Manganese-Well to effect Sandstones Issue Earth-Like Environment on Outmoded Mars

NASA Space Technology
In Could perhaps also 2017, NASA’s Curiosity rover noticed increased than usual amounts of manganese within the lakebed rocks within Gale crater, Mars. These sedimentary rocks include increased grain sizes than what’s standard for the lakebed rocks within the crater. This can existing that the authentic sediments had been fashioned in a river, delta, or attain the shoreline within the frail lake. In a new paper, Dr. Patrick Gasda from Los Alamos National Laboratory and his colleagues state about how manganese will had been enriched in these rocks — as an illustration, by percolation of groundwater by the authentic sediments or by the rock in a while — and what oxidant could well very effectively be to blame for the precipitation of manganese within the rocks. On Earth, manganese turns into enriched on memoir of of oxygen within the ambiance and this route of is mostly accelerated by the presence of microbes. Microbes on Earth can exercise the many oxidation states of manganese as energy for metabolism; if existence modified into expose on frail Mars, the increased amounts of manganese in these rocks alongside the lake shore could well be a significant energy offer for existence.
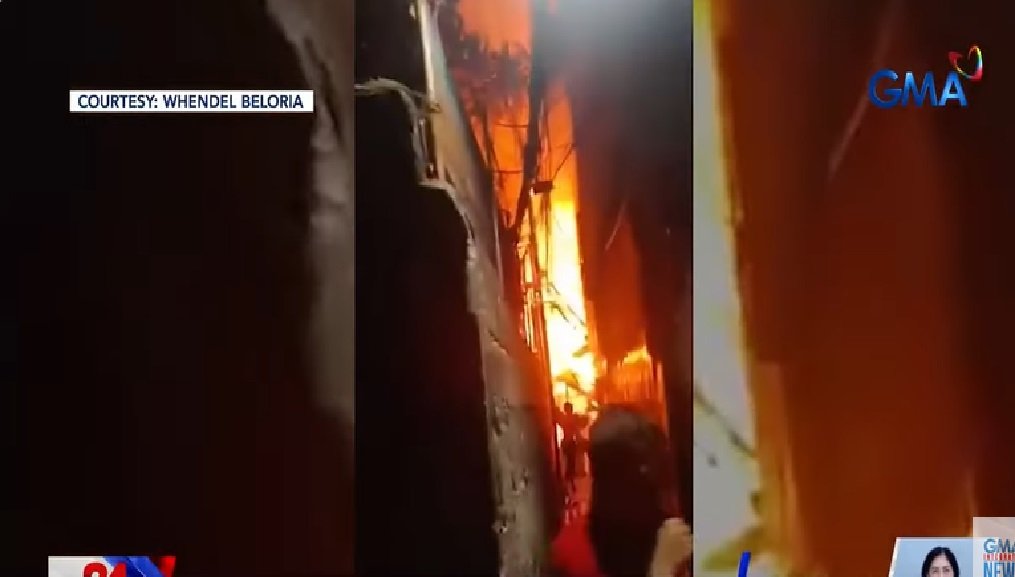
Mastcam mosaic from the Sol 1686 rover residing trying within the assist of the rover (downslope) at the transition point between the Sutton Island and Blunts Level Murray contributors. Images from Sols 1685-1689 boom sedimentary textures of darkish-toned manganese-effectively off sandstones and nearby rocks. Dashed line boxes within the natty mosaic are proven as insets alongside the bottom of figure. Small red outlines demonstrate the approximate areas and extent of ChemCam observations. At some stage in this transition characteristic, darkish-toned sandstones (presumably manganese-effectively off in accordance to ChemCam observations at three areas) overlie gentle-toned provides. Insets from left to correct: (a) Denning Brook, a manganese-effectively off honest-grained darkish-toned sandstone ChemCam observation; (b) and (c) two gentle-toned blocks with execrable-stratified textures, highlighted with yellow lines, 6 m away from Denning Brook and to the greater left within the natty mosaic; (d) darkish-toned provides (heart of mosaic); and (E1) Newport Ledge, (E2) AEGIS post 1685a, (E3) Sugarloaf Mountain, three skinny planar laminated darkish-toned sandstones. Image credit ranking: NASA / Caltech-JPL / MSSS.
