sept. 15. The spacecraft performed its main 243-day (the time it took Venus to complete one rotation) mission on Could per chance 15, 1991, imaging 83.7 percent of the planet’s ground at a decision of between 100 and 250 meters, surpassing the fashioned mission targets. It performed 5 more 243-day cycles, ending on Oct. 13, 1994, ending with a coverage of 98 percent of the planet. Within the summertime of 1993, controllers commanded Magellan to waft by Venus’ upper atmosphere and exercise aerobraking to circularize its orbit to allow detailed mapping of the planet’s gravity self-discipline. To bag more aerodynamic knowledge, controllers commanded Magellan to descend into the Venusian atmosphere on Oct. 13, 1994, and it burned up on entry, having performed one amongst basically the most a hit interplanetary missions all the way in which by 15,000 orbits of Venus. The spacecraft returned more knowledge than all of NASA’s old planetary missions blended.
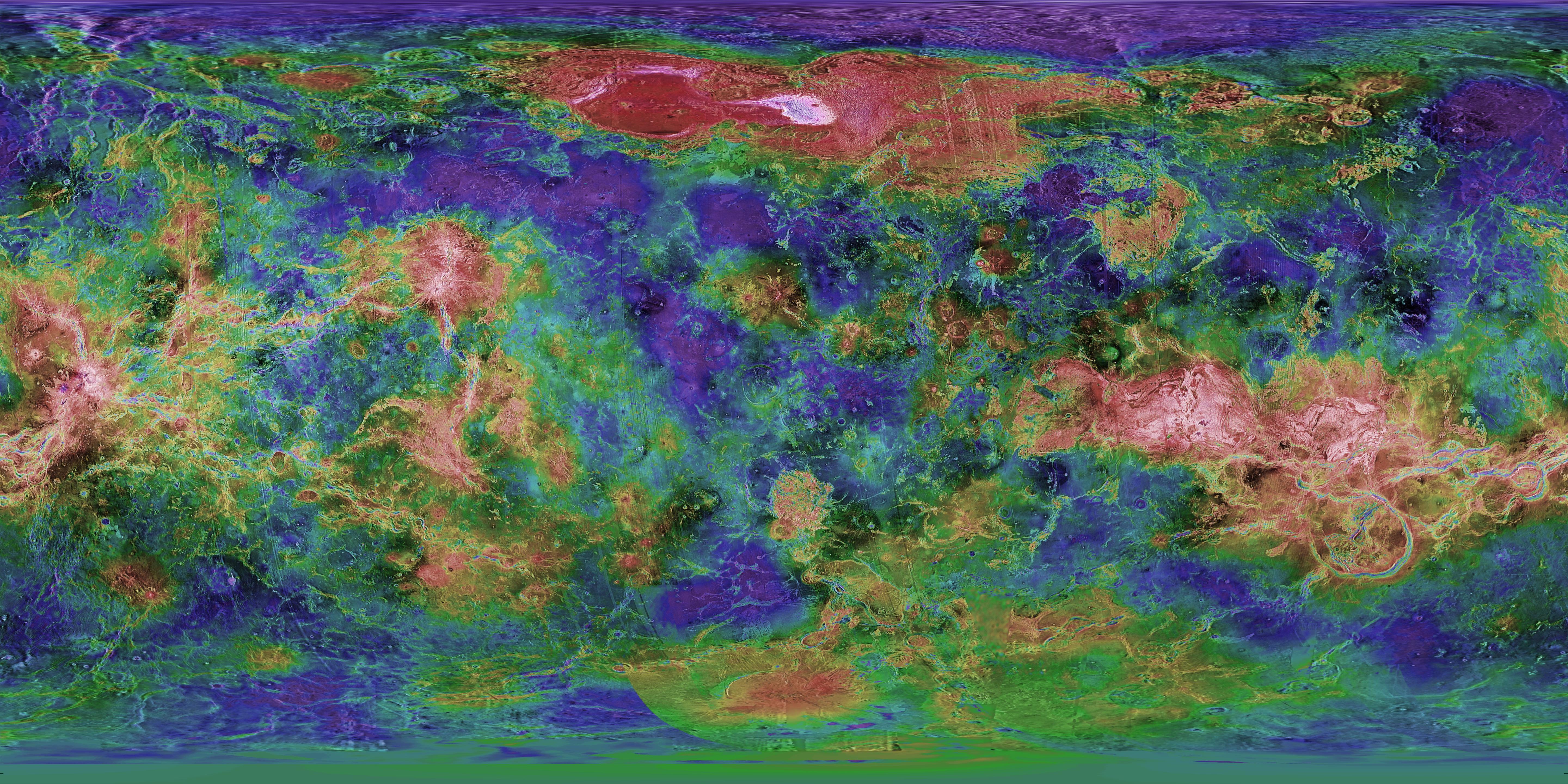
A topographic design of Venus in step with Magellan radar knowledge. Image credit rating: courtesy United States Geologic Provider.
Radar knowledge from Magellan allowed cartographers to fabricate the first, and to date, basically the most detailed, global design of Venus. The photos printed a ground dominated by volcanic parts with few impression craters, implying a geologically young ground, lower than 800 million years faded. Though Venus has a dense atmosphere, Magellan found little evidence of wind erosion, and the total absence of water makes erosion a extremely slack job on the planet.
Skills the crew narrated video of the STS-30 mission.
Read Lop’s recollections of the STS-30 mission in her oral history with the JSC Historical previous Procedure of job.
Discover more from Tamfis Nigeria Lmited
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.



 Hot Deals
Hot Deals Shopfinish
Shopfinish Shop
Shop Appliances
Appliances Babies & Kids
Babies & Kids Best Selling
Best Selling Books
Books Consumer Electronics
Consumer Electronics Furniture
Furniture Home & Kitchen
Home & Kitchen Jewelry
Jewelry Luxury & Beauty
Luxury & Beauty Shoes
Shoes Training & Certifications
Training & Certifications Wears & Clothings
Wears & Clothings
















