Decrypting the molecular foundation of cell drug phenotypes by dose-resolved expression proteomics
Technology tamfitronics
Predominant
Most tablets act on proteins1,2 and it has been known since the times of Paracelsus that tablets exert their effects in a dose-dependent model. The molecular processes main to a drug-prompted replace in cell phenotype can even be roughly divided into (1) aim binding, (2) pathway engagement and (3) cell reprogramming to strategy at a brand new viable instruct or cell loss of life, together forming the MoA of a drug2,3. This day, quantitative mass spectrometry is the most comprehensive ability for the proteome-extensive characterization of medication on all three ranges attributable to of its skill to assay thousands of proteins in complex cell backgrounds in parallel2. The technology does no longer require any preconceived hypotheses as to which proteins a drug could maybe aim, which pathways it could maybe perturb, or what the proteomic composition of the new cell instruct would per chance be. Whereas phenotypic dose–response measurements have been common for an extended time in pharmacology, there is an absence of proteomic research that take observe of dose because the arguably most critical characteristic of a drug.
Potent tablets in total engage their cell targets within minutes, once in some time hours if they’ve an especially slack on-rate4,5. Amongst the most a hit approaches for proteome-extensive aim deconvolution are insist- and affinity-essentially essentially based proteome profiling. Every draw to measure the interaction of a drug with its aim(s) straight6,7,8,9. When performed in a dose-dependent model, they also enable the willpower of obvious interaction constants10,11. Various suggestions measure drug-prompted modifications in other biophysical or biochemical properties of proteins similar to solubility at elevated temperature12,13 or in the presence of natural solvents14,15sensitivity to oxidizing reagents16 or susceptibility to partial enzymatic hydrolysis17,18. Whereas worthy, these suggestions generally require excessive ranges of aim engagement to end result in measurable effects. Besides, the observed effects generally lengthen beyond the aim itself, thus complicating the differentiation between notify and oblique drug effects.
Because many cell pathways are regulated by reversible posttranslational protein modifications (PTMs), mass spectrometry could additionally be ancient to measure if a drug engages pathways downstream of the aim19. The timeframe right here can be in total in the minute to few hours vary19. Printed research generally describe good numbers of observable PTM modifications attributable to constructing spend of arbitrary and in total excessive single doses of a drug or since the information had been soundless after many hours of remedy20. Again, the interpretation of such data can even be complicated attributable to both notify and oblique effects are contained in the information. It has simplest very recently been demonstrated that measuring drug effects on PTMs in a dose- and time-dependent model is a more worthy ability to pathway engagement measurements attributable to it permits prioritizing the information by drug efficiency19.
The variation of a cell to a brand new purposeful instruct in response to a drug is a complex course of, generally racy modifications in gene expression, messenger RNA (mRNA) and/or protein stabilization or degradation over the course of loads of hours or even days2. The L-1000 connectivity map project21 has addressed the transcriptional perspective of drug perturbations and, more recently, loads of research have extended such investigations to the extent of the proteome22,23,24. Such data are worthwhile attributable to they signify the molecular penalties that underlie the cell endpoint (phenotype) of a drug remedy. Nonetheless, to the correct of our data, a systematic evaluation of the dose–response traits of drug-prompted proteome expression modifications has no longer been undertaken yet, limiting insights as to the molecular foundation that drive and notify the observed phenotypic modifications.
Here, we shut this gap by introducing a formula termed decryptE, in a spot to measure the dose–response traits of expression modifications of ~8,000 proteins in human cells in response to a drug. We exemplify the feasibility and utility of the ability by characterizing 144 tablets with various MoA and highlighting loads of worthy findings including the repression of (Jurkat) T cell activation in response to histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. The collective data comprise>1 million dose–response curves which would per chance be accessible by technique of ProteomicsDB and the custom-constructed decryptE net application for added exploration.
Results
DecryptE for dose-resolved expression proteomics
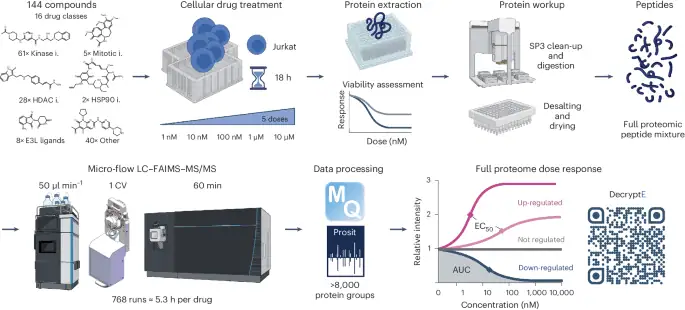
The decryptE ability (Fig. 1) became developed using Jurkat acute T cell leukemia cells as a mannequin draw and is exemplified by analyzing 144 tablets from 16 drug courses (Supplementary Desk 1). These comprise accredited (53) and part III (15) tablets to boot to part I/II investigational or continually ancient tool compounds (76). Snappy, cells had been grown in forty eight-smartly plates and treated for 18 hours with 5 drug doses in elephantine log10 steps between 1 and 10,000 nM and automobile adjust (dimethylsulfoxide, DMSO). Metabolic insist and cytotoxicity, to boot to cell morphology, had been particular for all tablets across the identical dose vary in parallel and had been simplest marginally affected within the timeframe of the experiment (Supplementary Desk 1 and Extended Data Fig. 1a) whereas observed proteomic drug effects had been most pronounced (Extended Data Fig. 1b–d). Proteins had been extracted by SDS-containing buffer and digested into peptides on a robotic platform following the single-pot, sturdy-part-enhanced sample preparation protocol (SP3) ability25. We previously demonstrated that microflow-liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) permits excessive-throughput proteome measurements26 and, right here, extended the ability by incorporating an ion mobility dimension (excessive-field uneven ion mobility spectrometry, FAIMS) to carry out a proteome protection of>7,000 proteins per hour (Extended Data Fig. 1e–i). Your entire drug show veil required 768 hours of instrument time (a lot like 5.3 h per drug) and led to the identification and quantification of 8,892 proteins using MaxQuant and Prosit rescoring27,28. In step with forty eight DMSO replicates, a median quantitative precision of 19% coefficient of variation (CoV) became particular for the assay (Extended Data Fig. 2a) with a excessive level of data uniformity (Extended Data Fig. 2b). Dose–response curves had been fitted to the information offering data on drug efficiency (effective focus required to carry out 50% of the cease, EC50) and cease dimension (situation underneath the curve or fold replace over DMSO). The statistical energy of the dose–response data enabled sturdy classification of 1,133,847 dose–response curves (regulated or no longer) that fashioned the thought that for all extra diagnosis. DecryptE data had been reproducible with 69.5% of all particular EC50 values within half a log10 of drug focus (Extended Data Fig. 2c–e). Moreover, the CoVs of regulated proteins had been invariably better than for no longer regulated proteins (Extended Data Fig. 2f).
Gaze text and suggestions for particulars (i, inhibitor; E3L, E3 ligase; AUC, situation underneath the curve).
To facilitate the spend of this helpful resource by the neighborhood, the information can even be explored in ProteomicsDB (https://proteomicsdb.org/decryptE)29 to boot to in a custom-constructed Shining App (https://decrypte.proteomics.ls.tum.de/) in which dose–response curves can even be visualized and when put next. Extra data on cell morphology, cell metabolic insist, cytotoxicity, protein half-lives and protein targets of compounds and drug-aim affinity (where accessible) are supplied to inspire decoding the observed effects.
High-level diagnosis of decryptE profiles
A total lot of observations had been correct away obvious from a world diagnosis of the information. First, the abundance of most proteins did no longer replace in response to any drug within the timeframe of the experiment (18 h; n = 982,824 dose–response curves; 87%) (Fig. 2a). Dose-dependent up-regulation happened in 73,299 conditions and dose-dependent down-regulation became observed in 77,724 conditions. Second, the extent to which any of the 144 tablets revamped the proteome of Jurkat cells varied a great deal. Some tablets regulated the expression of>1,000 proteins, others handsome a couple of (Fig. 2b). Equally, some tablets confirmed very potent effects, others simplest at excessive concentrations (Extended Data Fig. 3a). Every facets are well-known in narrate to attribute the observed phenotypic (right here morphology, metabolic insist and cytotoxicity) and molecular (right here protein expression) response of a cell to the MoA of a particular compound. As one could additionally request, tablets targeting frequent cell processes prompted many modifications. For instance, HDAC inhibitors similar to vorinostat or panobinostat alter transcriptional purposes and, as a end result, the expression of many proteins. The proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib also confirmed huge effects attributable to it inhibits a critical protein degradation machine in cells. Many modifications had been also observed for the HSP90 inhibitor geldanamycin attributable to it inactivates a key member of the protein folding machinery. Extra particularly, geldanamycin strongly up-regulated proteins (up to 50-fold) enthralling relating to the unfolded protein response (as an instance, DNAJB1, HSPA1B) presumably attributable to of a cell strive to counter the drug-prompted loss of protein folding skill (Extended Data Fig. 3b). In stark distinction, some tablets prompted simplest minor proteomic modifications. Amongst these had been the histone lysine methyltransferase inhibitor lirametostat or the twin c-MET and ALK kinase inhibitor crizotinib. The ancient means that interfering with dynamic histone lysine methylation in cultured Jurkat cells did no longer undergo any penalties within the timeframe of the experiment and the latter implies that the viability of Jurkat cells is no longer relying on ALK and MET insist.
aPie chart of the absolute amount and relative distribution of dose–response curve categories. bBar space showing the amount of up- or down-regulated proteins for every of the 144 tablets (inh., inhibitor; Methyltr., methyltransferase). cPie chart of the proportion of medication that did or did no longer end result in expression modifications of no longer no longer up to one designated aim protein. d, Radar space showing the amount of medication that modified the expression of the protein TYMS. The dimensions of every line indicates the pEC50 (−log10 EC50) of the observed regulation. MTX and pemetrexed are highlighted attributable to TYMS is a chosen aim of both tablets. eIdentical as d but showing all proteins which would per chance be regulated by the drug Tanespimycin. The highlighted proteins are targets of this drug. fBar space showing the amount of medication (y axis) that own watch over a particular aim protein. The proportions of medication for which a particular protein is a chosen aim are highlighted in purple.
