NASA finds extra points with Boeing’s Starliner, but crew originate plan for June 1

NASA Space Technology
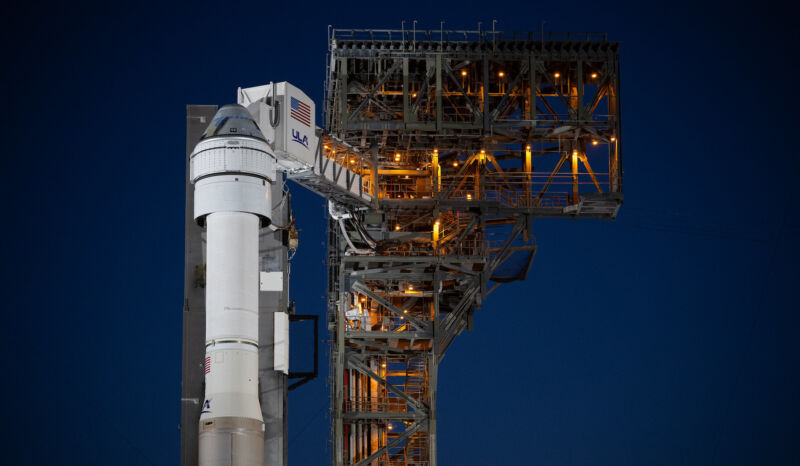

Lengthen / Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft atop its Atlas V rocket on the originate pad earlier this month.
Senior managers from NASA and Boeing suggested journalists on Friday that they thought to originate the first crew take a look at flight of the Starliner spacecraft as quickly as June 1, following lots of weeks of detailed prognosis of a helium leak and a “invent vulnerability” with the ship’s propulsion draw.
Intensive data opinions over the final two-and-a-half weeks settled on a probable cause in the support of the leak, which officers described as tiny and stable. In some unspecified time in the future of these opinions, engineers also constructed self perception that even supposing the leak worsened, it may perhaps now not add any unacceptable threat for the Starliner take a look at flight to the World Plight Space, officers acknowledged.
But engineers also chanced on that an unlikely mix of technical mess ups in Starliner’s propulsion draw—representing 0.77 p.c of all that you simply would perchance perhaps also bear in mind failure modes, in line with Boeing’s program manager—may forestall the spacecraft from conducting a deorbit burn on the finish of the mission.
“As we studied the helium leak, we also looked all the device by strategy of the rest of the propulsion draw, appropriate to make certain we did now not hang any rather a extensive selection of issues that we needs to be about,” acknowledged Steve Stich, manager of NASA’s commercial crew program, which awarded a $4.2 billion contract to Boeing in 2014 for enlighten of the Starliner spacecraft.
“We chanced on a invent vulnerability… in the prop [propulsion] draw as we analyzed this particular helium leak, where for sure failure cases which can perhaps be very far-off, we did now not hang the aptitude to bring collectively the deorbit burn with redundancy,” Stich acknowledged in a press conference Friday.
These two complications, uncovered one after the different, hang saved the Starliner take a look at flight grounded to enable time for engineers to search out workarounds. This is the first time astronauts will wing into orbit on a Starliner spacecraft, following two unpiloted demonstration missions in 2019 and 2022.
The Starliner program is running years in the support of time tablebasically attributable to complications with the spacecraft’s draw, parachutes, and propulsion draw, supplied by Aerojet Rocketdyne. Instrument woes decrease short Starliner’s first take a look at flight in 2019 sooner than it may perhaps dock on the World Plight Space, and moreover they compelled Boeing to wing an unplanned 2nd take a look at flight to compose self perception that the spacecraft is safe ample for astronauts. NASA and Boeing delayed the 2nd unpiloted take a look at flight nearly a twelve months to conquer an danger with corroded valves in the ship’s propulsion draw.
Final twelve months, appropriate about a months sooner than it turned into presupposed to originate on the crew take a look at flight, officers chanced on a invent danger with Starliner’s parachutes and chanced on that Boeing set in flammable tape contained in the capsule’s cockpit. Boeing’s vital person-crossed Starliner sooner or later seemed ready to wing on the long-delayed crew take a look at flight from Cape Canaveral Plight Power Space, Florida.
NASA commander Butch Wilmore and pilot Suni Williams had been strapped into their seats internal Starliner on Might perchance well 6 when officers halted the countdown attributable to a corrupt valve on the spacecraft’s United Initiating Alliance Atlas V rocket. ULA rolled the rocket support to its hangar to interchange the valve, with an secret agent in direction of one more originate strive in mid-Might perchance well.
But ground groups detected the helium leak in Starliner’s service module in the aftermath of the scrubbed countdown. After some preliminary troubleshooting, the leak fee grew to approximately 70 psi per minute. Since then, the leak fee has stabilized.
“That gave us discontinue because the leak fee grew, and we desired to fancy what turned into the explanation for that leak,” Stich acknowledged.



 Hot Deals
Hot Deals Shopfinish
Shopfinish Shop
Shop Appliances
Appliances Babies & Kids
Babies & Kids Best Selling
Best Selling Books
Books Consumer Electronics
Consumer Electronics Furniture
Furniture Home & Kitchen
Home & Kitchen Jewelry
Jewelry Luxury & Beauty
Luxury & Beauty Shoes
Shoes Training & Certifications
Training & Certifications Wears & Clothings
Wears & Clothings