“It is refined for manganese oxide to catch on the surface of Mars, so we didn’t search recordsdata from to obtain it in such excessive concentrations in a shoreline deposit,” Dr. Gasda acknowledged.
“On Earth, these forms of deposits happen the complete time on memoir of of the excessive oxygen in our ambiance produced by photosynthetic existence, and from microbes that assist catalyze those manganese oxidation reactions.”
“On Mars, we don’t include proof for existence, and the mechanism to originate oxygen in Mars’ frail ambiance is unclear, so how the manganese oxide modified into fashioned and concentrated right here is admittedly puzzling.”
“These findings show hide increased processes occurring within the Martian ambiance or surface water and displays that more work wants to be carried out to attain oxidation on Mars.”
To measure manganese abundances in lakebed rocks within Gale crater, Dr. Gasda and co-authors dilapidated the ChemCam instrument onboard NASA’s Curiosity rover.
“ChemCam is an atomic emission spectroscopy instrument that makes exercise of laser-introduced on breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) to quantify elemental abundances expose in a target,” they explained.
“The ChemCam LIBS makes exercise of a pulsed laser emitting a 1,067 nm beam that’s focused onto a target up to 7 m from the rover, which produces an analytical footprint of 350-550 μm.”
“Every laser pulse ablates and ionizes a cramped (nanograms to micrograms) amount of subject cloth.”
“Gentle emitted from the plasma fashioned by every laser pulse is smooth by the ChemCam telescope, and spectra are recorded by the ultraviolet, violet, and considered to attain infrared spectrometers.”
The sedimentary rocks explored by the Curiosity rover are a combine of sands, silts, and muds.
The sandy rocks are more porous, and groundwater can more without issues lumber by sands when in contrast with the muds that carry out up lots of the lakebed rocks in Gale crater.
The researchers checked out how manganese will had been enriched in these sands — as an illustration, by percolation of groundwater by the sands on the shore of a lake or mouth of a delta — and what oxidant could well very effectively be to blame for the precipitation of manganese within the rocks.
On Earth, manganese turns into enriched on memoir of of oxygen within the ambiance, and this route of is mostly accelerated by the presence of microbes.
Microbes on Earth can exercise the many oxidation states of manganese as energy for metabolism; if existence modified into expose on frail Mars, the increased amounts of manganese in these rocks alongside the lake shore would had been a significant energy offer for existence.
“The Gale lake atmosphere, as published by these frail rocks, presents us a window into a liveable atmosphere that appears to be like to be surprisingly linked to places on Earth as of late,” acknowledged ChemCam most important investigator Dr. Nina Lanza, a researcher at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
“Manganese minerals are favorite within the shallow, oxic waters chanced on on lake shores on Earth, and it’s excellent to obtain such recognizable facets on frail Mars.”
The team’s paper modified into printed within the Journal of Geophysical Examine: Planets.
_____
PJ Gasda et al. 2024. Manganese-Well to effect Sandstones as an Indicator of Outmoded Oxic Lake Water Stipulations in Gale Crater, Mars. JGR: Planets 129 (5): e2023JE007923; doi: 10.1029/2023JE007923



 Hot Deals
Hot Deals Shopfinish
Shopfinish Shop
Shop Appliances
Appliances Babies & Kids
Babies & Kids Best Selling
Best Selling Books
Books Consumer Electronics
Consumer Electronics Furniture
Furniture Home & Kitchen
Home & Kitchen Jewelry
Jewelry Luxury & Beauty
Luxury & Beauty Shoes
Shoes Training & Certifications
Training & Certifications Wears & Clothings
Wears & Clothings