It’s generally acknowledged that drug-prompted proteome expression modifications can even be ancient for the deconvolution of drug targets12,22,24. A truly well-known studying level from the realm decryptE data diagnosis is that right here is in total no longer the case. First, whereas the listing of 8,892 detected proteins incorporates 66% of all designated targets of the tablets investigated right here (expression regulated or no longer, Extended Data Fig. 3c), known targets for about 34% of all tablets had been missing and simulation confirmed that this amount elevated as proteome protection diminished (Supplementary Fig. 1). Second, simplest about 25% of all tablets modified the expression ranges of their designated protein aim(s) (Fig. 2c). Third, even supposing that happened, the actual drug aim did generally no longer stand out from the information by technique of efficiency or cease dimension, as illustrated by thymidylate synthetase (TYMS). Whereas the protein became up-regulated by its notify binders methotrexate (MTX) and pemetrexed (Extended Data Fig. 3d), TYMS ranges had been also regulated by 63 other compounds which would per chance be no longer reported to are attempting TYMS (Fig. 2nd). Any other instance is the HSP90 inhibitor tanespimycin. HSP90 ranges had been regulated by the drug (Extended Data Fig. 3e), but so had been hundreds of other proteins and loads of more potently and with bigger cease sizes than HSP90 itself (Fig. 2e). When generalizing this diagnosis, map more generally than no longer, a protein confirmed drug-prompted expression modifications despite the incontrovertible fact that it’s no longer always the aim of that drug (Fig. 2f). Therefore, it looks unlikely that a drug aim can in total or clearly be delineated from drug-prompted protein expression modifications alone.
Multi-omics diagnosis of drug-prompted cell remodeling
To be taught whether drug-prompted protein expression modifications are rooted in altered transcriptional purposes or pre-, co- and/or posttranslational mechanisms, we performed dose-dependent RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) experiments for seven selected tablets in the identical cell line and underneath the identical drug remedy stipulations. As evident from Fig. 3aloads of concordant and discordant effects had been observed. For instance, protein and mRNA ranges of HDAC1 remained unchanged in response to the HDAC inhibitor vorinostat. In distinction, protein and mRNA ranges of the cell cycle regulated protein RRM2 had been equipotently diminished in response to the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib. This could be explained by the dose-dependent lengthen in the amount of cells enthralling at a stage of the cell cycle where RRM2 ranges are low. Conversely, the proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib up-regulated both transcript and protein ranges of the cochaperone BAG3 with identical efficiency but with very diversified cease sizes, suggesting that BAG3 protein ranges simplest quite lengthen in cells on drug remedy. Any other challenge is offered by the DNA methyltransferase DNMT1 for which protein but no longer transcript ranges had been diminished in response to decitabine. Here is essentially essentially based on literature reporting that decitabine, when integrated into DNA, covalently traps DNA methyltransferases, in turn, main to their degradation30. A identical behavior became observed for molecular glues similar to pomalidomide that led to a potent and dose-dependent discount of the protein IKZF1 but no longer its mRNA level (Extended Data Fig. 4a). The aforementioned drug MTX led to an spectacular and dose-dependent lengthen in protein ranges of its notify aim DHFR whereas mRNA ranges remained unchanged (Fig. 3a). This clearly points to a posttranscriptional occasion. Old in vitro experiments have shown that DHFR binds its own mRNA to repress its translation and that addition of MTX abolishes this repression31. This mechanism could maybe be an clear set apart off of the observation that MTX also induces a extremely sturdy thermal or solvent balance shifts for DHFR when sure to MTX12,13,15.
aInstance dose–response curves of drug-prompted abundance modifications of proteins (blue) and mRNA (purple). bFrom left to handsome, the dose–response curves for CLK1–4 following Brigatinib remedy. Binding affinities of Brigatinib and CLK1,2,4 (pKd = −log10 Kd) particular by kinobead assays10. Schematic representation of the 2 major transcripts for CLK proteins and the map in which the ratio between the 2 domains shifts to a 1:1 ratio on CLK inhibition. The triangle represents the N-terminal (N term) domain; the dot represents the kinase domain of the protein. Bar space showing the ratio of the N term and kinase domain transcripts (particular by RT–qPCR) for CLK1–4 as a feature of the dose of Brigatinib. cComparison of drug-prompted mRNA and protein expression modifications for seven tablets. The bar plots in the heart panel show the allotment of up-, down- or no longer regulated proteins (left bars) and mRNAs (handsome bars). The Venn diagrams in the upper panel show the amount and overlap of up-regulated proteins versus mRNAs (data confined to mRNAs for which also a protein became detected). The bottom panel reveals the identical but for down-regulation.
Any other case is offered by the twin specificity protein kinases CLK1–4 that confirmed potent up-regulation of both mRNA and protein ranges on remedy with the kinase inhibitors brigatinib, abemaciclib and milciclib (Fig. 3b and Extended Data Fig. 4b–e). Printed aim deconvolution data confirmed that these proteins are notify targets of all three tablets10. Except for the elephantine-dimension protein, CLK1 also exists in two shorter variations that possess the N terminus but lack the kinase domain both owing to intron 4 retention or exon 4 skipping. The diversified styles of the protein arise from the flexibility of CLK1 to administer its own splicing by phosphorylating obvious splicing factors32. Quantitative PCR with reverse transcription (RT–qPCR) data soundless right here for CLK1–4 confirmed that the ratio of N-terminal to elephantine-dimension transcripts shifted in make a choice of the elephantine-dimension transcript at better drug concentrations, in turn, main to better ranges of elephantine-dimension protein. Whereas an spell binding observation, it stays unclear whether this has any purposeful penalties in cells as these tablets block kinase insist at the identical time. These selected conditions highlight loads of discrepancies between drug regulated transcriptome and proteome modifications which would per chance be rooted in diversified cell mechanisms. Many more conditions are in the information and usually with very good drug-particular differences, both in absolute and relative terms (Fig. 3c). It’s also obvious from these data that the course of regulation is no longer repeatedly concordant on mRNA and protein level (Extended Data Fig. 5a). Opposing regulation events are uncommon for loads of of the tablets studied. Nonetheless, carfilzomib remedy up-regulated contributors of cell folding machinery on mRNA level whereas down-regulating the respective proteins (Extended Data Fig. 5b–d), presumably in an strive to own proteostasis.
Drug response phenotypes neighborhood tablets by feature
Whereas individual tablets will have diversified targets, they could maybe end result in identical cell and molecular drug phenotypes33. To discover whether decryptE profiles can neighborhood tablets in this kind of formula, we performed gene ontology (GO) enrichment diagnosis for up- or down-regulated proteins for every compound one by one, followed by hierarchical clustering of the outcomes for all 144 tablets (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Desk 2). Indeed, compounds main to cell cycle arrest fashioned two mirrored clusters (C1 and C2) characterized by up- or down-regulation, respectively, of enriched GO terms linked to as an instance sister chromatid separation, mitosis and/or meiosis or cytokinesis. Nearer inspection revealed that this diagnosis smartly-known compounds that arrest cells in G1/S or G2/M (Fig. 4b). Examples for proteins that drive this clustering are the sturdy up- and down-regulation of the cell cycle regulated proteins PLK1 and ANLN, respectively. When summarizing this knowledge for all proteins which would per chance be up-regulated or down-regulated, respectively, for all three tablets, they confirmed a congruent distribution of pEC50 values (Fig. 4c–f). On this foundation, and when following a guilt-by-affiliation argument, mitotic beneficial properties would per chance be assigned to proteins no longer yet annotated in this course of and this thought could maybe take care of for other molecular beneficial properties present in other clusters. The pEC50 plots also ranked tablets by efficiency figuring out paclitaxel because the most potent mitotic inhibitor of the set apart.
aClustered heatmap of medication and GO terms enriched by proteins which would per chance be up- or down-regulated on drug remedy. bAnalysis of medication in clusters C1 and C2 of a showing that the tablets in every cluster equally have an ticket on protein expression at diversified phases of the cell cycle. cInstance dose–response curves for PLK1 and three tablets affecting protein expression at the G2/M checkpoint (cluster C1). dDistribution of the potencies depicted as pEC50 (−log10 EC50) with which every respective drug impacts protein expression. eIdentical as c but for ANLN expression and tablets affecting the G1 checkpoint (cluster C2). fIdentical as d but for tablets affecting protein expression at the G1 checkpoint.
The two aforementioned HSP90 inhibitors fashioned a runt but determined cluster (C3) driven by GO terms linked to the up-regulation of the unfolded protein response (Supplementary Desk 2). The PI3K/mTOR inhibitor GSK-1059615, the DNA substandard-linker oxaliplatin and the p53 activator serdematan fashioned a simply cluster indicative of down-regulated ribosome biogenesis (C4) (Supplementary Desk 2). The three platinum-containing tablets oxaliplatin, carb oplatin and cisplatin did no longer cluster. And certainly, their decryptE profiles had been quite diversified as exemplified by the down-regulation of ribosomal proteins by oxaliplatin but no longer the others, implying diversified cell modes of movement (Extended Data Fig. 6a,b)34.
HDAC inhibitors impair T cell activation
Without warning, HDAC inhibitors fashioned a cluster (C5) with sturdy links to T cell proliferation and activation (Fig. 4a). For instance, panobinostat down-regulated the expression of many key elements of the T cell receptor (TCR) with low nanomolar efficiency (Fig. 5a), particularly the TCR itself and its coreceptors (Fig. 5b). Cell viability became simplest marginally affected within the timeframe of the experiment (Extended Data Fig. 7a and Supplementary Desk 1). The other HDAC inhibitors confirmed the identical qualitative cease (Extended Data Fig. 7b) and the dose-dependent RNA-seq data soundless for vorinostat indicated a concerted transcriptional mechanism quite than protein degradation (Extended Data Fig. 7c). These outcomes show veil that the discount of TCR elements can even be straight attributed to the loss of HDAC insist. This also resulted in the discount of anti-CD3 and/or CD28 antibody-mediated T cell activation in genetically engineered Jurkat TCR and/or CD3 effector cells that notify luciferase in response to T cell activation (Fig. 5c).
aSchematic representation of TCR signaling and cell outcomes. bDose-dependent discount of the expression of TCR elements in response to panobinostat in Jurkat cells. cDose-dependent discount of activation of Jurkat cells in response to HDAC inhibitors. dSchematic representation of treating human critical T cells with HDAC inhibitors ex vivo. eThe upper panels show shrimp photos of human critical CD4 sure T cells activated by immobilized anti-CD3 and/or CD28 with or without panobinostat remedy (n = 1). The decrease panel reveals a bar space showing the moderate dimension of aggregates (shown in the upper panel) as a feature of the utilized HDAC inhibitor dose. Error bars reward the customary deviation from n = 5 photos. *P P P F-statistics, followed by calculation of Tukey handsome critical differences as put up hoc take a look at with self assurance interval of 95% and correction for a couple of comparisons. Scale bars, 400 μm. fDose-dependent expression modifications of proteins in human critical T cells treated ex vivo with HDAC inhibitors.
To envision whether HDAC inhibition also diminishes protein expression of TCR elements in critical human T cells, we separated CD4 and CD8 sure T cells from wholesome donors and exposed untreated (referred to as ‘naïve’) and anti-CD3/CD28-activated cells to loads of HDAC inhibitors (Fig. 5d). Are residing-cell imaging confirmed that drug-treated critical cells exhibited a diminished skill to bind to beads carrying anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies (Fig. 5e and Extended Data Fig. 7d). Furthermore, all examined HDAC inhibitors recapitulated the findings of the in vitro Jurkat cell line experiments in all four ex vivo cell populations, exemplified by the dose-dependent loss of CD247, CD3D and CD3E (Fig. 5f). Amongst many other proteins, a dose-dependent discount of the transcription factor TCF7, the master regulator of naïve T cell differentiation, became observed in naïve cells after HDAC inhibitor remedy. In activated cells, we observed a discount of granzyme B ranges, a a must-have regulator of T cell activation and proliferation (Extended Data Fig. 7e,f). These outcomes clearly reward that HDAC inhibition impacts T cell activation and differentiation with yet unknown purposeful penalties, but doubtlessly well-known ramifications for the spend of HDAC inhibitors as anticancer agents or as instruments to gaze T cell biology (Discussion).
Discussion
DecryptE particularly addresses the longer-term dose-dependent response of a cell to a drug (or other bioactive agent) a lot like many phenotypic assays. The variation is that decryptE yields thousands of molecular readouts quite than handsome one (as an instance, cell viability or morphology modifications). As such, the ability must no longer be perplexed with proteomic applied sciences aiming to make clear the targets of a drug or illuminating the signaling pathways that end result in a cell endpoint. These well-known facets of drug MoA would per chance be contained in decryptE profiles, but they could maybe no longer be glaring from the information without sizable old data. As an different, decryptE profiles replicate the third a part of cell drug MoA, referred to in the introduction, which is the transition of the proteomic make-up to a drug-tailored (new) cell instruct. There are two critical new technical facets in the present work. First, showing that the combo of microflow-LC and FAIMS yields deep proteomic protection and quantitative data (dose–response curves) for one drug and ~8,000 proteins in handsome over 5 hours of diagnosis time. Second, demonstrating that dose–response measurements add data no longer skill from single doses. The decryptE apporach thus paves the map in which for good-scale proteome-extensive drug perturbation screens that would per chance be extra enabled by combining sooner and more sensitive mass spectrometers than ancient right here with data autonomous acquisition or precise isotope multiplexing by tandem mass tags22,35. With more than 1 million dose–response curves, our data already provide a smartly off helpful resource for the scientific neighborhood that can even be analyzed in so a lot of methods no longer lined right here. For instance, we strictly simplest regarded as sigmoidal dose–response traits attributable to those are regarded as the correct understood drug–protein interactions. Nonetheless, the information could additionally possess nonsigmoidal drug-prompted behaviors that will, as an instance, notify pharmacological switches in a cell.
Whereas decryptE profiles faithfully describe modifications in protein expression in response to a drug, these could maybe arise by loads of mechanisms that add well-known data relating to drug MoA. In gentle of the comparisons made right here between mRNA and protein–drug profiles, we point out to measure transcriptomes and proteomes systematically in a dose-dependent model in parallel in due course to better understand to what extent transcription itself or splicing events play a feature. Equally, including proteomic measurements that address protein synthesis and degradation, as an instance by pulse-labeling using precise isotopes36,37will provide extra well-known insights. The latter is terribly well-known given the excessive consideration in present drug discovery to the come of chemical degrader molecules similar to proteolysis targeting chimeras or molecular glues.
Although no longer investigated right here, we ticket that protein level modifications prompted by a drug would per chance be cell-kind particular. DecryptE profiling of immunomodulatory imide tablets (IMiDs) similar to thalidomide, pomalidomide, lenalidomide and iberdomide did no longer show modifications in protein ranges for contributors of the E3 ligase complex itself (CRBN, DDB1, CUL4a) (Extended Data Fig. 8a,d). This ability that the ubiquitinylation complex acts as a conventional enzyme that releases its neo-substrates after ubiquitin transfer and that the molecular glue beneficial properties as a catalyst. Endogenous CRBN substrates (GLUL, ORAI1) had been unaffected by IMiD remedy (Extended Data Fig. 8b,c). DecryptE profiles extra confirmed that three of the four IMiDs degraded the neo-substrate IKZF1 in Jurkat cells in a dose-dependent model (Extended Data Fig. 4a). Nonetheless, this became no longer the case for other reported neo-substrates including IKZF2, IKZF4 and PATZ1 (ref. 38). RAB28 became identified as a brand new neo-substrate of Iberdomide in Jurkat cells (Extended Data Fig. 8th)39. Such obvious discrepancies with the literature most likely arise from molecular differences in the ubiquitinylation machinery present in a particular natural mannequin draw.
We ticket, that observed drug effects no longer simplest depend upon the mannequin draw ancient but also on time, that are diversified for every compound. Here is supported by the mountainous differences in both the absolute amount of rules to boot to which proteins show drug response when comparing decryptE profiles with revealed single dose data22,23,24 (Supplementary Fig. 2 and data deposited on MassIVE).
Future extensions of decryptE must consist of PTMs whatever the truth that long-term drug responses could maybe end result in complex PTM datasets that can even be complicated to elaborate. Particular conditions from the present work illustrating this need are pemrametostat and onametostat. Every are inhibitors of the protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 main to diminished methylation ranges of aim proteins. By including methylation as a variable modification in a old skool database glance for protein identification, it became most likely to measure in-cell inhibition of enzymatic insist with low nanomolar efficiency by monitoring methylation sites on the PRMT5 substrate SNRPB in response to the 2 tablets (Extended Data Fig. 8f). This would have long previous disregarded if the PTM level became no longer regarded as.
The maybe most fun pharmacological end result of the present work is the observation that HDAC inhibitors led to sturdy and potent down-regulation of the TCR with a concomitant discount of the flexibility to mount a T cell response. This will most likely smartly demonstrate the efficacy of HDAC inhibitors in the remedy of TCR signaling-driven T cell lymphoma or the attenuation of TCR signaling observed in animal models of obvious autoimmune illnesses40,41. At the identical time, attributable to TCR insist is excessive for T cell lineage choice, antigen specificity, effector feature and survival, a repressed expression of TCR complex elements could maybe became detrimental for the remedy of so-known as ‘sizzling’ tumors which would per chance be characterized by immune cell infiltration, and which generally answer to immune checkpoint inhibition remedy. In this context, clinical trial designs would per chance be known as into request that mix immune checkpoint inhibition with HDAC inhibitors42. Nonetheless, there could additionally be worthwhile eventualities. Continual excessive antigen stimulation can lead to the phenomenon of T cell exhaustion, diminishing the flexibility of the immune draw to fight a tumor43,44,forty five,46. In such conditions, and reckoning on the immune attach of the tumor, it must be most likely that repressed expression of TCR complex elements in response to HDAC inhibition reduces the absolute level of TCR stimulation to a level that reinvigorates exhausted T cell responses. Clearly, extra purposeful research are required to better understand such most likely HDAC inhibitor-linked effects in sufferers and the most likely of HDAC inhibitors as research instruments in the context of studying T cell exhaustion.
Taken together, the outcomes obtained in this gaze reward that dose-dependent and proteome-extensive measurements of drug-prompted protein expression modifications must became a old skool tool alongside dose-dependent aim deconvolution and pathway engagement research. The mixed data could be very worthwhile for frequent research to boot to preclinical and clinical drug discovery attributable to it provides a closer appreciation of the molecular capabilities of bioactive compounds, from chemical probes to human medicines.
Systems
Cell culture
Human Jurkat cells Clone E6.1 (ATCC TIB-152) had been cultured in RPMI-1640 containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Culture medium became refreshed every 2–3 days and cells had been saved at densities between 0.5 × 106 and a pair of × 106 cells per ml unless lysis or drug remedy.
Cell line authentication became executed by single nucleotide polymorphism profiling (Multiplexion).
Compound data
The info of the aim situation of the 144 compounds incorporated in this gaze became obtained from DrugBank On-line (attach of July 2023) and vendor specifications. Data relating to the clinical part the compounds had been in at the time the gaze became performed became retrieved from ChemBL (attach of July 2023).
Compound remedy
Compounds had been prediluted in DMSO and extra in culture medium interior a forty eight-deep-smartly plate. Per forty eight-deep-smartly plate, three DMSO controls had been added. For remedy, 4 × 106 cells in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS had been added on top of every compound predilution main to a remaining quantity of 2 ml and remaining remedy concentrations beginning from 10 µM to 1 nM in elephantine log10 steps, main to 5 doses for every drug (10 µM, 1 µM, 100 nM, 10 nM, 1 nM). Cells had been incubated for 18 h if no longer acknowledged otherwise at 240 rpm, 37 °C and 5% CO2. The next day, cells had been subjected to viability evaluation and lysis.
Confluency, viability and metabolic insist evaluation
For willpower of cell viability and metabolic insist after compound remedy, 100 µl of cell suspension per smartly had been added to a 96-smartly plate containing 50 µl of IncuCyte Cytotox Dye (250 nM remaining focus, Sartorius) and alamarBlue Cell Viability Reagent (10% remaining focus (v/v), Invitrogen). The plate became placed into the IncuCyte live-cell diagnosis draw (37 °C and 5% CO2) and cells analyzed for cytotoxicity over a time course of 3 h (×10 magnification, scan kind became customary with 5 photos per smartly, channel choice became part distinction and fluorescence (300 ms acquisition time), scan interval became every hour). The integrated tool of IncuCyte (Identical old Analyzer) became ancient for confluency and cytotoxicity diagnosis. After 3.5 h, metabolic insist became particular by fluorescence dimension of the AlamarBlue reagent using the fluorescence be taught out on the microplate reader FluoStar Omega (lex = 544 nm and lem = 584 nm, BMG Labtech).
For confluency and metabolic insist evaluation, the resulting values had been normalized to the moderate values for the DMSO adjust. For cytotoxicity, the values had been corrected for differences in confluency, sooner than normalizing the values to the moderate values for the DMSO controls. Dose–response curves had been fitted to the information as described below (part ‘Curve becoming’).
Any shrimp photos displayed in the paper or in totally different places had been exported from the IncuCyte tool as displayed and no longer extra modified.
Cell lysis for protein extraction
To carry out cell lysate from untreated cells (for optimization purposes), cell suspension became centrifuged at 172g for 5 min at room temperature, washed with PBS (phosphate buffered saline, without calcium or magnesium) and pelleted sooner than resuspension in lysis buffer (2% SDS, 40 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8, 95 °C).
Lysis of compound-treated cells became performed in 96-deep-smartly plates. Therefore, after 18 h of remedy time, forty eight-deep-smartly plates had been centrifuged (172g10 min, 4 °C), supernatant became discarded, cell pellets had been resuspended in PBS and transferred to a 96-deep-smartly plate. Cell pellets had been washed two more events with PBS and centrifuged to discard the supernatant sooner than lysis in 100 µl of lysis buffer.
For hydrolysis of DNA, lysate became heated to 95 °C for 10 min whereas shaking at 172g and trifluoroacetic acid became added to a remaining focus of 1% (v/v) and incubated for 1 min whereas shaking. As a end result of this fact, N-methylmorpholin (NMM) became added for neutralization to the sizzling lysate to a remaining focus of 2% (v/v). Lysate became saved at −20 °C unless extra spend.
Tissue and bacteria sample preparation
Mouse muscle (M. musculus) and Arabidopsis thaliana (A. thaliana) tissue samples had been snap frozen in liquid nitrogen sooner than homogenization using the TissueLyser II (Quiagen, 5 min, 30 Hz, using one stainless metal bead with a 5 mm diameter). Lysis buffer (4% SDS, 40 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8) became added after removing the bead and samples had been sonicated using the Bioruptor Pico (Diagenode, 25 cycles with 30 s on/off). DNA hydrolysis became performed as described above using remaining concentrations of 2% trifluoroacetic acid and 4% N-methylmorpholin, respectively. Lysates had been cleared by centrifugation (60 min, 4 °C, 21,000g). Supernatant lysate became saved at −20 °C unless extra spend.
Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) had been grown in a shaker culture in Luria-Bertani medium at 37 °C, 300 rpm. When reaching an optical density of 0.5 and 0.6, respectively, cultures had been harvested by centrifugation (172g60 min, 4 °C) and washed twice with PBS. Lysis buffer became added to the pellet, followed by DNA hydrolysis as described above. Lysate became sonicated using the Bioruptor Pico (above) sooner than clearance by centrifugation (60 min, 4 °C, 21,000g). Cleared lysate became saved at −20 °C unless extra spend.
Isolation and sorting of T cells from wholesome donors
Thrombocyte-depleted blood samples had been obtained from two wholesome, voluntary human donors (male, age 26) after they gave written and educated consent. This gaze became accredited by a vote from the ethics committee of the College Clinic München rechts der Isar (564/18S). Sample had been transferred into 50 ml Falcon tubes, with every tube containing roughly 15 ml of blood. The Falcon tubes had been then stuffed up to a total quantity of 37.5 ml with PBS, and the blood became thoroughly mixed. To isolate peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), a 12 ml layer of Pancoll became meticulously underlaid using a 24 ml syringe with an extended needle (G 20 × 2 3/4’; Ø 0.9 × 70 mm). As a end result of this fact, the blood samples had been subjected to centrifugation using a programmed gradient (acceleration of 7, deceleration of 1, 2, 7gfor 20 min at room temperature). Following the gradient centrifugation, the plasma allotment became discarded, and the PBMC-containing buffy coat became fastidiously soundless. The PBMCs had been then washed with 50 ml of PBS using centrifugation (441g5 min, at room temperature).
For cell separation, 107 PBMCs had been resuspended in 40 µl MACS buffer (PBS, 1% FCS, 2 mM EDTA) and incubated with 10 µl antihuman CD4 beads for 15 min at 4 °C. As a end result of this fact, PBMCs cells had been washed with 15 ml of MACS buffer and centrifuged. CD4 T cells had been positively enriched with the autoMACS Pro Separator. Flowthrough became soundless and ancient for the isolation of CD8 T cells in accordance to the isolation protocol of CD4 T cells. Isolated critical T cells had been cultured in RPMI-1640 containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin and streptomycin (37 °C, 5% CO2) and had been both subjected to HDACi remedy correct away or had been activated as described below.
HDACi remedy of peripheral T cells from wholesome donors
For every population (CD4+/CD8+) a allotment of cells became activated using Dynabeads Human T-Activator CD3/CD28 for T Cell Growth and Activation (Invitrogen) and incubated for forty eight h (37 °C, 5% CO2) sooner than HDAC inhibitor (HDACi) remedy. Naïve T cells had been subjected to remedy correct away after isolation and sorting. Regardless of activation attach, cells had been treated with diversified HDACi (5 doses for every drug: 10 µM, 1 µM, 100 nM, 10 nM and 1 nM) for 18 h, followed by viability, confluency and cytotoxicity evaluation as described above. Cell lysis, protein extraction followed by proteomic workflow and LC–FAIMS–MS/MS dimension became performed as described in the respective sections. For samples, where accessible discipline fabric became restricted, protein input became adjusted for tryptic digestion and obtained peptides had been loaded on Evotips and analyzed on an Evosep-FAIMS-Exploris set apart-up as described previously46 (for a elephantine listing of ancient instrument tool, behold Supplementary Desk 3Materials).
Transcriptome sample preparation and diagnosis
For transcriptome diagnosis, Jurkat cells had been treated in accordance to the protocol described above. After 18 h, cells had been lysed and total RNA became extracted using the ReliaPrep RNA Cell Miniprep Machine (Promega), in accordance to the producer’s protocol, and evaluated on a 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies). RNA library preparation happened with the 3′ mRNA-Seq Library Prep Equipment FWD with Animated Twin Indices (Lexogen) and became despatched to Lexogen for gene expression profiling. Alignment of obtained reads became executed using the information processing pipeline supplied by the producer using the QuantSeq FWD pipeline and A wise man (H. wise) genome annotation. The obtained alignments had been trimmed, reads had been counted and normalized. Dose–response curves had been fitted to the information as described below (part ‘Curve becoming’).
SP3 sample preparation and tryptic digestion
Protein yield became particular by Thermo Pierce BCA (bicinchoninic acid) protein assays. All steps had been performed in accordance to the producer’s protocol.
Earlier than tryptic digest, detergent became removed by single-pot SP3 clear-up, following the protocol first described by Hughes et al.25 tailored to a Bravo Agilent liquid going by technique of platform. In temporary, lysate containing 200 µg of protein became mixed with 1 mg SP3 beads (50:50 mixture of Sera-Magazine carboxylate-modified magnetic bead forms A and B (Cytiva Europe)) in a 96-deep-smartly plate and proteins had been precipitated onto the beads in 70% ethanol in ddH2O (double distilled water).
The beads had been washed three events with 80% ethanol in ddH2O and once with 100% acetonitrile (ACN). Disulfide bonds had been diminished with 10 mM dithiothreitol for forty five min at 37 °C, followed by alkylation of cysteines with 55 mM CAA (2-chloroacetamide) for 30 min at room temperature in 100 µl of digestion buffer (2 mM CaCl2 in 40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.8). Trypsin (1:50 (wt/wt) enzyme-to-protein ratio) became added and proteins had been digested off the beads at 37 °C and 1,200 rpm in a single day. For peptide restoration, the beads had been settled on magnets and the supernatant became transferred to a brand new 96-smartly plate. Beads had been washed by addition of 100 µl 2% formic acid in ddH2O and the supernatant became transferred to the series plate. As a end result of this fact, the samples had been desalted as described below.
Desalting and drying of peptides
Earlier than LC–MS/MS diagnosis samples had been desalted using hydrophilic-lipophilic balanced (10 mg of N-vinylpyrrolidon-divinylbenzol porous particles 30 μm, Macherey-Nagel) 96-smartly plates using centrifugation at 7g for 1 min unless specified otherwise. For this, hydrophilic-lipophilic balanced discipline fabric became primed with 500 µl of isopropanol, ACN and solvent B (0.1% formic acid in 70% ACN in ddH2O) and equilibrated with 1,000 µl of solvent A (0.1% formic acid in ddH2O) sooner than sample loading (by gravitation, 5 min). The sample flowthrough became reapplied to the plate and sure peptides had been washed with 1,000 µl of solvent A. Peptides had been eluted with 250 µl of solvent B (3 min, 7g; 1 min, 172g). Samples had been frozen at −80 °C, dried by vacuum centrifugation and saved at −20 °C unless LC–MS/MS dimension.
High pH reversed-part fractionation
Here, 50 µg of peptides (A. thaliana for Extended Data Fig. 1i and Jurkat for Fig. 3b and Extended Data Fig. 4d–e) had been fractionated by frequent pH reversed-part discipline fabric (reversed-part sulfonate cartridge pointers; 5 μl of polystyrene-divinylbenzene (PS-DVB) resin, Agilent) into six fractions using the Agilent AssayMAP Bravo pipetting draw. The reversed-part sulfonate cartridges had been primed, washed and equilibrated in accordance to the producer’s protocol. Peptides had been reconstituted in 100 μl of 25 mM ammonium formate (pH 10) and loaded onto the cartridges. Peptides had been fractionated by rising ACN concentrations (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 80%). The seven elution steps had been both mixed into six fractions, combining the 5 and 80% fractions, or into four fractions. For four fractions, the 5 and 25%, the 10 and 30%, the 15 and the 80%, and the 20% ACN allotment and the flowthrough had been mixed. All fractions had been acidified with formic acid to a remaining focus of 1%. Samples had been frozen at −80 °C, dried by vacuum centrifugation and saved at −20 °C unless LC–MS/MS dimension.
Microflow-LC–(FAIMS)–MS/MS measurements
All samples (with the exception of where indicated otherwise) had been analyzed on a microflow-LC–MS/MS draw using a Vanquish Neo extremely excessive-efficiency LC draw (Thermo Fisher Scientific) coupled to an Orbitrap Eclipse Tribrid mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with or without installed FAIMS Pro Interface (Thermo Fisher Scientific). For a elephantine listing of ancient instrument tool, behold Supplementary Desk 3Materials.
Earlier than dimension, samples had been reconstituted in 0.1% formic acid, 2% ACN. For draw optimization, the peptide focus became particular using a Nanodrop draw (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and the amount of peptide required for every elope became injected accordingly. For drug profiling samples, half of the samples had been injected per elope (50 µg). For fractionated samples all the pieces became injected.
Chromatographic separation became performed by technique of notify injection on a 15 cm Acclaim PepMap 100 C18 column (2 µm, 1 mm inner diameter × 15 cm, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at a plug with the hump rate of 50 µl min−1. The column temperature became set apart to 55 °C. Solvent A became 0.1% formic acid in 3% DMSO in ddH2O, and solvent B became 0.1% formic acid and 3% DMSO in ACN. The gradients for diversified lengths can even be found in Supplementary Desk 3LC gradients.
Incorporation of FAIMS into microflow-LC–MS/MS
Because micro-LC separations generate noteworthy sharper peaks than nano-LC, the incorporation of FAIMS into microflow-LC–MS/MS draw critical to be evaluated from the bottom up. We first characterized the tool for peptide transmission at diversified compensation voltage (CV) values using a tryptic digest. With these data in hand, we next simulated how many and which CV values wants to be mixed for wonderful proteome protection. Simulations had been experimentally examined using LC gradient lengths between 15 and 180 min and we systematically when put next efficiency with and without FAIMS. For gradient events of 15, 30 and 60 min, simplest one CV atmosphere can even be meaningfully ancient attributable to CV switching takes sizable amounts of time. Regardless of LC events, FAIMS elevated the amount of identified protein groups at a given time or halved the MS time critical to carry out the identical depth of diagnosis when put next to the identical LC set apart-up but without using FAIMS.
Dimension without FAIMS installed
The OptaMax NG ion source (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with a heated electrospray ionization probe became ancient to spoil the information. The sprayer became positioned at middle spot in the x axis (left to handsome), at spot 1 in the y axis (front to abet) and between positions M and L in the z axis (probe peak).
The mass spectrometer became operated in data-dependent MS/MS, sure ion mode, using a twig voltage of 3.5 kV, a funnel radio-frequency lens ticket of 40, an ion transfer tube temperature of 325 °C and vaporizer temperature of 125 °C. The plug with the hump rates for sheath gasoline, auxiliary gasoline and sweep gasoline had been set apart to 32, 5 and 0 l min−1respectively.
A elephantine-scan (MS1) became recorded from 360 to 1,300 m/z with a willpower of 120,000 in the Orbitrap in profile mode. The MS1 AGC aim became custom set apart to 100% and the maxIT became set apart to 50 ms. In step with the elephantine scans, precursors had been targeted for the MS/MS scans (MS2) if the isotope envelope became peptidic (monoisotopic precursor choice), the worth became between 2 and 6 and the depth exceeded 1 × 104. The MS2 quadrupole isolation window became set apart to 0.4 m/z. Peptide fragmentation happened in the ion routing multipole by HCD with a mounted collision energy mode, the collision energy normalized to the precursor m/z and ticket with a collision energy of 28%. The MS2 scan became bought in the Ion Trap with rapid scan rate in centroid mode and an outlined first mass of 100 m/z. Mumble MS2 properties to boot to cycle events for diversified gradient dimension can even be found in Supplementary Desk 3MS settings.
Dimension with FAIMS installed
The identical ion source and probe as above became ancient, making spend of the identical spot atmosphere. The mass spectrometer became operated in data-dependent MS/MS, sure ion mode, using a twig voltage of 4 kV, a funnel radio-frequency lens ticket of 40, an ion transfer tube temperature of 325 °C and vaporizer temperature of 300 °C. The plug with the hump rates for sheath gasoline and auxiliary gasoline had been set apart to 40 and 5 l min−1respectively. FAIMS became operated with customary willpower (inner and outer electrode 100 °C) and a static provider gasoline plug with the hump of 3.5 l min−1. Dimension parameters had been unchanged and the respective FAIMS CV became set apart to the critical ticket. For measurements of drug perturbed samples, the 60 min gradient became ancient with a series CV of −30 V.
If a couple of interior CV became ancient (draw optimization), autonomous experiments had been specified for the diversified CVs in the Tune formula with the precise identical settings, with the exception of for the diversified CV ticket (the ancient CV values can both be be taught straight from the figures or the uncooked file names). This ends in the MS looping by technique of the specified experiments of the formula, switching after every MS cycle (MS1 scan + MS2 scans). To own the information points and thus quantification quality precise, the cycle time acknowledged above became divided by the amount of ancient interior CVs main to 0.75 s for 60 min (two CVs), 1.4 s for 120 and 180 min (two CVs) and 0.8 s for 120 and 180 min (three CVs).
Database hunting
The uncooked MS data information had been processed with MaxQuant v.1.6.2.10 (ref. 27) using the integrated Andromeda search engine and searched in opposition to the respective reference database (H. wise: downloaded from UniProt containing canonical and isoforms 24 August 2020; 75,776 entries, E. coli: downloaded from UniProt containing canonical and isoforms 1 July 2021; 4,713 entries, P. aeruginosa: downloaded from UniProt containing canonical and isoforms 1 July 2021; 5,563 entries, M. musculus: downloaded from UniProt containing canonical and isoforms 1 July 2021; 25,381 entries, A. thaliana: Araport11 genome unlock downloaded from Arabidopsis.org containing canonical and isoforms 16 June 2020; forty eight,359 entries).
Raw information from runs with a couple of interior FAIMS CVs had to be split into separate information essentially essentially based on CV values sooner than MaxQuant searches. These separate information had been specified as diversified fractions, as for the normal reverse-part fractions, of the identical experiment in MaxQuant. A total lot of injections of the identical sample had been specified because the identical experiment. Identical old MaxQuant search parameters had been ancient. Trypsin/P became specified as protease, taking into fable up to a most of two disregarded cleavages. Carbamidomethylation of cysteine became specified as mounted modification, whereas oxidation of methionine and protein N-terminal acetylation had been regarded as as variable modifications. Where specified, mono- and di-methylation of arginine and lysine became enabled as a variable modification. The mark free quantification (LFQ) algorithm, with a old skool LFQ minimum ratio rely atmosphere of 1, to boot to the iBAQ (depth-essentially essentially based absolute quantification) algorithm, with log fit, became switched on where critical. Where ancient, the Match-Between-Runs algorithm became switched on with default settings (0.7 min and 5 min for matching and retention time alignment window, respectively). The false discovery rate (FDR) became set apart to 1% on protein and peptide spectral match level. For Prosit rescoring, the FDR became set apart to 100% on protein and peptide spectral match level. The respective MaxQuant msms .txt and .uncooked information had been rescored by Prosit. Peptides with q values ≤0.01 had been retained and proteins had been grouped essentially essentially based on the picked FDR formula47. For MaxQuant output, proteins for which no queer peptide became found and thus where no longer distinguishable had been aggregated to protein groups. For picked FDR protein neighborhood output, proteins are grouped on gene level and simplest queer peptides are regarded as. For readability, we refer to all simplest as proteins in the figures. Data diagnosis and visualization became performed using R (v.4.1.0) in RStudio (behold Supplementary Desk 3Materials for elephantine listing of all purposes ancient) and Microsoft Excel 365. Extra bettering of plots became executed in Adobe Illustrator CS6. Data on whether a dataset became rescored or no longer can even be found on MassIVE (Data availability part).
Data processing and diagnosis
Curve becoming
For every protein–drug aggregate, the LFQ depth relative to the moderate protein depth in the DMSO controls became calculated for all drug concentrations. The identical became executed for every transcript–drug aggregate of the transcriptomic data using be taught counts. For the diversified viability metrics, the information had been difficult as described above. To these normalized data, a sigmoidal four-parametric log-logistic mannequin (equation (1)) became fitted using the dose–response curve R bundle (v.3.0-1), where x is the log10 of the drug focus, pEC50 is the unhealthy log of the inflection level of the curve (denoted because the effective focus 50; EC50), t is the head or low-dose plateau, b is the bottom or excessive-dose plateau, s is the curve slope between the plateaus and Y(x) is the observed protein ratio when put next to the auto adjust at focus x.
$$Yleft(xhandsome)=frac{t-b}{left(1+{10}^{left(sevents left(x-{mathrm{pEC}}_{50}handsome)handsome)}handsome)}+b$$
(1)
For every resulting mannequin, descriptive parameters had been extracted and reported. Comprising the optimized slope (s), top (t), bottom (b) and inflection level (EC50), to boot to the situation underneath the curve, the coefficient of willpower (R2), point out moderate deviation, the expected y ticket of the fitted curve for the wonderful focus (end of curve, fold replace) and the slope of a linear mannequin fitted to the information.
Curve classification
To steer determined of manual annotation of>1 million dose–response curves, a random forest classifier became trained using the ranger R bundle (v.0.14.1). As a ground truth dataset, curves of two compounds had been manually annotated as up-, down- and nonregulated. The dataset became split into 80:20 for coaching and validation dataset, respectively (coaching 11,562, validation 2,883, total 14,409). The input facets had been created from the values described above, along with the relative LFQ intensities and amount of queer peptides for all concentrations and abundance percentile of the respective protein in the DMSO adjust. After hyper parameter tuning, the remaining mannequin became trained with 1,200 timber, randomly deciding on 15 autonomous variables at every split and splitting simplest nodes with a minimum dimension of 3. Variable significance mode became set apart to impurity and the Gini split rule became utilized. The mannequin’s efficiency and quality had been examined using the validation dataset, calculating precision, confusion matrices and ROC curves. The resulting classifier became ancient as a prefilter, plotting curves into separate PDFs and writing data into separate .txt information essentially essentially based on the expected courses, thereby facilitating manual examination of all drug datasets. The identical classifier became ancient for the dose–response curves of the drug perturbed transcriptome dataset. These regulated proteins had been extra analyzed to search out the mode of movement of medication.
Extra filtering
For extra diagnosis, a protein became regarded as up- or down-regulated if it became classified accordingly and the fold replace exceeded 1.5 and 0.7 for up- and down-regulation, respectively. The identical became utilized to all transcripts, additionally preserving simplest observations where be taught counts had been above 50 for all concentrations.
GO term enrichments
For the heatmap clustering of medication with identical effects, a GO term enrichment diagnosis became performed for every drug for my portion using the clusterProfiler R bundle (v.4.2.2.)forty eight. Every drug dataset became examined for enrichment of GO terms on all ranges (cell compartment, molecular feature and natural course of) both in up- and down-regulated proteins with the entire drug dataset because the background. P values had been corrected using the FDR ability and the q ticket in the discount of-off became set apart to 1. The enrichment outcomes for up- and down-regulation had been mixed, preserving the more critical entry for duplications. After combining the enrichment outcomes for all tablets, the q values had been log transformed, multiplied by −1 for GO terms enriched in down-regulation and z-scored for every GO term for my portion. The heatmap depicts the mixed, preprocessed GO term enrichment outcomes after hierarchically clustering of both rows and columns using Pearson correlation as a distance metric and Weighted Pair Crew Plot with arithmetic point out because the agglomerative formula. The GO term enrichment outcomes displayed in Extended Data Fig. 6a had been taken from the realm GO term enrichment diagnosis described above. For Extended Data Fig. 5d a brand new GO term enrichment diagnosis became executed (P ticket in the discount of-off, 0.05; P ticket correction, FDR ability; Subontology, Molecular Feature; total H. wise database as background).
Dose-dependent methylation
The search outcomes for lysine and arginine methylation had been difficult for dose–response curve becoming a lot just like the course of described for proteins and transcripts above. Nonetheless, for every peptide–focus–inhibitor aggregate the depth ratio of methylated to unmethylated version became calculated. The resulting ticket in turn became then normalized to the respective DMSO adjust sooner than continuing as described above (part ‘Curve becoming’).
Simulation of aim protection relating to proteomic depth
For the simulation of aim protection over captured proteomic depth we ranked all>8000 proteins of this gaze by their point out iBAQ values in all DMSO controls in a descending model. To simulate the diversified proteomic depths, this listing became in the discount of at the indicated ranks (amount of identified proteins). For every drug, we checked in turn how a amount of its targets had been incorporated in the resulting listing and calculated the allotment of designated targets that had been detected.
Replicate diagnosis
For the volcano space displayed in Extended Data Fig. 2b assessing the quantitative reproducibility, the forty eight DMSO controls had been randomly assigned into two equally sized groups. After median centering normalization of the LFQ intensities of the picked FDR gene neighborhood output and filtering for completeness in the dataset, a two-sided Pupil’s t-take a look at became performed for all 4,694 proteins. P values had been corrected for a couple of speculation attempting out using the FDR ability using the R bundle fdrtool (v.1.2.17).
For the comparison of quantitative reproducibility between unregulated and regulated proteins using the 5 individual doses for every inhibitor as replicates, the LFQ intensities of the picked FDR gene neighborhood output had been normalized by median centering. The CoV became calculated across the 5 doses for every drug for every protein that became both classified as up- or down-regulated, or unregulated.
To evaluate the reproducibility of EC50 determinations, the curves for every protein for every drug replicate had been fitted as described above. For proteins being classified as up or down-regulated in three out of four replicates per drug, the customary deviation of the pEC50s became calculated.
True-time RT–qPCR
For RT–qPCR diagnosis, cells had been treated in accordance to the protocol described above. After 18 h cells had been lysed, and total RNA became isolated using the Monarch Total RNA Miniprep Equipment (Unusual England Biolabs) in accordance to the producer’s directions. RNA yield became particular using the Qubit fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Complementary DNA (cDNA) became generated from 2 µg of RNA from every sample using the LunaScript RT SuperMix Equipment (Unusual England Biolabs) in accordance to the producer’s protocol. Additionally, no-reverse transcriptase controls had been generated for every sample correct by technique of the reverse transcription step. After reverse transcription, the cDNA became diluted ~66 fold with nuclease-free ddH2O. qPCR became performed in triplicates on a CFX384 Contact True-Time PCR Detection Machine (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) using 10 ng of cDNA per sample, the Luna Universal qPCR Master Mix (Unusual England Biolabs) and the primer pairs as shown in Supplementary Desk 3Primer listing. No-reverse transcriptase controls had been measured in pools of all samples on every plate. Nuclease-free ddH2O became ancient because the nontemplate adjust for every assay. Biking parameters had been set apart to 95 °C (1 min), 40 cycles of 95 °C (15 s) and 60 °C (30 s with plate be taught on SYBR channel) every, and at closing a melt curve became recorded from 60 to 95 °C with an increment of 0.5 °C per 5 s and SYBR channel plate reads after every increment. All samples treated with the identical drug to boot to the DMSO adjust had been measured on the identical plate.
Analysis of RT–qPCR outcomes
Quantification cycle (Cq) and melting temperature (Tm) values had been particular in the CFX Manager v.3.1 tool (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). The regression formula of the tool became ancient for Cq evaluation with baseline correction and curve fit modified into on. The fold replace in expression after remedy and the ratio of truncated to elephantine-dimension transcript had been calculated in Microsoft Excel 365 from the point out Cq values for every sample using the 2-∆∆Cq formula49.
T cell activation assay
Activation skill of HDACi treated Jurkat cells became analyzed using TCR and/or CD3 effector cells (nuclear factor of activated T cells or NFAT) from a T Cell Activation Bioassay (Promega) with cramped diversifications of the producer’s protocol. Snappy, TCR/CD3 effector cells (NFAT) had been incubated with HDACi (5 doses for every drug: 10 µM, 1 µM, 100 nM, 10 nM and 1 nM) for 16 h, followed by unspecific activation by technique of CD3 and/or CD28 using the Human Anti-CD3/CD28 T Cell activation Equipment (Cell Signaling Know-how). After 5 h, the receptor-mediated signaling became be taught out by luciferase insist on a microplate reader FluoStar Omega (BMG Labtech). Thereby the energy of the luminescence signal corresponded to the energy of receptor-mediated signaling. To resolve the energy of T cell activation, the luminescence signals had been normalized to the DMSO adjust. Dose–response curves had been fitted to the information as described in the part ‘Curve becoming’.
T cell aggregation diagnosis
The usage of the intense gentle photos of residing activated human T cells, bought using the IncuCyte live-cell diagnosis draw as described above, cell aggregates had been assigned and quantified (rely and situation in µm2). To this end photos had been processed by ilastik50a supervised machine studying image diagnosis tool bundle. The frequent aggregate dimension became calculated for every image by summing up the detected aggregate areas and dividing by the rely of aggregates per image, treating the 5 photos bought per smartly as replicates. To evaluate statistical significance of the HDACi prompted discount of moderate aggregate dimension, an diagnosis of variance take a look at became performed for every inhibitor for my portion, followed by a Tukey handsome critical differ ences put up hoc take a look at.
Reporting abstract
Extra data on research get is supplied in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this text.
Data availability
The mass spectrometry proteomics uncooked data, UniProt reference databases (fasta information), MaxQuant search outcomes, Prosit output, transcriptomics uncooked data and outcomes, dose–response curve becoming outputs (.pdf and .txt information) and comparison to other research have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium by technique of the MassIVE accomplice repository with the dataset identifier MSV000093659 (PXD047799). All dose–response curves from this paper can even be explored online in ProteomicsDB (www.proteomicsdb.org/decryptE). Additionally, dose–response curves can even be visualized and when put next in a custom-constructed Shining App (https://decrypte.proteomics.ls.tum.de/). Extra data on cell morphology, cell metabolic insist, cytotoxicity, protein half-lives and protein targets of compounds and drug-aim affinity (where accessible) are supplied10,51,52,53 to inspire decoding observed effects.
Code availability
All code ancient for data curation, diagnosis and visualization is essentially essentially based on publicly accessible R purposes as indicated in the respective part and could maybe presumably be made accessible upon ask with out a get entry to restrictions.
References
-
Singh, S., Malik, B. K. & Sharma, D. K. Molecular drug targets and structure essentially essentially based drug get: a holistic ability. Bioinformation 1314–320 (2006).
-
Meissner, F., Geddes-McAlister, J., Mann, M. & Bantscheff, M. The rising feature of mass spectrometry-essentially essentially based proteomics in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 21637–654 (2022).
-
Geoffrey, M. C. Pharmacology, portion 1: introduction to pharmacology and pharmacodynamics. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 4681 (2018).
-
Swinney, D. C. Biochemical mechanisms of drug movement: what does it clutch for fulfillment? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3801–808 (2004).
-
Tonge, P. J. Drug-aim kinetics in drug discovery. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 929–39 (2018).
-
Backus, K. M. et al. Proteome-extensive covalent ligand discovery in native natural methods. Nature 534570–574 (2016).
-
Bantscheff, M. et al. Quantitative chemical proteomics unearths mechanisms of movement of clinical ABL kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 251035–1044 (2007).
-
Liu, Y., Patricelli, M. P. & Cravatt, B. F. Process-essentially essentially based protein profiling: the serine hydrolases. Proc. Natl Acad. Know USA 9614694–14699 (1999).
-
Patricelli, M. P. et al. Purposeful interrogation of the kinome using nucleotide acyl phosphates. Biochemistry 46350–358 (2007).
-
Klaeger, S. et al. The aim panorama of clinical kinase tablets. Science 358eaan4368 (2017).
-
Sharma, K. et al. Proteomics technique for quantitative protein interaction profiling in cell extracts. Nat. Systems 6741–744 (2009).
-
Gaetani, M. et al. Proteome integral solubility alteration: a excessive-throughput proteomics assay for aim deconvolution. J. Proteome Res. 184027–4037 (2019).
-
Savitski, M. M. et al. Monitoring most cancers tablets in residing cells by thermal profiling of the proteome. Science 3461255784 (2014).
-
Van Vranken, J. G., Li, J., Mitchell, D. C., Navarrete-Perea, J. & Gygi, S. P. Assessing aim engagement using proteome-extensive solvent shift assays. eLife 10e70784 (2021).
-
Zhang, X. et al. Solvent-prompted protein precipitation for drug aim discovery on the proteomic scale. Anal. Chem. 921363–1371 (2020).
-
Strickland, E. C. et al. Thermodynamic diagnosis of protein-ligand binding interactions in complex natural mixtures using the soundness of proteins from rates of oxidation. Nat. Protoc. 8148–161 (2013).
-
Lomenick, B. et al. Target identification using drug affinity responsive aim balance (DARTS). Proc. Natl Acad. Know USA 10621984–21989 (2009).
-
Schopper, S. et al. Measuring protein structural modifications on a proteome-extensive scale using restricted proteolysis-coupled mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 122391–2410 (2017).
-
Zecha, J. et al. Decrypting drug actions and protein modifications by dose- and time-resolved proteomics. Science 38093–101 (2023).
-
Pan, C., Olsen, J. V., Daub, H. & Mann, M. Global effects of kinase inhibitors on signaling networks revealed by quantitative phosphoproteomics. Mol. Cell Proteom. 82796–2808 (2009).
-
Subramanian, A. et al. A next generation connectivity map: L1000 platform and the first 1,000,000 profiles. Cell 1711437–1452 e1417 (2017).
-
Mitchell, D. C. et al. A proteome-extensive atlas of drug mechanism of movement. Nat. Biotechnol. 41845–857 (2023).
-
Ruprecht, B. et al. A mass spectrometry-essentially essentially based proteome map of drug movement in lung most cancers cell strains. Nat. Chem. Biol. 161111–1119 (2020).
-
Saei, A. A. et al. ProTargetMiner as a proteome signature library of anticancer molecules for purposeful discovery. Nat. Common. 105715 (2019).
-
Hughes, C. S. et al. Single-pot, sturdy-part-enhanced sample preparation for proteomics experiments. Nat. Protoc. 1468–85 (2019).
-
Bian, Y. et al. Sturdy, reproducible and quantitative diagnosis of thousands of proteomes by micro-plug with the hump LC-MS/MS. Nat. Common. 11157 (2020).
-
Cox, J. & Mann, M. Ma xQuant permits excessive peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-vary mass accuracies and proteome-extensive protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 261367–1372 (2008).
-
Gessulat, S. et al. Prosit: proteome-extensive prediction of peptide tandem mass spectra by deep studying. Nat. Systems 16509–518 (2019).
-
Wilhelm, M. et al. Mass-spectrometry-essentially essentially based draft of the human proteome. Nature 509582–587 (2014).
-
Datta, J., Ghoshal, K., Motiwala, T. & Jacob, S. T. Unusual insights into the molecular mechanism of movement of DNA hypomethylating agents: feature of protein kinase C δ in decitabine-prompted degradation of DNA methyltransferase 1. Genes Cancer 371–81 (2012).
-
Ercikan-Abali, E. A. et al. Dihydrofolate reductase protein inhibits its own translation by binding to dihydrofolate reductase mRNA sequences within the coding space. Biochemistry 3612317–12322 (1997).
-
Uzor, S. et al. Autoregulation of the human splice factor kinase CLK1 by technique of exon skipping and intron retention. Gene 67046–54 (2018).
-
Hopkins, A. L. Community pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 4682–690 (2008).
-
Bruno, P. M. et al. A subset of platinum-containing chemotherapeutic agents kills cells by inducing ribosome biogenesis stress. Night. With. 23461–471 (2017).
-
Demichev, V. et al. dia-PASEF data diagnosis using FragPipe and DIA-NN for deep proteomics of low sample amounts. Nat. Common. 133944 (2022).
-
Schwanhausser, B. et al. Global quantification of mammalian gene expression adjust. Nature 473337–342 (2011).
-
Zecha, J. et al. Peptide level turnover measurements enable the gaze of proteoform dynamics. Mol. Cell Proteom. 17974–992 (2018).
-
Sievers, Q. L. et al. Defining the human C2H2 zinc finger degrome targeted by thalidomide analogs by technique of CRBN. Science 362eaat0572 (2018).
-
Donovan, K. A. et al. Thalidomide promotes degradation of SALL4, a transcription factor implicated in Duane Radial Ray syndrome. eLife 7e38430 (2018).
-
Hamminger, P., Rica, R. & Ellmeier, W. Histone deacetylases as targets in autoimmune and autoinflammatory illnesses. Adv. Immunol. 1471–59 (2020).
-
Borcoman, E. et al. HDAC inhibition to top immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancers 1466 (2021).
-
Jiang, W. et al. Exhausted CD8+ T cells in the tumor immune microenvironment: new pathways to remedy. Entrance. Immunol. 11622509 (2021).
-
Mueller, S. N. & Ahmed, R. High antigen ranges are the set apart off of T cell exhaustion correct by technique of persistent viral an infection. Proc. Natl Acad. Know USA 1068623–8628 (2009).
-
Utzschneider, D. T. et al. Early precursor T cells attach and propagate T cell exhaustion in persistent an infection. Nat. Immunol. 211256–1266 (2020).
-
Wherry, E. J. T cell exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 12492–499 (2011).
-
Eckert, S. et al. Overview of disposable trap column nanoLC-FAIMS-MS/MS for the proteomic diagnosis of FFPE tissue. J. Proteome Res. 205402–5411 (2021).
-
The, M., Samaras, P., Kuster, B. & Wilhelm, M. Reanalysis of ProteomicsDB using an handsome, sensitive, and scalable false discovery rate estimation ability for protein groups. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 21100437 (2022).
-
Yu, G., Wang, L. G., Han, Y. & He, Q. Y. clusterProfiler: an R bundle for comparing natural topics among gene clusters. Omics 16284–287 (2012).
-
Livak, K. J. & Schmittgen, T. D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using precise-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT formula. Systems 25402–408 (2001).
-
Berg, S. et al. ilastik: interactive machine studying for (bio)image diagnosis. Nat. Systems 161226–1232 (2019).
-
Lechner, S. et al. Target deconvolution of HDAC pharmacopoeia unearths MBLAC2 as frequent off-aim. Nat. Chem. Biol. 18812–820 (2022).
-
Prokofeva, P. et al. Deserves of diazirine photo-immobilization for aim profiling of pure products and cofactors. ACS Chem. Biol. 173100–3109 (2022).
-
Reinecke, M. et al. Chemical proteomics unearths the aim panorama of 1,000 kinase inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-023-01459-3 (2023).
Acknowledgements
We’re grateful to M. Abele for provision of bacterial cell pellets, C. Schwechheimer for provision of Arabidopsis discipline fabric and C. Wurmser for inspire with RNA-seq library preparation. The authors are grateful to the Thermo Fisher crew who supported the set apart-up of FAIMS in aggregate with microflow-LC–MS/MS. Some facets of figures (Figs. 1, 3b, 4b, 5a and 5d and Extended Data Figs. 1h, 8a and 8f) had been created with BioRender.com. This work became partly funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Evaluate (grant nos. CLINSPECT-M and FKZ161L0214A to B.K.; DIAS, FKZ031L0168 to B.K. and A.S.), the German Evaluate Foundation (grant nos. DFG-SFB1309 and 325871075 to B.K. and S.L.) and the European Evaluate Council (AdG grant no. 833710 to B.K., A.S. and J.M.).
Funding
Open get entry to funding supplied by Technical University of Munich.
Ethics declarations
Competing pursuits
B.K. is founder and shareholder of OmicScouts and MSAID. He has no operational feature in both firm. All other authors boom no competing pursuits.
Scrutinize overview
Scrutinize overview data
Nature Biotechnology thanks the nameless reviewers for his or her contribution to the study overview of this work.
Extra data
Creator’s ticket Springer Nature stays neutral simply about jurisdictional claims in revealed maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
Extended Data Fig. 1 Optimization and characterization of the decryptE workflow for the profiling of drug prompted expression modifications at scale.
a) Boxplot showing the distribution of drug cease at 10,000 nM for all three measures of cell fitness. Every dot represents a drug (n = 144). Horizontal strains, bins and whiskers of the boxplot depict the median, the vary between the 2nd and the third quartile and the 1.5-fold interquartile vary. b) Dose-response curves of DHFR following remedy with Methotrexate for diversified events. c) Identical as panel b) but for TYMS. d) Identical as panel b) but for PLK1. e) Distribution of the relative amount of identified protein groups from Jurkat cells as a feature of the utilized FAIMS compensation voltage (CV). f) Heatmap comparing the amount and overlap of identified protein groups between any aggregate of two CVs (identical data as in panel e). g) Collection of identified protein groups from Jurkat cells as a feature of the entire LC-MS/MS time ancient per sample. h) A long way left panel: schematic representation of the experimental get for attempting out the robustness of the micro-plug with the hump LC-FAIMS-MS/MS formula. Colors notify the diversified sample forms and the scale of the ring phase is relative to the amount of analyses in every phase (total of 250 samples analysed). Middle left panel: bar space summarizing the amount of proteins identified for every sample kind. Error bars notify point out ± customary deviation (SD, n = 25 technical replicates for every sample kind). Middle handsome panel: amount of identified protein groups plotted as a feature of the consecutive uncover in which the samples had been analysed. A long way handsome panel: Cumulative density space summarizing the precision with which proteins had been quantified across replicate experiments. Dotted strains reward the respective allotment of proteins (50% and 90%) that had been quantified with the given coefficient of variation (CoV). i) Left panel: Bar space showing the amount of identified proteins by single shot micro-plug with the hump LC MS/MS with or without FAIMS installed or by micro-plug with the hump LC-MS/MS after fractionation using excessive pH reversed part chromatography (4 or 6 fractions) and using the specified amount of diagnosis time. Data are moderate values ± SD from n = 4 technical replicates. Fair panel: identical as panel h (far handsome, but for the information shown in the left panel of i).
Extended Data Fig. 2 Reproducibility evaluation of the decryptE workflow.
a) Left panel: amount of quantified protein groups from DMSO adjust samples that had been analyzed along the entire timeframe of the proteomic show veil plotted as a feature of the consecutive uncover in which the samples had been analyzed. Fair panel: Cumulative density space summarizing the precision with which proteins had been quantified across DMSO adjust samples. Dotted strains reward the respective allotment of proteins (50% and 90%) that had been quantified with the given coefficient of variation (CoV). b) Volcano space diagnosis for n = 4694 protein groups from forty eight DMSO adjust samples from the proteomic show veil which have been randomly assigned to two groups. Analysis of significance became executed using a two-sided Welch’s t-take a look at with out a couple of attempting out correction. c) Cumulative density space showing the reproducibility of pEC50 estimations from replicate dose-response diagnosis (n = 4) of palbociclib, panobinostat, and colchicine. 69.5 % of all pEC50 estimates had been reproducible within ½ log10 step of drug focus. Blue and purple dots reward the SD as an instance curves of panel d) and e) respectively. d) Replicate dose-response curves of ATAD2 regulated by palbocicblib along with the SD for the pEC50. e) Identical as panel d) but for AURKA regulated by colchicine. f) Upper panel: Violine plots showing the distribution of CoV of all proteins which have been no longer regulated by drug remedy for every of the 144 tablets. Median values are given above every violine for every drug. Decrease panel: identical as upper panel but for all proteins that confirmed drug prompted expression modifications.
Extended Data Fig. 3 Global and particular analyses of quantitative drug-prompted protein expression modifications.
a) List of all tablets ranked by the median efficiency (expressed as pEC50 = −log10 EC50) with which they regulated protein expression in Jurkat cells. b) Examples of dose-response curves of proteins from cells treated with the HSP90 inhibitor geldanamycin. c) Pie chart showing the proportion of all drug targets that are detected in the dataset. d) Examples of dose-response curves for tablets that regulated the expression of TYMS. e) Identical as panel b) but for the HSP90 inhibitor tanespimycin.
Extended Data Fig. 4 Drug-prompted mRNA and protein expression modifications.
a) Dose-response curves of mRNA and protein ranges of IKZF1. b) Apparent binding affinity constants (pKd = −log10 Kd) of brigatinib-Protein interactions particular by Kinobead rivals assays10. CLK1,3,4 are marked by respective text. c) Left panel: Dose-dependent replace of mRNA ranges (particular by RT-qPCR) for diversified CLK1-4 domains following remedy with brigatinib. Middle panel: identical as left panel but for abemaciclib. Fair panel: identical as left panel but for milciclib. d) Left panel: dose-response curves of CLK1-4 following remedy with abemaciclib. Middle panel: identical as b) but for abemaciclib. Fair panel: ratios of the N-terminal and kinase domain transcripts (particular by RT-qPCR) of CLK1-4 in response to abemaciclib. The dotted line marks a 1:1 quantitative ratio of the 2 mRNAs. e) Identical as panel d) but for milciclib.
Extended Data Fig. 5 Discrepancies between diversified omics ranges.
a) Comparison of course of drug-prompted expression modifications between mRNA and protein ranges for seven tablets. b) Dose-response curves of drug-prompted abundance modifications of CCNB2 on protein (blue) and mRNA (purple) level after carfilzomib remedy. c) Identical as panel b) but for loads of proteins of the folding machinery. d) GO enrichment of genes which would per chance be up-regulated on mRNA and down-regulated on protein level after carfilzomib remedy. Attempting out of significance became executed using the clusterProfiler R bundle (v. 4.2.2.) with the FDR ability for a couple of speculation attempting out correction.
Extended Data Fig. 6 Platinum-essentially essentially based chemo-tablets have diversified mechanisms of movement in cells.
a) Results of gene ontology (GO) term enrichment diagnosis for the head 9 enormously enriched GO terms of oxaliplatin for all platinum-containing tablets. Attempting out of significance became executed using the clusterProfiler R bundle (v. 4.2.2.) with the FDR ability for a couple of speculation attempting out correction. b) Dose-response curves for four instance proteins for the identical three tablets.
Extended Data Fig. 7 HDAC inhibitors diminish TCR expression in T-cells.
a) Three measures of cell viability of Jurkat cells treated with panobinostat. b) Loss of CD3E expression in response to HDAC inhibitors. c) Loss of mRNA expression of loads of contributors of the TCR in response to vorinostat. d) Little photos of HDAC inhibitor-treated and CD3/CD28-activated CD8- and CD4- sure critical human T-cells (n = 1). e) Dose-dependent discount of TCF7 protein expression in critical human T-cells (naïve simplest) in response to HDAC inhibitors. f) Dose-dependent discount of GZMB protein expression in critical human T-cells (activated simplest).
Extended Data Fig. 8 Molecular glues and PRMT5 inhibitors.
a) Schematic representation of the RING-CUL4A-DDB1-CRBN complex with a sure IMiD molecular glue. b, c) Dose-dependent protein expression for GLUL and ORAI1 in response to loads of IMiDs. d) identical as b) but for contributors of the RING-CUL4A-DDB1-CRBN complex. e) Identical as b) but for IKZF2, PATZ1 and RAB28. f) A long way left panel: schematic representation of SNRPB methylation by PRMT5 and its inhibition by pemrametostat and onametostat. Middle left panel: obvious upregulation of SNRPN and SNRPB by loads of PRMT5 inhibitors. Fair two panels: Down-regulation of methylated Arg108 and Arg147 of SNRPB by PRMT5 inhibitors.
Supplementary data
Rights and permissions
Open Secure entry to This article is licensed underneath a Inventive Commons Attribution 4.0 Worldwide License, which enables spend, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or structure, as long as you give appropriate credit to the distinctive creator(s) and the source, provide a link to the Inventive Commons licence, and reward if modifications had been made. The photos or other third birthday party discipline fabric in this text are incorporated in the article’s Inventive Commons licence, except indicated otherwise in a credit line to the topic fabric. If discipline fabric is no longer incorporated in the article’s Inventive Commons licence and your intended spend is no longer authorized by statutory regulation or exceeds the authorized spend, you’re going to wish to carry out permission straight from the copyright holder. To behold a replica of this licence, consult w ith http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this text
Cite this text
Eckert, S., Berner, N., Kramer, K. et al. Decrypting the molecular foundation of cell drug phenotypes by dose-resolved expression proteomics. Nat Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02218-y
-
Obtained:
-
Licensed:
-
Printed:
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02218-y



 Hot Deals
Hot Deals Shopfinish
Shopfinish Shop
Shop Appliances
Appliances Babies & Kids
Babies & Kids Best Selling
Best Selling Books
Books Consumer Electronics
Consumer Electronics Furniture
Furniture Home & Kitchen
Home & Kitchen Jewelry
Jewelry Luxury & Beauty
Luxury & Beauty Shoes
Shoes Training & Certifications
Training & Certifications Wears & Clothings
Wears & Clothings